By implementing sustainable machining practices and advanced coolant recycling systems that comply with the ISO 14001 Environmental Management System, you can not only significantly reduce the carbon footprint in your manufacturing process but also improve process stability through refined management.
These Methods Help Your Business Immediately
Look at the key metrics below. These are not empty concepts, but quantified results based on actual operating data from our factory:
| Core Metric | Technical Description & Parameter Boundaries |
|---|---|
| Resource Recovery & Cost Reduction | Turns waste costs into money by recoIncreased coolant recovery rate from 40% to over 95%, reducing waste disposal costs by 80%. Recovered 98% of attached cutting oil using centrifugal separation technology. |
| Operational Efficiency Enhancement | Used real-time monitoring systems to control coolant concentration fluctuations within ±0.5% Brix, significantly reducing tool wear caused by insufficient lubrication and improving OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness) by 12%. |
| Environmental Impact Reduction | According to ISO 14064 standards, the carbon footprint per part was reduced by 15%. Completely eliminated disorderly discharge of emulsion. |
| Regulatory Compliance Assurance | Automated recording systems ensure all discharge data complies with strict EPA RCRA and EU CBAM (Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism) requirements, achieving 100% traceability. |
| Zero-Discharge Capabilities | Implemented vacuum distillation technology to treat wastewater, producing only a small amount of solid residue, achieving true “Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD).” |
By optimizing cutting parameters (such as Vc and fz) in conjunction with efficient cooling systems, we have tangibly reduced energy consumption and emissions.
Key Takeaways
Core of Closed-Loop Systems: It’s not just circulation; it is a complete loop including oil removal, sterilization, and filtration (precision must reach 10 microns).
Energy Efficiency Management: Use IE4 or IE5 efficiency class motors to drive machine tools, reducing energy consumption by 40% in standby mode.
Lean & Training: Employees must master the standardized operation of using Refractometers and pH strips, which is key to preventing problems before they arise.
Table of Contents
Sustainable Machining and Carbon Footprint
Specific Paths to Emission Reduction
Transitioning to sustainable machining is not just a slogan; it is the practice of green manufacturing standards like ASTM E2986.
Traditional high-energy roughing (e.g., large depth of cut, low feed) is not only inefficient but also generates excessive cutting heat, accelerating coolant degradation. This method consumes more electricity and generates more scrap carbide due to short tool life.
Sustainable machining aligns highly with the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDG 12). This is not just about using green energy, but about process optimization.
Our Experience Implementing Closed-Loop Systems
Taking the membrane filtration recovery system introduced in our factory as an example, it is not a panacea, but the results are significant when handling water-soluble coolants:
- Lessons from MDA & Local Application: Referencing MDA’s approach, we equipped every CNC machine with an Oil Skimmer. This not only recovers coolant but, more importantly, removes “Tramp Oil.”
- Lessons from Failure: We used to neglect tramp oil removal, leading to an outbreak of anaerobic bacteria within 3 months, causing the coolant to stink and be scrapped. Now, by strictly controlling tramp oil content to <1%, coolant life has been extended to over 18 months.
- Data Speaks: By reducing the frequency of fluid changes, we decreased new fluid purchases by 65%.
Business Benefits: More Than Just Environmental Protection
The Economics & Compliance
Sustainable machining directly affects the factory’s P&L (Profit and Loss).
- Reduced Compliance Costs: Avoided the risk of huge fines due to wastewater COD/BOD exceedances.
- Export Advantages: For our German clients, providing a green manufacturing declaration compliant with RoHS and REACH standards has become a prerequisite for obtaining orders.
- Financing Convenience: Green manufacturing enterprises find it easier to obtain low-interest equipment loans from banks.
Strategy & Competitiveness Matrix
| Strategy | Specific Impact on Competitiveness (Engineer’s View) |
|---|---|
| Reducing Material Waste | Introduced Nesting Software, increasing sheet utilization from 75% to 88%, directly lowering raw material costs. |
| Coolant Optimization | Using long-life semi-synthetic coolants; although the unit price is higher, the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) dropped by 30% annually. |
| Energy Efficiency Upgrades | Installed Variable Frequency Drives (VFD) to control high-pressure coolant pumps, automatically lowering frequency during non-cutting times for significant energy savings. |
Why Sustainability Matters in CNC Machining

Environmental Drivers & Regulatory Boundaries
In CNC machining, one must always be alert to environmental red lines.
- Hazardous Waste Classification Red Line: According to regulations, ordinary metal chips (e.g., aluminum, steel) must be strictly separated from hazardous waste (e.g., oil sludge, grinding sludge). Mixed storage makes recycling impossible and skyrockets disposal costs by 10 times.
- Disposal Compliance: Licensed third-party vendors must be commissioned for hazardous waste transfer, and manifests must be kept for at least 5 years for inspection.
Market Demands: What Customers Are Watching
More and more Tier-1 customers are requiring us to provide Scope 1 and Scope 2 carbon emission data.
- Green Supply Chain: Customers look not only at product tolerances but also at whether your production process involves PFAS (Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances).
- ESG Principles Penetration: In the CNC turning field, equipment using Dry Cutting or Minimum Quantity Lubrication (MQL) technology is more favored by the high-end market.
Advanced Coolant Recycling and CNC Cooling Systems
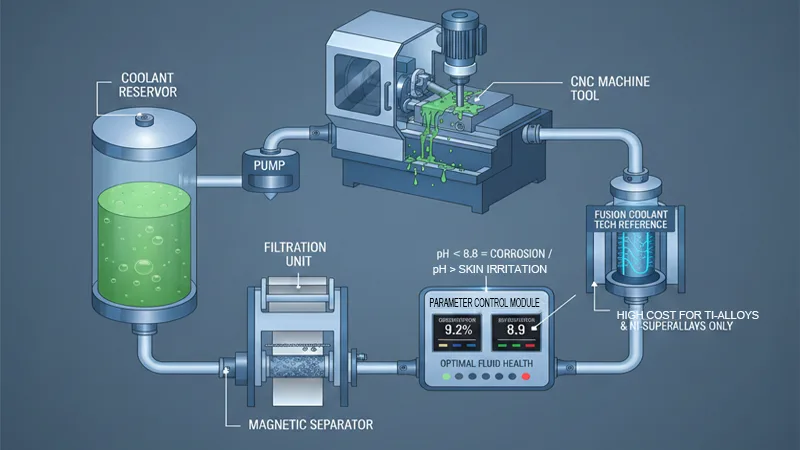
Closed-Loop Systems: Operation & Field Practice
To make coolant run in a “closed loop,” the core lies in maintaining fluid health indicators.
- Parameter Control: The closed-loop system works effectively only when the concentration is maintained at 8-10% and the pH value between 8.8-9.2. A pH that is too low causes equipment corrosion, while one that is too high causes operator skin irritation.
- Filtration Precision: We introduced 10-micron paper band filters and magnetic separators. Without filtering fine particles, they form a “sandblasting effect” at high-pressure nozzles, damaging the workpiece surface.
- Fusion Coolant Systems Tech Reference: While supercritical CO2 cooling is excellent, the cost is currently high, making it mainly suitable for Hard-to-cut materials like titanium alloys and nickel-based superalloys.
CO₂ Reduction Metrics
Energy Consumption Comparison: Traditional high-pressure, high-flow cooling systems consume immense energy. After introducing VFD-controlled closed-loop systems, pump energy consumption dropped by 45%.
Toxicity Reduction: Closed-loop systems significantly reduced the frequency of adding Biocides, improving workshop air quality.
Eco-Friendly Coolants: Bio-Based & Nano Technology
Applicability of Biodegradable & Nano Coolants
Not all machine tools are suitable for a direct switch to bio-based coolants.
- Compatibility Warning: Before switching to bio-based coolants, machine tool seal materials must be checked. Older NBR (Nitrile Rubber) seals may swell when exposed to certain ester base oils and must be replaced with Viton (Fluoroelastomer).
- Nano Fluid Advantages: Coolants with added nano-graphene or aluminum oxide particles increased tool life by 25% when turning HRC 50+ hardened steel.
Practical Boundaries of Minimum Quantity Lubrication (MQL)
While MQL technology is eco-friendly, it has clear process applicability limits:
- Suitable Scenarios: Extremely suitable for milling aluminum alloys and shallow hole drilling.
- Unsuitable Scenarios: For deep hole drilling (depth-to-diameter ratio > 5D) or heavy-duty turning of stainless steel (e.g., 304/316), MQL is prone to causing chip adhesion and drill breakage due to insufficient chip evacuation and heat removal capabilities. In these cases, High-Pressure Coolant (HPC) must be used.
- Usage Standards: Typical MQL usage is controlled at 10-50 ml/hour, far below the 20-50 ml/min of traditional wet machining.
Sustainable Machining Practices: Material & Waste Management
Material Optimization & AI Poka-Yoke

- Near-Net-Shape: For high-volume orders, we advise customers to switch from bar stock machining to forgings or castings, which can reduce material removal volume by over 40%.
- AI Poka-Yoke: Using in-machine probes (Renishaw Probe) for on-machine inspection. If the first piece is not qualified, mass production never starts, eliminating bulk scrap.
Maximizing Scrap Value
- Briquetting: Loose aluminum chips have high volume, oxidize quickly, and have a low recovery rate. We use briquetting machines to compress chips into high-density blocks. This not only squeezes out residual coolant (for reuse) but also increases the recovery smelting rate of scrap aluminum from 70% to 95%, raising the selling price by 15% per ton.
Energy-Efficient Machining & Resource Conservation
High-Efficiency Tools & Parameter Optimization
Selecting high-performance coated tools (e.g., TiAlN or AlCrN coatings) allows us to work under dry cutting conditions.
| Metric | Traditional Process | High-Efficiency/Dry Process | Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Annual Energy Costs | $3.2M | $2.4M | 25% reduction |
| Material Removal Rate (MRR) | Low | High (Using Trochoidal Milling) | 40% Efficiency Boost |
| Tool Life | Short (Thermal shock causes cracks) | Long (Stable temperature) | 30% Life Extension |
Equipment Update Strategy: New equipment must have a “Sleep Mode,” automatically cutting off power to hydraulic and chip conveyor motors after 10 minutes of inactivity.
Implementing Sustainability: From Assessment to Execution
Assessment & Baseline
To implement green manufacturing, you first need to crunch the numbers.
- Step 1: Install smart meters and flow meters to collect at least 1 month of baseline data.
- Goal Setting: E.g., “Reduce coolant consumption by 20% while maintaining production volume.”
- Team Building: Establish a cross-functional team that must include equipment maintenance personnel, as they know best which machines leak oil the most.
System Integration & Waste Treatment Details
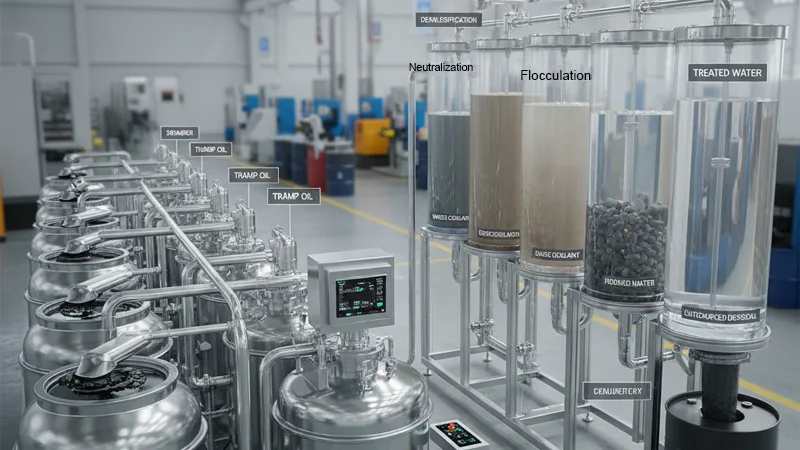

Tramp Oil Treatment: Skimmers must be installed in every coolant tank, or a central centrifuge must be used. Tramp oil not only affects machining quality but is also a breeding ground for bacteria.
Waste Fluid Neutralization: Before outsourcing disposal, waste coolant needs demulsification and flocculation pre-treatment to reduce water content, thereby lowering disposal costs charged by weight.
Training and Monitoring
Why Does Training Fail?
Often, workers remove oil mist collectors or privately increase coolant concentration because they find it troublesome.
- Hands-on Training: Teach operators how to use a refractometer and mandate recording a concentration reading every morning before startup.
- Incentive Mechanism: Include “coolant maintenance” in 5S assessments and reward teams that extend the fluid change cycle.
- Monitoring Dashboards: Display energy and consumable data in real-time on workshop screens to visualize waste.
Real-World Case Studies: Data & Lessons
Industry Success Stories & Our Practice
- Illinois Shop Case: They saved $25,000 using chip briquetting machines. We introduced similar equipment and found that, besides saving money, we could recover about 3% of cutting oil, which can be reused after simple filtration.
- German Prototyping Shop: 70% coolant reduction was credited to MQL usage. However, when machining nickel-based alloys, we found we had to switch back to wet machining, proving that a hybrid process path is the most realistic choice.
- TSMC & MDA: While large closed-loop systems are good, for High-Mix Low-Volume contract manufacturers, flexibility is more important. We adopted mobile filtration carts that serve different machines in rotation, resulting in a higher Return on Investment (ROI).
Network shows these tools help you reach goals and protect the environment. You can lower waste and emissions with smart systems and by improving your work.
The Future of Sustainability in Machining
Overcoming Barriers: Cost & Tech Thresholds
Initial Investment Pain Point: A closed-loop circulation system requires an initial investment of about $20,000-$50,000. However, considering the rising costs of coolant and hazardous waste disposal, the payback period is usually 14-18 months.
Tech Fear: Workers might resist MQL systems, thinking “it’s not clean without water flushing.” This requires adjusting nozzle angles and air pressure parameters to prove the machining results and change their mindset.
Trends & Innovations: Industry 4.0
IoT Monitoring: We are testing spindle load monitoring systems. When tool wear causes abnormal load spikes, the system automatically alarms and stops the machine, protecting the tool and avoiding part scrappage and energy waste due to tool breakage.
Cryogenic Machining: Utilizing liquid nitrogen (LN2) for cooling. Although currently only used for high-value medical device parts, this represents the future direction of “pollution-free machining.”
FAQ
It’s not just simple filtration. It involves physical separation (centrifugation), chemical adjustment (automatic pH and concentration dosing), and biological control (sterilization or bacteriostasis), aimed at circulating coolant indefinitely rather than periodically discharging it.
Yes. The carbon emissions from producing 1 liter of synthetic coolant are far higher than its physical volume. Extending its life by 2x is equivalent to reducing upstream chemical production emissions and downstream waste incineration emissions by 50%.
Absolutely not. You must consult the machine tool manufacturer first. Paint, seals, and cable jackets on certain older machine models can be dissolved by biological ester oils. A 48-hour immersion test is mandatory.
It is extremely effective for non-hard-to-cut materials (like aluminum, copper, free-cutting steel) and open machining (like face milling, external turning). However, use it with caution in deep grooves or deep hole machining where chip evacuation is difficult, to prevent overheating due to chip accumulation.
Based on our factory data, for mobile filtration units, it’s about 8-12 months; for central concentration filtration systems, it typically takes 24-36 months, but this brings more stable machining quality.
Beyond environmental sentiment, customers care more about supply chain stability. A supplier that could be shut down for rectification at any time due to environmental violations is a major risk. Green manufacturing proves the standardization of our management and the long-term continuity of our business.


