When you look at a foundry and a manufacturer, you see they are different. A foundry makes metal castings from raw materials. A manufacturer uses those castings or other parts. They make finished products. This difference affects your choices in the supply chain. Foundries have 65% of the market share. Fabless companies have 35%.
| Category | Percentage of Market Share |
|---|---|
| Foundries | 65% |
| Fabless Companies | 35% |
Knowing what a foundry and manufacturer do helps you choose what is best for your business.
Key Takeaways
- Foundries make metal castings from raw materials. Manufacturers use those castings to make finished products. Foundries melt and shape metals. Manufacturers do assembly, machining, and finishing. You should pick the right supplier for your project needs. Think about product type, cost, and customization. Foundries are important for making strong and complex metal parts. These parts are used in industries like automotive and construction. Manufacturers can use many materials, like metals and plastics. They can make many different products. Knowing what foundries and manufacturers do helps you choose better for your business. Machining is important for both foundries and manufacturers. It helps make parts precise and high quality. You should also think about reliability and innovation. This is important when picking a foundry or manufacturer for your project.
Table of Contents
Foundry and Manufacturer Overview
What is a Foundry
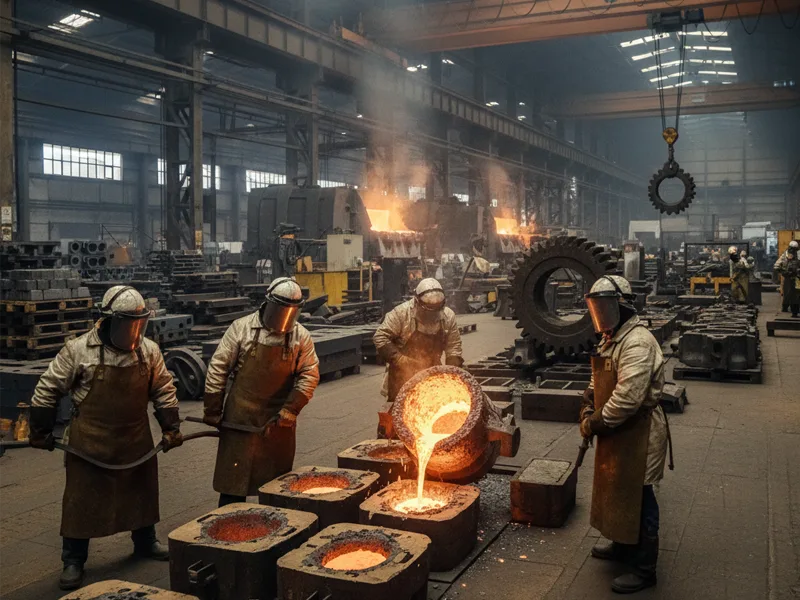

You might ask what a foundry does. A foundry is a place where metal castings are made. Workers melt raw metals like iron, steel, aluminum, or copper. They heat the metal until it turns into a liquid. The hot liquid metal is poured into a mold. The mold has the shape of the part you want. The metal cools down and becomes solid. Then, the casting is taken out of the mold. This gives you a rough metal piece that looks like the mold.
Foundries work at the start of making things. You use a foundry to turn raw metal into simple shapes or parts. These castings often need more work before they are finished. Foundries are important in car making, building, and the machine industries. People use foundries when they need strong metal parts with special shapes.
Tip: If you want a metal part with a certain shape or size, a foundry can make it by casting.
What is a Manufacturer
A manufacturer takes things a step further. You go to a manufacturer to turn castings or other materials into finished products. Manufacturers use many steps, like machining, welding, putting parts together, and finishing. They might start with castings from a foundry. They can also use plastics, composites, or ready-made metal parts.
Manufacturers add value to the parts they use. They turn simple parts into products you can use or sell. For example, a manufacturer can take a metal casting and cut it to the right size. They put it together with other parts and add coatings or finishes. The final product matches what you need and is ready to sell.
Manufacturers can make lots of the same product or just a few special ones. Some make many items at once, while others make custom products. You pick a manufacturer when you want a finished product, not just a basic part.
Note: The biggest difference between a foundry and manufacturer is when they work in the process. A foundry makes the basic metal shape. A manufacturer finishes the product.
When you look at both, you see each has a special job in the supply chain. Knowing what they do helps you choose the right one for your needs.
Core Functions and Processes
Foundry Processes
When you work with a foundry, you focus on casting. Foundries use casting to shape metal into parts. Workers melt metals like iron, steel, or aluminum. They pour the hot metal into molds that match the part’s shape. As the metal cools, it becomes solid and takes the mold’s form. This is important for making strong and complex parts for many uses. Foundries use special machines to control heat and check quality. This process happens early in the supply chain. Raw metal turns into shapes that can be used later.
Tip: Casting is how many things you use every day start out. It changes raw metal into the first shape needed for more work.
Manufacturer Processes
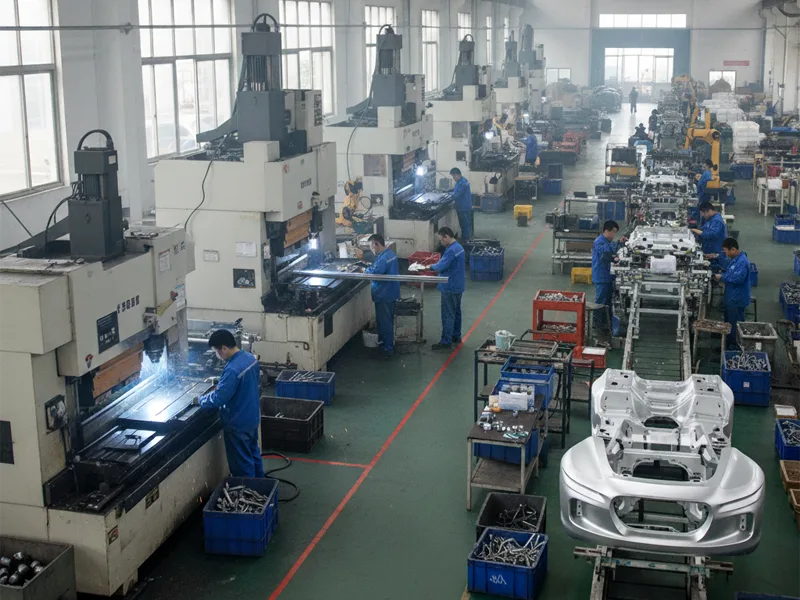

Manufacturers work after casting is done. They use many different steps to make products. These steps include machining, forming, joining, and putting parts together. Machining cuts, drills, or shapes parts to exact sizes. Forming bends or rolls in metal without taking any away. Joining connects parts with welding or glue. The assembly puts all the pieces together to finish the product.
Here is a table that shows common manufacturing process types and what they do:
| Manufacturing Process Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Repetitive Manufacturing | Makes the same items over and over, often with assembly lines. |
| Discrete Manufacturing | Makes many different products, needs setup and change time. |
| Job Shop Manufacturing | Makes small batches or custom products in a shop. |
| Continuous Process Manufacturing | Runs all day and night, uses recipes to make products. |
| Batch Process Manufacturing | Like continuous, but works in groups and needs cleaning and setup. |
| Machining | Shapes materials by milling, turning, or drilling. |
| Casting | Pours liquid material into a mold to make solid parts. |
| Extrusion | Pushes material through a die to make shapes. |
| Injection Molding | Uses melted plastic to form products. |
| Forming | Changes the metal shape by bending or rolling, keeping all the metal. |
| Joining | Connects parts by welding or gluing. |
| 3D Printing | Builds parts by adding layers from a digital file. |
You pick the right process for your product’s needs. Manufacturers can make lots of the same thing or just a few special items.
Materials and Equipment
Foundries and manufacturers use different materials and tools. Foundries mostly use metals like iron, steel, aluminum, and copper. They need furnaces, molds, and pouring tools. The table below shows common casting methods, materials, and main equipment:
| Casting Method | Common Materials Used | Essential Equipment Needed |
|---|---|---|
| Investment Casting | Multifaceted metal parts | Molds, furnaces |
| Sand Casting | Silica-based materials | Sand molds, pouring equipment |
| Plaster Casting | Gypsum and water | Molds, mixing equipment |
| Permanent Mould Casting | Reusable materials | Reusable molds, low-pressure systems |
| Die Casting | Zinc alloys | Die casting machines, molds |
Manufacturers use more kinds of materials. These include metals, plastics, composites, and ready-made parts. Their tools depend on the job. You see CNC machines for cutting, welding stations for joining, and assembly lines for putting things together. Manufacturers also use robots and machines to work faster and better.
Note: The materials and tools you choose depend on your product’s design and quality. Knowing what foundries and manufacturers do helps you pick the best one for your project.
Key Differences
Foundry and Manufacturer Comparison
When you look at a foundry and a manufacturer, you see they are not the same. They work in different ways, make different things, and have their own place in how products are made. Knowing these differences helps you pick what is best for your project or business.
Process Differences
Foundries and manufacturers use different steps to make things:
| Aspect | Foundry | Manufacturer |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Melts and prepares metals for casting | Produces finished products from castings |
| Process Focus | Creates and maintains molds | Assembles and finishes components |
| Equipment Utilization | Uses furnaces, molds, and crucibles | Uses machines for assembly and finishing |
| Impact on Quality | Directly affects casting quality | Relies on quality of cast components |
| Layout Importance | Affects workflow and casting efficiency | Affects production line efficiency |
A foundry melts metal and pours it into a mold. The goal is to make strong metal parts with a certain shape. The steps are melting, pouring, and letting the metal cool. How the foundry is set up and how workers use the molds can change how well things turn out.
A manufacturer takes those metal parts and makes them into finished products. They use machines to cut, drill, weld, and put parts together. Their job is to make sure the final product is just right. The way the factory is set up helps workers do their jobs faster and better.
Product Differences
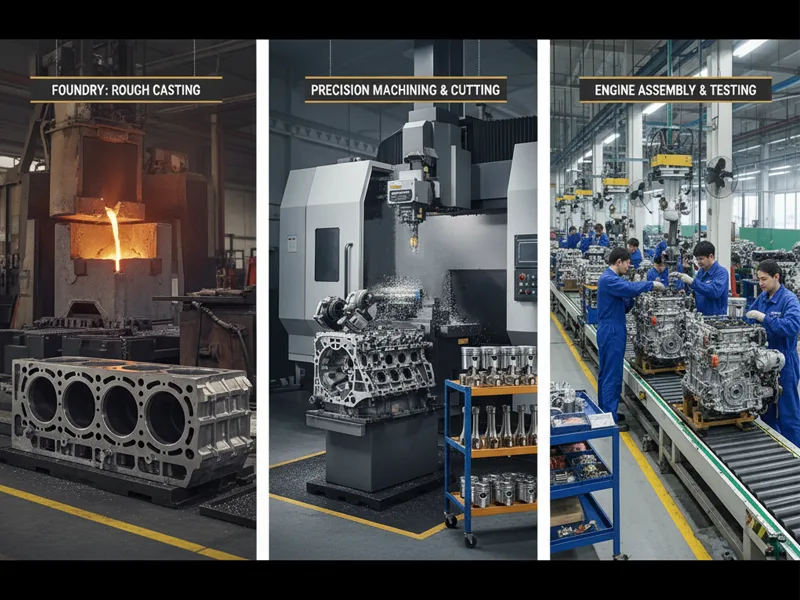
The things you get from a foundry and a manufacturer are not the same:
- Foundries make metal parts called castings. These parts have the shape you need but are not finished yet.
- Manufacturers make finished products. They take castings, cut them to the right size, put them together with other parts, and add coatings or paint.
For example, a foundry can make an engine block. A manufacturer will take that block, cut it, add pistons and other parts, and build a whole engine.
Supply Chain Roles
Foundries and manufacturers have different jobs in how products move from start to finish.
| Aspect | Foundries | Manufacturers |
|---|---|---|
| Logistics Activity | Lower, due to specialized production | Higher, due to bulk importing and fast response |
| Supply Chain Position | Upstream, focused on raw material processing | Downstream, pushing products to retailers |
- Foundries are at the start of the supply chain. They turn raw materials into shapes that can be used later. They help make new materials and ways to cast metal. Some foundries also do extra work, like cutting and finishing, to save time and money.
- Manufacturers are closer to the end of the supply chain. They put parts together, finish them, and send them to stores or customers. They deal with more shipping and have to get parts quickly. Manufacturers buy lots of parts at once to keep costs down and keep making products.
Note: In some industries, like making computer chips, foundries make the chips. Manufacturers use those chips to build things like computers and phones. This way, each group does what they are best at—foundries make parts, manufacturers put them together and sell them.
You can see that foundries and manufacturers both have important jobs. When you need help, think about what you need. If you want raw metal parts, go to a foundry. If you want a finished product, choose a manufacturer.
Capabilities and Machining Solutions
What Foundries Can Do
Foundries can do things most manufacturers cannot. They turn raw metal into big or complex shapes. They use special ways to package parts and can mix chiplets from different places. Some foundries help design and make products from start to finish. They are good at making lots of hard parts for cars, planes, and electronics.
| Unique Capability | Description |
|---|---|
| Advanced Packaging Techniques | Foundries are leaders in packaging, especially for 2.5D integration. |
| Mix and Match Chiplets | They join chiplets from different places for better results. |
| Full-Stack Design and Fab Service Model | Foundries help with both design and making for many types of products. |
| Specialized High-Yield Production | They make many complex systems at once, unlike regular manufacturing. |
But foundries also have some problems:
- Mistakes can happen, like dirt or errors in making parts.
- The process can change, so some parts may not be the same.
- Bad materials or design can make parts fail.
- It is harder to test small parts for problems.
- Heat and stress can bend or break parts.
- Some issues, like electromigration, can hurt how long parts last.
- Newer ways of making parts can make it harder to get good results every time.
Note: Foundries are best when you need special metal parts, advanced ways to put things together, or lots of castings with special needs.
What Manufacturers Can Do
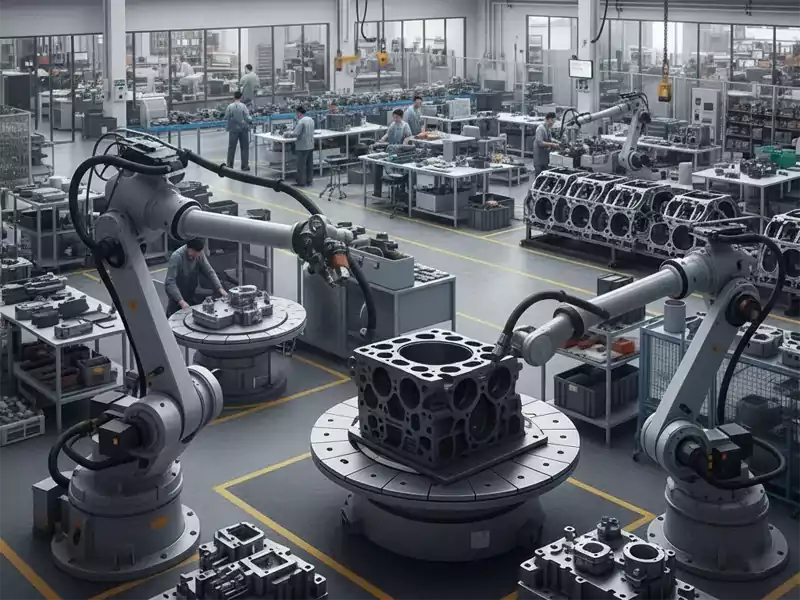

Manufacturers take castings and other parts and finish them. They are good at putting things together, cutting, welding, and making products look nice. They work with many materials, like metal, plastic, and composites. Many use robots and machines to work faster and better.
Manufacturers can:
- Build complicated products from many pieces.
- Add coatings or finishes to protect or decorate.
- Put in electronics, wires, or other parts.
- Make products just the way customers want.
- Make lots of products at once or just a few special ones.
Manufacturers make sure every part is good before it goes to the customer. They help turn rough castings into things people can use or buy.
Machining in Manufacturing
Machining is important in both foundries and manufacturing. It helps make parts very exact and smooth. Machining works with many materials, like metal, plastic, and composites. It lets you make custom shapes and change things quickly.
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Versatility | Machining makes parts from many materials for many uses. |
| Precision | It makes very exact and detailed shapes, better than some other ways. |
| Modification Ease | You can change parts fast by changing how you machine them. |
| Automation | Machines can work by themselves, saving time and making parts the same. |
Machining helps fix castings from foundries. It cuts off extra metal, drills holes, or adds small details. In manufacturing, machining makes sure parts are the right size and shape. For example, aluminum casting makes tricky shapes easily. Machining then finishes those shapes so they are ready to use or sell.
Tip: If you need parts that are very exact or have a special look, machining is a good choice. It is important for both foundries and manufacturers and helps make great products.
Foundries and manufacturers each have their own strengths. Machining helps both work together to make the best parts for your project.
When to Choose a Foundry or Manufacturer
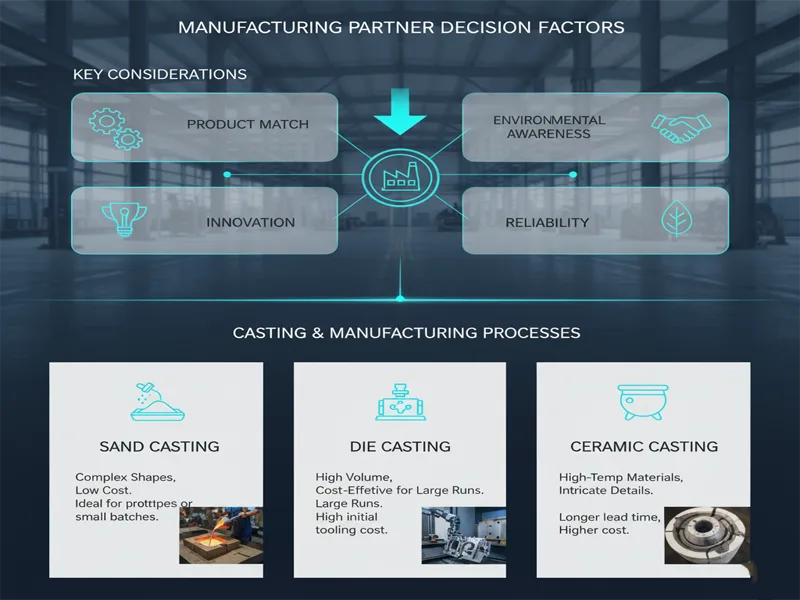
Decision Factors
When you pick between a foundry and a manufacturer, you should think about a few things. Your choice can change how good your project is, how much it costs, and how long it takes. Here are some important things to keep in mind:
- Product alignment: Make sure the supplier’s way of working fits your product. This helps you get the right quality and price.
- Innovation: Choose a partner who can change and come up with new ideas. This helps your business stay ahead.
- Value: Find suppliers who give you good quality, service, and are dependable. They should help your business do better.
- Environmental awareness: Many companies want suppliers to use eco-friendly ways. This helps your brand and is good for the planet.
- Reliability: Pick a supplier you can count on to deliver on time and keep things running.
You also need to think about what kind of casting or manufacturing you want. Sand casting is good for tricky shapes and does not cost too much. Die casting works best if you need lots of parts, but costs more at the start. Ceramic casting is good for materials that melt at high temperatures, but it takes longer and costs more.
Tip: Always choose a supplier whose skills match what your project needs. This gives you the best results.
Industry Scenarios
Different industries need different things. Your choice depends on how many products you want and if you need special designs.
- Additive manufacturing (AM) is smart for small batches or custom parts. It costs less at first and lets you change designs fast.
- Casting is better if you need lots of parts. Once you have the molds, you save money as you make more.
- AM is great for aerospace and healthcare. You can make hard shapes and change designs quickly.
- Casting is best for cars and big machines. These need strong parts and lots of them.
If you want tough parts that are always the same, casting is usually best. If you want to change things quickly, AM or a manufacturer with advanced machines may be better.
Cost and Customization
Cost and making things your way are big parts of your choice. Here is a table that shows the usual costs for different services:
| Manufacturing Service | Hourly Rate | Per Project |
|---|---|---|
| Rapid Prototyping Services | $65 – $125 | $50 – $1,000 |
| 3D Printing | $40 – $125 | $300 – $1,000 + cost per item |
| Injection Molding | N/A | $1,000 + cost per item |
| CNC Machining | N/A | $1,000 + cost per item |
| Supportive Assistance | $28 – $60 hourly | N/A |
If you want a special part or just a few, rapid prototyping or 3D printing keeps costs low and lets you change designs easily. For lots of parts, casting or injection molding saves money over time. CNC machining is best when you need parts that are very exact and of high quality.
Note: Think about your project’s size, budget, and if you need special designs before you pick a foundry or manufacturer. The right choice helps you save money and get the best product for your needs.
Foundry and Manufacturer Examples
Real-World Example: Foundry
Foundries help many industries by making important parts. They give basic materials for building, roads, and the environment. The table below shows some foundry examples and what they make:
| Foundry Example | Product Type | Location |
|---|---|---|
| Resource Recovery Corporation | Asphalt paving, landfill liners, soils | Western Michigan |
| Potting Soil Facility | Manufactured potting soil | Indiana |
| City of Reedsburg Industrial Park | Construction material | Reedsburg, Wisconsin |
| Cement Manufacturer | Cement production | Michigan (Midwest USA) |
| Asphalt Pavement | Asphalt ingredient | Indiana |
| Raingarden Installation | Stormwater management | Seven Hills, Ohio |
| Residential Construction | Structural fill | Tennessee |
| National Retail Store | Site development | Wisconsin |
| Marion County Fairgrounds | Berm creation | Indianapolis |
| Old Gravel Mining Pit | Backfill material | Wisconsin |
| Local Construction Projects | Road base | Pennsylvania |
| Airport Runway | Subbase fill | Wisconsin |
| Coal Mine Reclamation | Manufactured soil | Pennsylvania |
Foundries give raw materials and castings for many projects. These things help start the supply chain. They make it possible for manufacturers to do their work later.
Real-World Example: Manufacturer
Manufacturers take castings or raw materials and make finished products. They work in many areas, like food and cars. The table below shows the types of manufacturers and what they make:
| Manufacturer Type | Example Products |
|---|---|
| Food Production | Organic energy bars |
| Textile Production | Textiles and materials (cotton, wool) |
| Apparel and Footwear | Clothing, footwear, accessories |
| Automotive Parts | Engines, transmissions, car components |
You might drive a car, wear shoes, or eat snacks. Manufacturers make these things. They use parts from foundries and other places. Then, they put them together, finish them, and package the final product.
Machining Case Study
Machining helps both foundries and manufacturers make better parts. It makes things more exact and of high quality. Here are some real examples:
- In aerospace, CNC machining makes hard parts faster and with fewer mistakes. This saves money and makes things safer.
- In medical device making, CNC machining creates very exact parts. This means devices work better and last longer.
- NASA used AI and special machining to make a lighter arm for a Mars mission. Baker Industries used 5-axis CNC machines to make this part. They met strict rules and finished early.
- Machine learning now helps find mistakes faster. Some factories find 25% more problems, so fewer bad products go to customers.
Tip: If you need very exact parts or want to save time and money, machining is a good idea. It helps you get great results, whether you use a foundry, a manufacturer, or both.
Summary Table
Foundry vs Manufacturer at a Glance
If you want to compare foundries and manufacturers, this table helps. It shows the biggest differences between them side by side. This makes it easier to pick which one is right for you.
| Aspect | Foundry | Manufacturer |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A place where workers melt and shape metals | A place where workers make finished goods from castings or materials |
| Main Focus | Changes raw metal into cast parts | Puts together machines and finishes products |
| Key Processes | Makes patterns, melts metal, pours, cleans, and checks parts | Machines, welds, assembles, coats, and packages items |
| Materials Used | Uses iron, steel, aluminum, and copper | Uses metals, plastics, composites, and electronics |
| Output | Makes metal castings like engine blocks and gears | Makes finished things like cars and electronics |
| Workforce | 72,009 workers; 17.6% are women; most finished high school | Workers come from many jobs and industries |
| Average Salary | $65,893 for men, $58,842 for women | Pay changes by job and skill |
| Growth Projection | Fewer workers in 10 years, but more output | Growth depends on the industry, and often goes up in tech |
| Largest Occupation | Most are firstline supervisors (5,721 people) | Many are production workers, engineers, or technicians |
| Industry Role | Starts the process by making basic or half-finished parts | Finishes the process by making goods for stores or customers |
| Example | “This car part came from a foundry.” | “This car was put together by a manufacturer.” |
Tip: Look at this table when you need to pick between a foundry and a manufacturer. It helps you find the best fit for your project.
Foundries and manufacturers both have special jobs. Foundries make the first parts you need. Manufacturers use those parts to build things you use every day. When you know what each one does, you can make smarter choices for your business or project.
You can see that foundries and manufacturers have different jobs. Foundries make raw castings. Manufacturers use those castings to make finished products. Knowing this helps you pick the right partner for your project.
When you know what each does, you can plan better. For example:
- You can save money by using new materials and tools.
- You can work better by thinking about long-term costs, not just the first price.
When you plan your next steps, try this process:
- Get clear quotes and needs from your customers.
- Use a checklist to ask good questions about your product.
- Make 3D models and test them to improve your design.
- Try making a sample to check the quality.
- Give your customer a full report to help them choose.
Some people think changing casting methods is too hard or costs too much. But today’s ways make setting up and using new methods much easier than you think. If you know these facts, you can make better choices and skip common mistakes when planning your production.
FAQ
A foundry gives you raw metal castings. A manufacturer gives you finished products. Foundries make basic shapes from metal. Manufacturers use those shapes to make things you can use.
Yes, you can use both for one project. You get castings from a foundry first. Then you send them to a manufacturer. The manufacturer can machine, put together, or finish the parts. This way, you can watch quality and control costs.
Machining helps make parts very exact. It lets you get smooth surfaces and tight fits. You can also use machining to change or fix castings before they are finished.
Tip:
Sand casting is good for tricky shapes and small amounts. Die casting works best if you need many parts and want a smooth surface. Your choice depends on how much money you have, your design, and how many you need.
| Foundries | Manufacturers |
|---|---|
| Iron, steel, aluminum, copper | Metals, plastics, composites, electronics |
You pick the material that fits what your product needs.
Manufacturers check parts with tests and inspections. They use machines like CNC and other tools. These checks help make sure every part is made right.
Yes, you can ask for custom castings from a foundry. You can also ask a manufacturer to machine, put together, or finish parts just how you want.


