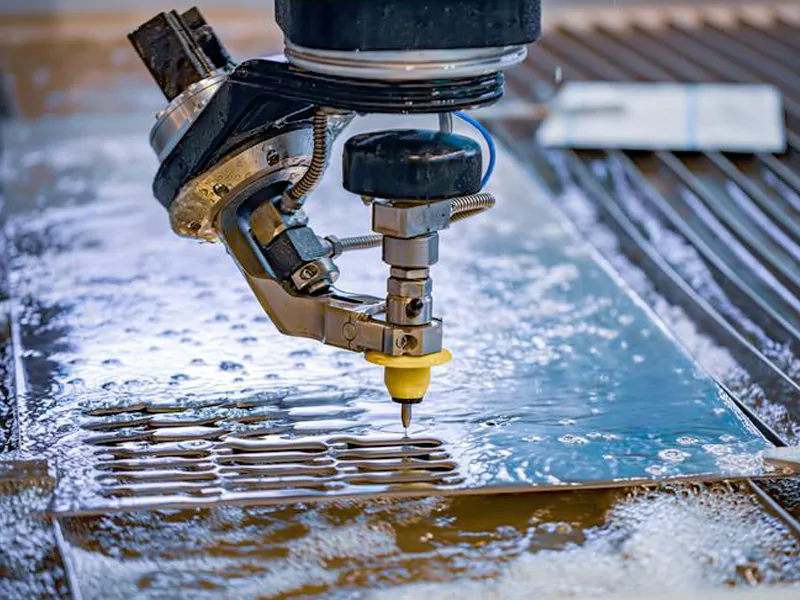
You use waterjet cutting when you want to cut things without heat. Waterjet cutting uses a strong stream of water. Sometimes, it mixes with tiny rough particles. This helps cut metals, plastics, ceramics, and composites. The process is cold, so it keeps materials safe from heat. Many industries use waterjet cutting. Aerospace, automotive, and defense need it for their work. Waterjet cutting is precise and flexible. You can cut detailed shapes and thick materials with this method. It is non-traditional machining process.
Key Takeaways
- Waterjet cutting uses a strong stream of water to cut things. It does not use heat, so it stops damage like bending or melting. This method can cut many materials. It works on metals, plastics, glass, stone, and composites. It cuts with high accuracy and leaves smooth edges. Waterjet cutting is good for materials that cannot take heat. It keeps their properties safe and stops any heat damage. The process can make detailed designs and tricky shapes. This makes it useful for aerospace, car, and electronics industries. Waterjet cutting can cut thick materials. It can cut up to 12 inches of aluminum. It can also cut 8 inches of hard metals like titanium. You pick pure or abrasive waterjet cutting based on the material. Pure waterjet is best for soft things. Abrasive waterjet is better for hard things. Waterjet cutting is good for the environment. It makes very little waste and no bad fumes. This makes it safer for many uses. Most cuts do not need extra finishing. This saves time and money when making things.
Table of Contents
Waterjet Cutting Basics
What Is Waterjet Cutting
You use waterjet cutting to shape or split materials without heat. This method uses a strong stream of water. Sometimes, it mixes with abrasive particles. The water moves very fast and hits the material hard. This breaks the surface and cuts through it. Waterjet cutting is a cold process. It works by speeding up erosion. First, the fast water or abrasive hits the material. This makes tiny cracks and changes its shape. Then, the steady impact grinds away small pieces. This slowly removes the material. You can see these steps in the table below:
| Phase | Description |
|---|---|
| Deformation Wear Phase | First, high-speed abrasive particles hit and make small cracks. |
| Erosion Wear Effect | Next, the steady impact grinds and pulls out tiny pieces. |
Waterjet cutting is special because it does not use heat. You can cut plastics, rubber, and composites without changing them. This makes waterjet cutting different from other methods of machining. You do not have to worry about melting, burning, or warping.
Unique Features
Waterjet cutting has many features that make it stand out. It is a cold process, so there are no heat marks or stress. The edge stays smooth and clean. You lose very little material when you cut. Here are the main features:
- Waterjet cutting does not make a heat-affected zone, so you avoid warping and keep sharp corners.
- You can use waterjet cutting on metals, glass, and stone.
- The process lets you make detailed and complex cuts with high accuracy.
- You get a better edge than with laser or plasma cutting.
- The kerf, or cut width, is very small—about 0.6 mm.
- Waterjet cutting keeps the material properties the same, which is important for special uses.
- You can cut thick, reflective, or heat-sensitive materials.
- The edge quality is the best you can get.
Here is a table showing the main benefits of temperature-sensitive materials:
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| No Thermal Distortion | The process does not make heat, so there is no risk of heat damage. |
| Preservation of Material Properties | Keeps the material’s natural properties, which is important for things like medical devices. |
| Precision and Clean Edges | Gives you clean, precise edges, so you do not need extra finishing. |
Tip: If you need to cut materials that cannot take heat, waterjet cutting is the best choice.
Applications
You find waterjet cutting in many industries because it works on many materials and shapes. Here are the top uses:
- Aerospace: You can cut titanium and composite parts for planes. The process keeps the material strong and safe from heat.
- Automotive: You can make gaskets, panels, and detailed parts with clean edges and little waste.
- Construction: You can shape stone, tile, and other building materials to fit exact designs.
- Electronics: You can cut circuit boards and delicate cases without hurting sensitive parts.
Waterjet cutting is important in these industries. In the automotive field, it has the biggest market share at 29.63%. Aerospace is next, growing at about 4.3% to 4.6%. The electronics industry uses waterjet cutting more each year.
| Industry | Revenue Share (%) | Role in Industry |
|---|---|---|
| Automotive | 29.63% | Making very accurate parts |
| Aerospace | N/A | Cutting expensive materials |
| Electronics | N/A | N/A |
| Industry | Market Share Contribution | Growth Rate (CAGR) |
|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Largest (29.63%) | N/A |
| Aerospace | Second most dominant | 4.3% to 4.6% |
| Electronics | Growing | N/A |
| Industry | Key Materials Used | Application in Industry |
|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Titanium, Inconel, Carbon Fiber | Aircraft skins, engine parts |
| Automotive | N/A | Vehicle manufacturing |
| Aerospace & Defense | Aluminum, Stainless Steel, Titanium Alloys | Aerospace and defense vehicles and equipment |
You can see that waterjet cutting helps you get clean, safe, and high in many fields. This makes it a top choice for modern manufacturing and design.
Waterjet Cutting Process
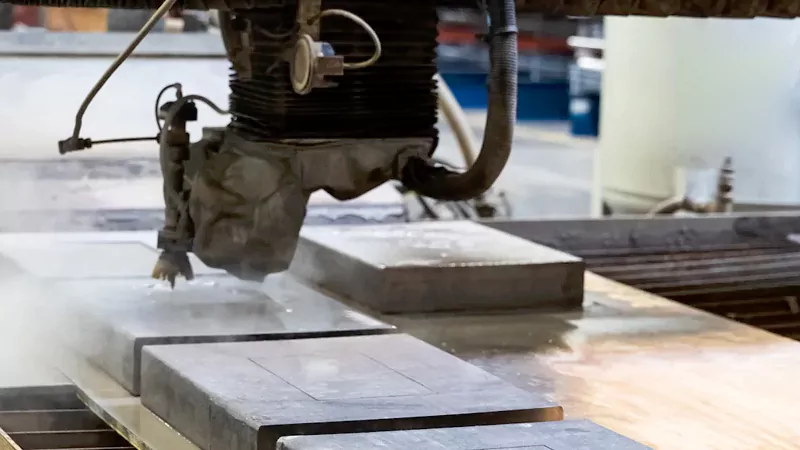

Main Components
A waterjet cutting system has many important parts. Each part helps the machine cut things. You need to know these parts to see how it works.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| High-Pressure Pump | Makes the force needed for cutting. |
| Cutting Head | Brings together water and abrasive particles for cutting; very important for accuracy. |
| Flow Regulator | Controls the mix of water and abrasive for good cutting. |
| Mixing Chamber | Mix abrasive particles with water to make a strong jet. |
| Focusing Tube | Makes the water stream into a thin jet for cutting. |
| Abrasive Delivery System | Puts abrasive particles into the water to help cut better. |
| Chiller | Keeps the pump cool so it does not get too hot. |
| Drainage System | Takes away the water and debris made during cutting. |
| Water Filtration System | Cleans the water to protect the machine parts. |
| Control Panel | Lets you control and watch the cutting process. |
Pump
The high-pressure pump is the first step. It takes tap water and makes it very strong, over 40,000 psi. This gives the water enough power to cut hard things. The chiller keeps the pump cool, so it works well.
Nozzle
The nozzle is where the action happens. Water goes through a tiny hole made from sapphire or diamond. This makes a thin, strong jet. If you need to cut harder things, the system adds an abrasive in the mixing chamber. The focusing tube shapes the jet for careful cutting.
Cutting Head
The cutting head puts everything together. It mixes the high-pressure water and abrasive. The cutting head must be clean and lined up correctly. If you keep the hole and tube in good shape, you get a strong jet. This gives you smooth edges and a small kerf width, about 0.5 mm to 1.3 mm. You can get very tight tolerances, as close as ±0.003” for small parts.
Note: The way the cutting head is set up changes how good your cuts are.
Step-by-Step
You can break the waterjet cutting process into easy steps. Each step shows how the main parts work together to cut without heat.
Pressurization
- The pump makes the water very strong, over 40,000 psi.
- The chiller keeps the pump at the right temperature.
- The flow regulator controls how much water and abrasive material go in.
Erosion Action
- The strong water goes through the tiny hole, making a fast jet.
- For tough jobs, the abrasive delivery system adds garnet or other abrasives to the mixing chamber.
- The mixing chamber mixes the abrasive with the water jet.
- The focusing tube makes the jet thin and powerful.
Material Removal
- The cutting head points the jet at the material.
- The strong water and abrasive hit the surface and make tiny cracks.
- The steady jet wears away and removes small pieces.
- The drainage system takes away water and debris.
- The filtration system cleans the water so you can use it again.
Tip: Mixing water and abrasive the right way helps you get smooth edges.
How the Components Work Together
The pump, nozzle, and cutting head work as a team. The pump gives the water its power. The nozzle and hole focus that power into a sharp jet. The cutting head mixes water and abrasive for hard jobs. The mixing chamber and focusing tube keep the jet strong and accurate. The drainage and filtration systems keep your area clean and the machine working well.
- Waterjet cutting uses moving energy, not heat, to cut things.
- The hole and focusing tube must be lined up for the best results.
- You get smooth, clean edges and do not need much extra work.
| Factor | Impact on Precision |
|---|---|
| Orifice and Focusing Tube | Must be lined up and kept clean for a strong jet. |
| Edge Quality | Smooth, clean edges depend on the cutting head’s condition. |
| Kerf Width | Usually between 0.020″ and 0.050″; smaller tubes make thinner cuts. |
| Alignment | Lining up the parts is very important; if not, the jet is weaker. |
- Tolerances for small parts can be as close as ±0.003″ to ±0.010″.
- Kerf width is usually between 0.020″ and 0.050″.
- You get smooth, clean edges that need little extra work.
Remember: Waterjet cutting is special because it uses cold, strong water and abrasives to cut almost anything. You do not get heat damage and you get clean, exact cuts every time.
Types of Waterjet
Waterjet cutting has two main ways to cut things. You can pick pure waterjet cutting or abrasive waterjet cutting. Each one works best for certain jobs and materials. It is important to know how each type works. This helps you pick the right one for your project.
Pure Waterjet
Pure waterjet cutting uses only a strong stream of water. No abrasive particles are added. The water moves fast and hits the material hard. This method is best for soft or thin materials. You can use it for felt, foam, food, paper, rubber, and thin plastics. Pure waterjet cutting does not leave heat marks. The material stays safe, and the edges are clean.
Tip: Pure waterjet cutting is best for soft materials. It will not damage them.
You can see how pure waterjet cutting works in this table:
| Type of Cutting | Mechanism Description | Suitable Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Pure Waterjet Cutting | Uses high-pressure water to cut without abrasives. | Softer materials |
Here are some things you can cut with pure waterjet cutting:
- Felt
- Foam
- Food products
- Paper
- Rubber
- Thin plastics
Pure waterjet cutting is used in packaging, textiles, and food processing. It gives fast, clean cuts. You do not need extra finishing.
Abrasive Waterjet
Abrasive waterjet cutting mixes water with fine abrasive particles. The abrasive makes the waterjet stronger. You can cut hard and thick materials with this method. Use abrasive waterjet cutting for ceramic, metal, plastic, and stone. The abrasive helps the waterjet grind and cut tough surfaces. You get smooth edges and very accurate cuts.
Note: Abrasive waterjet cutting is great for hard materials like steel and stone.
Look at this table to see how abrasive waterjet cutting works:
| Type of Cutting | Mechanism Description | Suitable Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Abrasive Waterjet Cutting | Adds fine abrasive particles to the water for better cutting. | Harder materials |
You can use abrasive waterjet cutting for many jobs:
- Cutting metal sheets for machines
- Shaping stone for buildings
- Making ceramic parts for electronics
- Cutting thick plastics for cars
Abrasive waterjet cutting lets you cut almost any material. You can work with thick, hard, or heat-sensitive things. There is no heat damage or rough edges.
Here is a table that shows which materials work best for each waterjet type:
| Cutting Type | Best Suited Materials |
|---|---|
| Pure Waterjet | Felt, Foam, Food products, Paper, Rubber, Thin plastics |
| Abrasive Waterjet | Ceramic, Metal (steel, aluminum, copper), Plastic, Stone |
If you need to cut hard materials, use abrasive waterjet cutting. You will get clean and accurate cuts.
Pick pure waterjet cutting for soft materials. Pick abrasive waterjet cutting for hard materials. Waterjet cutting lets you work with many types of materials. You get strong cutting power and clean results.
Materials Cut by Waterjet
Metals
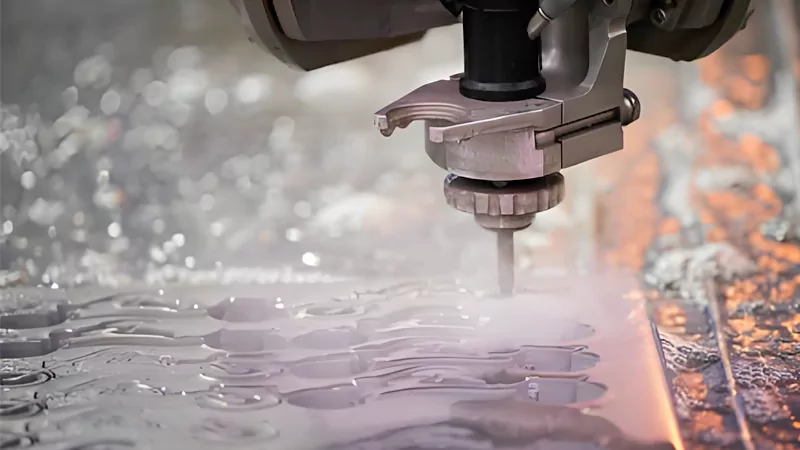

Waterjet cutting can cut many kinds of metals. This method does not use heat. The metal does not bend or change. The waterjet can cut thin or thick metal sheets. You get smooth edges and exact shapes.
Here are some metals you can cut with a waterjet:
- Steel
- Aluminum
- Titanium
- Mild steel
- Tool steel
- Inconel
- Hastelloy
- Alloy steel
- Nickel alloys
- Bronze
Many industries use waterjet cutting. Aerospace, automotive, and manufacturing all use it. Steel is strong, so it is often cut. Aluminum is easy to cut because it melts at a low temperature. Titanium is light and strong, so it is good for planes. Inconel and Hastelloy do not get damaged by heat or rust. You can cut these metals without heat problems. The waterjet can cut thick plates and small, detailed parts.
Tip: If you need to cut hard or heat-sensitive metals, waterjet cutting works best.
Stone
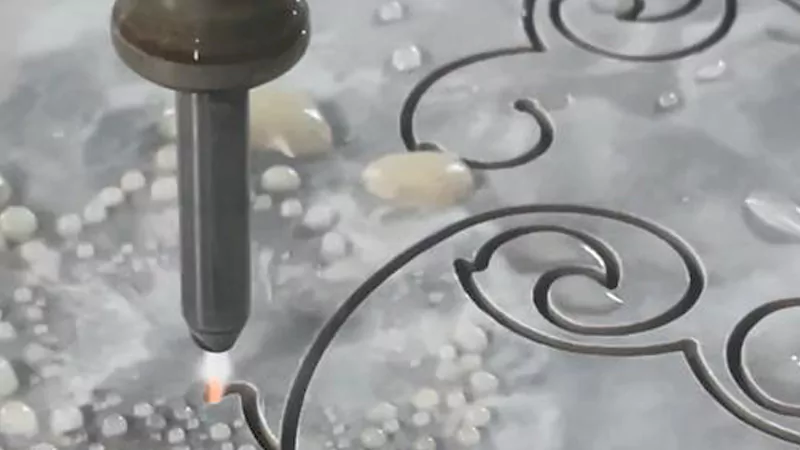

Waterjet cutting can shape many types of stone. The waterjet can cut hard stones like granite, marble, and slate. You can make patterns or straight lines for tiles, counters, and art.
A waterjet cutter can cut thick stone. You can cut stone up to 300 mm (12 inches) thick. This works for thin tiles and big stone slabs. The stone does not crack or chip. You get smooth edges and less waste.
- Maximum stone thickness: Up to 300 mm (12 inches)
- Typical cut range: 25 to 30 cm (10 to 12 inches) in hard materials
You can use waterjet cutting for custom floors, wall panels, and stone art. The waterjet can cut curves and sharp corners easily.
Glass
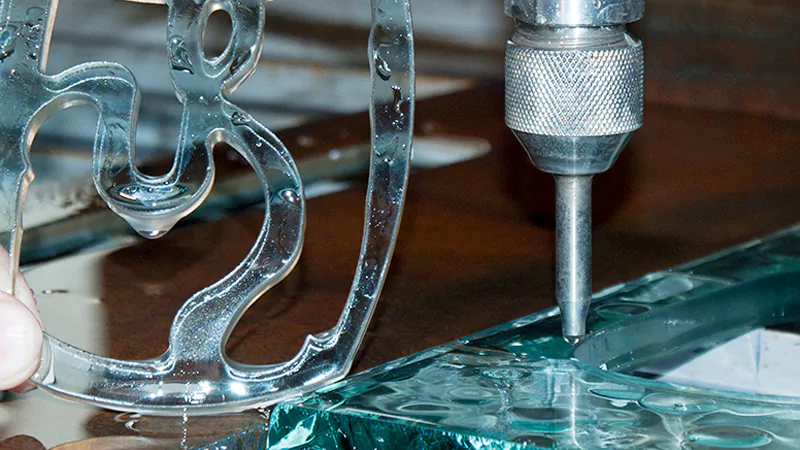

Waterjet cutting works well for glass. You can cut glass sheets, mirrors, and even layered glass. The cold process keeps the glass from breaking from heat. You get smooth edges and detailed shapes.
Cutting glass needs special care. Piercing is the most important step. You should pierce glass at low pressure. This stops cracks and chips. You also need to hold the glass well. A good support helps absorb the waterjet’s force. Using a finer abrasive gives a smoother cut and less chipping.
Here are some tips for cutting glass with a waterjet:
- Use a smaller nozzle for a focused stream.
- Support the glass to stop stress.
- Cut slower to avoid cracks.
- Pierce at low pressure to stop shattering.
| Technique/Consideration | Description |
|---|---|
| Control Cutting Speed | Slower cutting lowers pressure on thin glass and stops cracks. |
| Controlled Lead-Out | A careful finish at the end of cuts stops cracks or chips. |
| Use of Finer Abrasives | Finer abrasives make a focused stream and lower stress on glass. |
| Proper Piercing | Low pressure piercing lowers the risk of breaking the glass. |
You can use waterjet cutting for stained glass, mirrors, and glass panels. The process gives smooth edges and keeps the glass strong.
Plastics
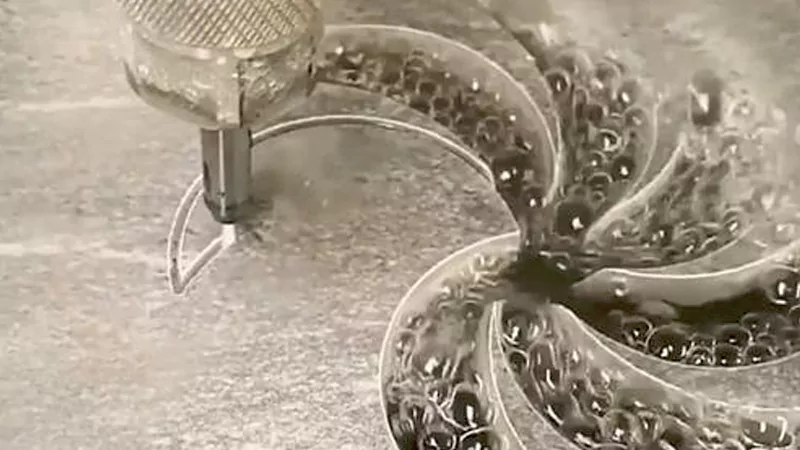

You can use waterjet cutting to shape many plastics. This method works well because it uses strong water. The water is cold, so the plastic does not melt or burn. The plastic stays strong and smooth. You get clean edges and detailed shapes. You do not need to do extra finishing.
Many plastics work well with waterjet cutting. Here are some of the best types:
- Engineering plastics like polycarbonate, acrylic, HDPE, UHMW PE, ABS, PEEK, and PTFE are tough and last long. These are used in machine parts and industrial products.
- Polyethylene is flexible and does not break easily. It is used for containers and packaging.
- Nylon is strong and does not wear out fast. You can cut gears, bearings, and moving parts from nylon.
Waterjet cutting works for thin and thick plastic sheets. You can cut simple or complex shapes. The water does not make the plastic change color or shape. You do not get rough edges or burrs. This means you spend less time finishing the parts.
If you need to cut plastics for signs, guards, or custom parts, waterjet cutting is a good choice. You can switch between plastics without changing tools. The process works for small or big jobs. You get accurate results every time.
Tip: Always check the thickness and type of plastic before you cut. Some plastics, like PVC, can make harmful fumes with other cutting methods. Waterjet cutting does not have this problem.
You can trust waterjet cutting for plastics when you want fast, smooth, and accurate cuts. The strong water makes it easy to cut designs, holes, and slots. You can even stack sheets and cut many parts at once.
Composites
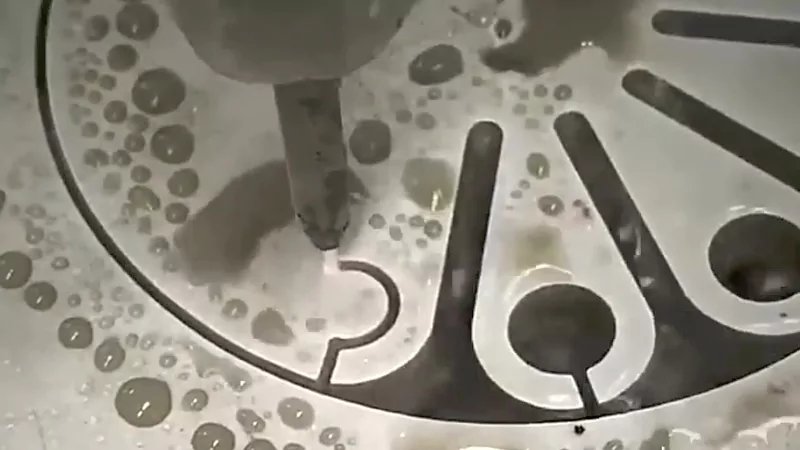

Waterjet cutting is great for cutting composite materials. Composites mix two or more things, like carbon fiber and resin, to make strong and light parts. Other cutting methods can cause problems like layers coming apart, burning, or rough edges. Waterjet cutting uses cold, strong water to stop these problems.
You can cut composites fast and with high accuracy. The process does not use heat, so there is no warping or damage. The thin water stream removes only a little material, so there is less waste. You get a smooth finish and often do not need extra work.
Here is a table showing how waterjet cutting is better than other ways for composites:
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Fast Process | Waterjet can cut composites in one pass, making it much faster. |
| Reduced Wastage | The thin water stream means you waste less material. |
| High-Quality Cutting | Waterjet gives a smoother finish, so the parts look better. |
| Accuracy | Waterjet is very precise and makes small cuts, good for fitting parts together. |
| Cold Cutting Process | No heat means the material does not get damaged. |
| No Distortion | No heat means the material does not bend or warp. |
| Safety | The machine is controlled by computers, so it is safer for workers. |
You can use waterjet cutting for composites in planes, cars, and sports gear. The strong water cuts carbon fiber, fiberglass, and layered materials easily. You get tight fits and clean edges, which are important for parts that must fit together.
If you want to avoid damage and get the best results, pick waterjet cutting for your composite projects. The process keeps your materials strong and your parts looking good.
Waterjet Cutting vs Other Methods
Laser
You might wonder how waterjet cutting is different from laser cutting. Both can make very exact cuts, but they work in different ways. Laser cutting uses a strong light beam to cut things. It works on metals, plastics, wood, glass, and ceramics. But laser cutting has trouble with shiny materials and thick pieces. Most lasers can only cut things up to 30-40 mm thick.
Waterjet cutting uses a strong stream of water, sometimes with abrasive particles. You can cut almost anything with it, like metals, composites, stone, glass, ceramics, and even food. Waterjet cutting can handle much thicker materials, up to 250-300 mm. You do not have to worry about heat damage because waterjet cutting is a cold process.
Here is a table to help you compare the two methods:
| Cutting Method | Material Compatibility | Precision and Quality |
|---|---|---|
| Laser Cutting | Metals, plastics, wood, glass, ceramics; limited with reflective materials and thicknesses up to 30-40 mm. | Very high precision with a kerf width around 0.15 mm; excellent for intricate cuts and tight tolerances. |
| Waterjet Cutting | Virtually any material, including metals, composites, stone, glass, ceramics, and food; thicknesses up to 250-300 mm. | Good accuracy with a kerf width of about 0.5 mm; no heat-affected zone, preserving material properties. |
Note: If you need to cut thick or heat-sensitive materials, waterjet cutting gives you more options.
Plasma

Plasma cutting uses electricity and gas to make a super hot plasma jet. This jet melts and blows away the material. You can use plasma cutting for metals like steel and aluminum. Plasma cutting is fast and good for thick metal plates. But it makes a heat-affected zone, which can change the material near the cut.
Waterjet cutting does not use heat, so you do not get warping or changes in the material. You can cut more types of materials, not just metals. Plasma cutting costs less to run, about $15 per hour. Waterjet cutting costs about $30 per hour. Most of the waterjet cost comes from abrasives.
| Cutting Method | Operating Cost per Hour | Main Cost Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Plasma Cutting | $15 | Electricity, gases, consumables |
| Waterjet Cutting | $30 | Electricity, consumables, abrasives (75%) |
Tip: Pick waterjet cutting if you want clean edges and no heat damage, even if it costs more.
Mechanical

Mechanical cutting uses tools like saws, drills, or mills. These tools touch the material to cut it. You can use mechanical cutting for many things, but it can leave rough edges. You might need to smooth them out later.
Waterjet cutting gives you clean, smooth edges that usually do not need more work. The high-pressure water does not make a heat-affected zone. This keeps the material’s natural properties. Mechanical cutting can cause stress and tiny cracks in the material. It also wears out the tools faster.
| Cutting Method | Edge Quality |
|---|---|
| Waterjet Cutting | Produces clean, smooth edges that typically do not require additional finishing. |
| Mechanical Cutting | Often leaves rough edges that may need further processing. |
- Waterjet cutting: No heat-affected zone, less tool wear.
- Mechanical cutting: Can cause stress and micro-cracks, and more tool wear.
Waterjet cutting stands out because it uses high-pressure water to cut without heat or stress. You get better edge quality and your tools last longer.
Key Differences
When you look at waterjet and other cutting methods, you notice many big differences. Each way of cutting has things it does well and things it does not. Knowing these differences helps you pick the best way to cut your stuff.
1. Cutting Process
A waterjet uses a strong stream of water to cut things. Sometimes, it mixes in abrasives to help. It does not use heat. Laser and plasma cutting use heat to melt or burn. Mechanical cutting uses sharp tools that touch the material.
2. Material Compatibility
A waterjet can cut almost anything. It works on metals, stone, glass, plastics, and composites. Laser and plasma are best for metals and some plastics. Mechanical cutting works for many things, but can have trouble with very hard or thick stuff.
3. Edge Quality and Precision
Waterjet makes smooth and clean edges. You do not see burn marks or rough spots; the quality of the cut is higher than in other ways. Laser cutting is very exact but can leave a heat-affected zone. Plasma cutting is fast, but edges can be rough. Mechanical cutting often needs extra work to make the edges smooth.
4. Thickness Range
Waterjet can cut thick materials, even up to 12 inches. Laser and plasma work best on thin sheets. Mechanical cutting depends on the tool and what you are cutting.
5. Environmental Impact
Waterjet is cleaner and safer than most other ways. It does not make heat, fumes, or dust in the air. It uses less energy and makes less waste. Tools last longer because they do not touch the material. Waterjet cutting is also quieter.
Here is a table that shows how waterjet is different from traditional cutting:
| Feature | Traditional Cutting | Waterjet Cutting |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Generation | High | None |
| Airborne Pollutants | Yes | None |
| Energy Consumption | High | Moderate to Low |
| Material Waste | Significant | Minimal |
| Tool Wear | Frequent | Minimal |
| Noise Levels | High | Lower |
Waterjet uses water and natural abrasives to cut. You do not see heat or fumes. This keeps your work area safe and clean. The material stays the same and does not warp or burn.
Cutting with heat can change the shape and strength of your material. You might need to fix these problems later. Waterjet does not have this risk. You get cleaner cuts and save time.
6. Cost and Maintenance
Waterjet costs more to use than plasma or mechanical cutting. Most of the cost comes from abrasives. You save money on tools because they last longer. You also spend less time cleaning up and finishing parts.
Tip: If you want clean and exact cuts with less harm to the environment, waterjet is a good choice.
Think about your material, how thick it is, and what you need before you choose a cutting method. Waterjet gives you many options, keeps you safe, and makes high-quality cuts.
Advantages and Limits
Advantages
No Heat
You do not have to worry about heat with a waterjet. The cutting does not make a heat-affected zone. This means you avoid warping or color changes. You also do not get tiny cracks. The material stays safe inside. You can cut things like plastics, composites, and tempered glass without damage.
Waterjet cutting does not make a heat-affected zone. This is a big reason people choose waterjet cutting.
Here is a table that shows how waterjet compares to other ways:
| Cutting Method | Heat-Affected Zone | Microstructure Alteration |
|---|---|---|
| Waterjet | No | No |
| Laser | Yes | Yes |
| Plasma | Yes | Yes |
| Flame | Yes | Yes |
Precision
Waterjet cutting gives you very exact cuts. Cutting accuracy is very high. You can make small shapes and tight fits. The edges are smooth and do not have burrs. Most jobs do not need extra finishing. The edge stays clean, even on thick pieces.
- Waterjet cutting does not make heat, so the material stays strong.
- You can cut detailed designs and shapes from many angles.
- You can cut one sheet or many stacked sheets.
Versatility
Waterjet works on lots of materials. You can cut metal, stone, glass, plastic, and composites. You do not need to change tools for different jobs. A waterjet can cut thick and thin pieces. The cutting thickness can achieve 12 inches of aluminum or 8 inches of titanium. Waterjet is used in aerospace, cars, buildings, and electronics.
Here is a table that shows how waterjet stands out:
| Feature | Waterjet Cutting | Other Cutting Technologies |
|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | High precision with small cuts | Often less exact |
| Thickness | Can cut very thick pieces | Usually only thin pieces |
| Edge Quality | Makes smooth, burr-free edges | May need extra work for thick pieces |
| Material Distortion | No bending from heat | Can bend heat-sensitive materials |
| Heat Affected Zone | No HAZ, keeps material strong | Makes HAZ, changes material |
| Material Limitations | Cuts many types of materials | Only some materials |
| Sustainability | Good for the environment, uses recyclable stuff | Makes fumes, needs air cleaning |
| Application Versatility | Used in many industries | Used mostly in a few fields |
Tip: You can cut more than one layer at once. This saves time and helps you work faster.
Limits
Speed
Waterjet cutting is slower than laser cutting for thin pieces. The process takes longer because it uses erosion, not melting. If you need to make thin sheets fast, you should look at other ways.
- Waterjet cutting is slower for thin materials.
- You need to plan for longer times on big jobs.
Cost
You need to think about the cost before picking a waterjet. The machines cost more to buy than laser machines. The process uses abrasives, which adds to the cost. You spend more each hour than with plasma or mechanical cutting.
- Waterjet machines cost more to buy.
- Using abrasives makes each cut cost more.
Thickness
A waterjet can cut thick pieces, but there are limits. For aluminum, you can cut up to 12 inches thick. For hard metals like titanium or tool steel, the limit is 8 inches. If you try to cut thicker pieces, the edge may not look as good.
- A waterjet can cut a 10-inch thick block of aluminum.
- Harder materials have lower thickness limits for good cuts.
Note: Always check the type and thickness of your material before you start cutting.
Choosing Waterjet Cutting
Best Uses
Waterjet cutting works in many industries because it cuts many materials. This method gives you clean and exact cuts without using heat. If you want to keep your material strong and safe, waterjet is a good pick. People use a waterjet when they need accuracy and want to protect the material.
Here is a table that shows where waterjet is used most:
| Industry/Field | Application Description |
|---|---|
| Prototyping | Makes models and samples with sharp corners and small details. |
| Laboratory Equipment | Cuts stainless steel and alloys while keeping them strong. |
| Oil and Gas | Slices tough materials like Inconel for underwater equipment. |
| Mining | Cuts stone, even up to 100 feet thick, for special projects. |
| Food Processing | Slices meat and vegetables cleanly, keeping food safe and fresh. |
| Aerospace | Shapes turbine blades and jet parts from hard materials. |
| Automotive | Cuts engine parts with high accuracy for better performance. |
| Defense and Military | Makes complex parts from kevlar and composites using advanced cutters. |
| Marine | Shapes rubber and composites for boats and watercraft. |
| Medical Equipment | Cuts new materials for surgical tools with great precision. |
| Construction | Shapes fiberglass, metals, and cement boards for buildings. |
| Electronics | Cuts sensitive parts without heat damage. |
| Job Shops | Handles many types of materials and custom jobs. |
| Metal Service Centers | Cuts large sheets of metal quickly and accurately. |
You can see that waterjet helps in many areas. If you need to cut thick stone, shape metal, or slice food, a waterjet gives a smooth result. You do not have to worry about heat or rough edges.
Tip: If your project needs very exact cuts or uses materials that do not like heat, waterjet is often the best way.
Decision Factors
Before you choose a waterjet for your job, you should think about some important things. These points help you know if a waterjet is right for you. You want the best results for your time and money.
Here is a table to help you compare what matters most:
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Expertise and Industry Knowledge | Pick a provider who knows how to do special cutting jobs and can help you. |
| Cutting Technology and Capabilities | Check if the machines and software can make tricky shapes and keep tight sizes. |
| Turnaround Time | Make sure the provider can finish your job on time. |
| Cutting Precision and Tolerance | Ask for samples to see if the cuts are good enough, especially for strict jobs. |
| Quality Control | Look for strong quality checks and certifications like ISO 9001. |
| Cost and Value | Know the price and see if it fits your budget and project needs. |
You should talk with your provider about what you want to do. Ask if they have worked with your material before. Make sure they use new machines for the best cuts. If you need your job done fast, check their schedule. Always look at sample cuts to see the quality. Good providers will show you how they check quality and explain their prices.
Note: Picking the right waterjet service means looking at skill, machines, timing, quality, and cost. This helps you get the best value for your project.
You can count on waterjet for cold and exact cutting. It works on many things like metal, glass, and composites. You do not get heat damage, and the edges are always smooth. Waterjet is great for thick or shiny materials. It gives the best results for these jobs. The table below explains why waterjet is a good choice:
| Criteria | Description |
|---|---|
| No thickness limitations | Cuts thin or thick materials with ease |
| No heat input | Keeps material strong and unchanged |
| Simple material change | Switch materials quickly with only speed adjustments |
| High accuracy | Achieves the tightest tolerances for precision work |
- Waterjet gives the most accurate cuts and tightest fits.
- You can use more cutting heads to finish jobs faster.
- It is easy to take care of and adjust.
Think about what you need to cut, the shape you want, and your project before picking a cutting method.
FAQ
You can cut metal, stone, glass, plastic, rubber, foam, and composites. Waterjet cutting works on thick and thin pieces. You do not need to worry about heat damage.
Waterjet cutting does not use heat. You keep the material’s strength and shape. You do not see warping, burning, or melting.
You can cut up to 12 inches of aluminum. For steel and hard metals, you can cut up to 8 inches. Stone can be cut up to 12 inches thick.
Yes, you can use waterjet cutting for food. The process does not use heat or chemicals. You get clean slices and keep food fresh.
Waterjet cutting gives you tight tolerances. You can get accuracy as close as ±0.003 inches for small parts. The edges stay smooth and clean.
Most parts do not need extra finishing. Waterjet cutting gives you smooth edges. You save time and money on post-processing.
You can stack sheets and cut many layers at the same time. This helps you finish jobs faster and saves material.
Pure waterjet uses only water. You cut soft materials like foam and rubber. Abrasive waterjet adds grit. You cut hard materials like metal and stone.
Tip: Always choose the right waterjet type for your material. This gives you the best results.


