High-end hardware demands a synthesis of superior aesthetics and long-term functional integrity. Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) vacuum coating delivers a high-luster finish coupled with a formidable protective barrier. This process enhances the substrate’s structural resilience, ensuring hardware retains its “like-new” appearance under rigorous use. PVD significantly outperforms conventional finishing methods in mitigating scratches, mechanical wear, and oxidation.
Comparative Performance Analysis
| Surface Treatment | Durability & Performance Characteristics |
|---|---|
| PVD Coatings | Exceptional surface hardness, chemically inert, and environmentally sustainable (low VOCs). |
| Traditional Methods | Lower abrasion resistance and higher environmental impact compared to vacuum deposition. |
| Electroplating | Higher environmental footprint; PVD offers superior hardness and is a cleaner, “green” alternative. |
| Anodizing | PVD provides higher surface hardness and superior wear resistance compared to standard anodic films. |
| Black Oxide & Parkerizing | PVD offers vastly superior corrosion resistance and longevity compared to these conversion coatings. |
Investing in PVD technology ensures your hardware benefits from a premium aesthetic while maximizing its operational lifespan.
Key Takeaways
- Exceptional Durability: PVD vacuum coating applies a dense, high-hardness layer at the atomic level, offering peerless resistance to abrasion, corrosion, and impact.
- Technological Superiority: The PVD process ensures a more durable bond and longer lifecycle than legacy coating methodologies, making it the definitive choice for high-specification hardware.
- Environmental Stewardship: PVD is an eco-friendly “dry” process. It eliminates the need for toxic chemical baths, produces minimal waste, and aligns with modern sustainability standards.
- Maintenance & Longevity: Through routine non-abrasive cleaning, PVD-coated components can maintain their decorative and functional properties for decades. Choosing PVD is a commitment to both enduring style and engineering excellence.
Table of Contents
What Is PVD Vacuum Coating?
PVD Process Overview
For hardware that demands both distinctive aesthetics and extreme longevity, Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) offers a cutting-edge solution. PVD is a vacuum-based thin-film coating technology that deposits a high-density, resilient layer onto a substrate. The process is executed through a series of precision-engineered stages to ensure maximum film integrity:
- Surface Pre-treatment: Comprehensive ultrasonic cleaning and degreasing to ensure an impurity-free substrate.
- Vacuum Evacuation: Removing atmospheric gases and moisture from the chamber to create a high-vacuum environment.
- Thermal Conditioning: Heating the chamber to a stabilized temperature to promote optimal film adhesion.
- Sputtering or Evaporation: Utilizing high-energy sources to vaporize the source material (target) into individual atoms or plasma.
- Reactive Gas Introduction: Introducing controlled gases (e.g., Nitrogen or Oxygen) to create specific chemical compounds (Nitrides/Carbides) for color and hardness.
- Deposition & Film Growth: The vaporized material condenses on the hardware, forming a uniform, thin film.
- Controlled Cooling: Regulated temperature reduction to prevent thermal shock before removal.
- Post-treatment & Quality Control: Final inspection and finishing to ensure color consistency and structural durability.
This process results in a coating only a few microns thick that achieves atomic-level bonding with the substrate. The result is an ultra-hard surface that is virtually immune to peeling, flaking, or wear.
Luxury Appeal of PVD
Beyond its functional superiorities, PVD coatings provide a sophisticated visual and tactile experience. They allow for a diverse palette of premium finishes—ranging from Rose Gold and Graphite to Brushed Nickel and Champagne—without compromising the metallic feel of the hardware. These finishes are engineered to remain tarnish-free even in high-traffic or high-touch environments.
| Property | Technical Description |
|---|---|
| Aesthetic Excellence | Delivers a premium metallic luster in a wide spectrum of customizable, brand-aligned finishes. |
| Abrasion & Wear Resistance | Achieves high surface hardness (often exceeding 2500 HV), providing a formidable shield against mechanical damage. |
| Corrosion & Chemical Stability | Provides an inert barrier that prevents oxidation, tarnishing, and salt-spray corrosion in humid environments. |
| Oleophobic & Low-Maintenance | Features a high-density surface that resists fingerprints and contaminants, requiring no harsh chemical cleaners. |
| Sustainable Manufacturing | A “dry” vacuum process that produces zero hazardous runoff, utilizing non-toxic, eco-friendly precursors. |
PVD vacuum coating represents the pinnacle of surface technology, merging unrivaled beauty with industrial-grade durability. With a functional lifespan often exceeding ten years, PVD-coated hardware is the definitive choice for premium architectural and consumer applications.
PVD Coating Durability
Hardness and Wear Resistance
In the realm of high-specification hardware, surface integrity is paramount. Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) creates a high-density, metallurgically bonded layer that fundamentally transforms the substrate’s surface properties. This thin-film deposition ensures exceptional resistance to mechanical deformation and abrasive wear.
PVD coatings typically register between 1800 HV and 3500 HV on the Vickers Hardness scale. To put this in perspective, PVD finishes are significantly harder than tool steel and conventional chrome plating, providing a near-impenetrable shield against scratches and surface fatigue.
- Structural Integrity: The coating maintains the hardware’s geometric precision and aesthetic luster under high-stress conditions.
- Thermal Stability: PVD films remain chemically and mechanically stable at elevated temperatures, ensuring performance in demanding industrial or kitchen/bath environments.
- Tribological Advantages: The smooth, dense morphology of the coating results in a low coefficient of friction. This reduces surface drag, enhancing the performance of moving components and often reducing the need for external lubricants.
- Extended Lifecycle: By significantly mitigating surface wear, PVD technology reduces the “total cost of ownership” by extending the replacement intervals of premium hardware.
Corrosion Protection & Environmental Resilience

For hardware exposed to high humidity, coastal air, or chemical cleaning agents, PVD serves as a critical barrier against oxidation and galvanic corrosion.
Validated through rigorous Salt Spray Testing (neutral salt spray), PVD coatings can withstand over 1,000 hours of exposure without signs of pitting or tarnish. This level of performance ensures that the hardware remains structurally sound and visually pristine in the most corrosive environments.
- Chemical Inertness: The coating is chemically stable, protecting the underlying metal (such as stainless steel, brass, or zinc alloys) from acidic or alkaline exposure.
- Substrate Versatility: PVD can be applied at relatively low temperatures (150°C–450°C), allowing for the protection of heat-sensitive materials without compromising their mechanical properties.
- Sustainable Longevity: The combination of corrosion resistance and UV stability means the finish will not fade, peel, or tarnish, even when exposed to direct sunlight or moisture for decades.
| Feature | Technical Benefit for High-End Hardware |
|---|---|
| Exceptional Hardness | Prevents localized deformation, scratching, and impact damage. |
| Superior Wear Resistance | Maximizes the operational lifespan of high-contact components. |
| Corrosion Protection | Provides an airtight barrier against oxidation, salt-air, and humidity. |
| Surface Passivation | Maintains aesthetic consistency and functional integrity over time. |
PVD coating durability has established a new benchmark for the hardware industry. By integrating extreme hardness with superior chemical resistance, PVD offers a finish that is not only visually stunning but technically superior to any traditional coating methodology.
PVD Vacuum Coating Lifespan
Typical Lifespan Range
Longevity is a hallmark of Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) technology. PVD coatings offer a significantly extended service life compared to traditional finishing methods. Under standard operational conditions, PVD coatings typically maintain their integrity for 10 to 20 years on architectural hardware, while high-wear items like jewelry typically see a lifespan of 2 to 10 years. With proper maintenance, these coatings can protect the underlying substrate for several decades, making PVD the premier choice for luxury hardware that demands permanent aesthetic and structural performance.
Comparative Longevity Analysis
| Coating Type | Lifespan & Durability Comparison |
|---|---|
| PVD Coatings | 3x to 5x the lifespan of conventional organic/spray coatings. |
| Electroplating | PVD offers superior wear resistance and does not chip or peel like traditional plating. |
The functional lifespan of a PVD finish is a variable of the film thickness, deposition environment, and the frequency of mechanical abrasion. For instance, PVD gold-functionalized surfaces offer a “lifetime” finish that resists the tarnishing and fading common in traditional gold-leaf or thin-film electroplating.
Factors That Optimize and Extend Lifespan
To maximize the lifecycle of PVD-coated hardware, several technical and maintenance factors must be considered. Precision during the deposition phase and proper field care are essential for long-term success.
- Application-Specific Coating Selection: Selecting the appropriate compound is vital. Chromium Nitride (CrN) is the industry standard for superior corrosion resistance, while Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC) is utilized when extreme surface hardness and low friction are required.
- Optimized Material Compatibility: Matching the coating material to the specific properties of the substrate ensures a synergistic bond, preventing galvanic corrosion.
- Rigorous Process Control: Maintaining high-vacuum integrity and precise temperature regulation during deposition ensures maximum adhesion strength, preventing delamination.
- Maintenance Protocols: Routine cleaning with pH-neutral solutions prevents the accumulation of particulate matter that could eventually lead to surface abrasion.
- Environmental Management: While PVD is highly resilient, minimizing exposure to extreme pH environments or abrasive industrial cleaners will preserve the high-luster finish.
- Advanced Post-Processing: The application of Nano-coatings (e.g., Anti-Fingerprint/AF treatments) can provide an additional sacrificial layer, further shielding the PVD film from oils and atmospheric contaminants.
By adhering to these standards, PVD-coated hardware delivers a superior Return on Investment (ROI) through reduced replacement costs and maintained brand prestige.
Pro-Tip: To preserve the molecular integrity of the finish, clean PVD hardware using only a soft cloth and mild soap. Avoid abrasive pads or chloride-based cleaners, which can compromise the protective barrier over time.
PVD vs. Other Surface Treatments
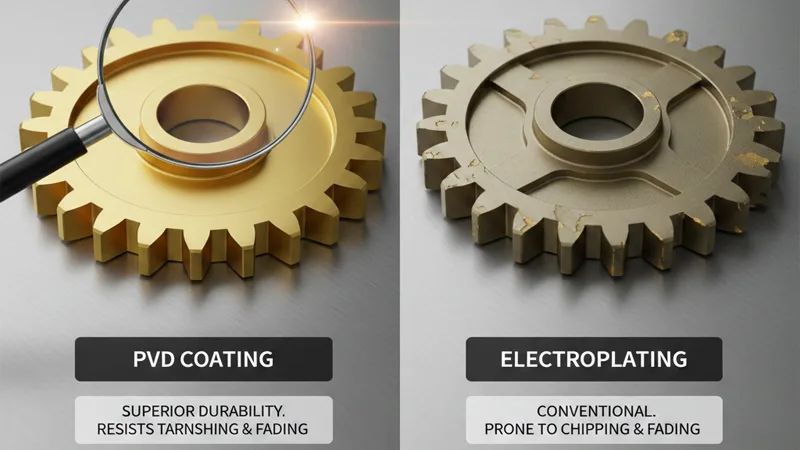
Comparative Analysis: PVD vs. Electroplating
For premium hardware where aesthetic brilliance and surface longevity are non-negotiable, PVD offers a significant technological leap over traditional electroplating. While electroplating provides a bright finish and is effective for softer base metals, PVD coatings offer vastly superior abrasion resistance and color stability. Unlike electroplating, which can be prone to wear and tarnish over time, PVD-treated hardware maintains its original luster even under high-frequency contact. For example, PVD-functionalized gold on stainless steel substrates can maintain its integrity for 3 to 10 years in consumer applications.
| Economic Factor | PVD Vacuum Coating | Traditional Electroplating |
| Initial Investment | Higher upfront capital/processing cost. | Lower initial processing cost. |
| Long-term Value | Minimal maintenance and extreme durability lead to a lower Total Cost of Ownership. | High frequency of replacement or refinishing increases long-term costs. |
Comparative Analysis: PVD vs. Powder Coating

Powder coating is often utilized for vibrant colors, but it is susceptible to UV degradation, chipping, and “orange peel” textures. In contrast, PVD is a high-precision vacuum process that delivers superior hardness and color retention.
| Performance Metric | PVD Vacuum Coating | Powder Coating |
|---|---|---|
| Surface Hardness | Up to 3300 HV (Vickers) | Approx. 100–200 HV |
| Scratch Resistance | Exceptional; molecularly bonded to the substrate. | Moderate; prone to localized chipping and peeling. |
| UV & Color Stability | Excellent; resistant to fading under direct sunlight. | Subject to oxidation and fading over time. |
Technical Advantages of PVD Titanium Coating:
- Extreme Hardness: Reaches up to 3300 HV, significantly outperforming organic finishes.
- Superior Corrosion Resistance: Engineered to withstand saline environments and acidic exposure.
- Environmental Sustainability: A “green” dry process that avoids the toxic chemical baths associated with other finishes
- Enhanced Aesthetics: Provides a metallic “cool-to-the-touch” feel in finishes like Gold, Onyx Black, and Champagne Bronze.
Anodizing and Industrial Alternatives
Anodizing is a specialized conversion coating for aluminum that provides good corrosion resistance. However, PVD is a more versatile deposition technology that increases surface hardness and wear resistance across a wider variety of substrates (Steel, Zinc, Brass, etc.). By utilizing materials like Titanium Nitride (TiN) and Chromium Nitride (CrN), hardware can achieve industrial-grade resilience.
| Surface Treatment | Corrosion Resistance | Wear Resistance |
|---|---|---|
| Anodic Oxidation | High (Substrate specific) | 4x to 6x better than untreated aluminum |
| PVD Coating | Superior | Highest (10x to 50x better than untreated) |
| Nitriding | High | High (Limited to ferrous metals) |
Technical Considerations for PVD Implementation:
- Film Thickness: Standard decorative films range from 0.5 to 2.0 microns. While ultra-hard, they are not intended to provide structural impact resistance for soft base metals.
- Surface Preparation: PVD is a “line-of-sight” deposition that replicates the underlying surface topography. Achieving a mirror finish requires high-quality pre-process polishing.
- Process Sophistication: The requirement for high-vacuum chambers and specialized cathode technology results in a higher processing premium compared to bulk dipping methods.
For high-end hardware manufacturers, PVD vacuum coating remains the most robust choice for delivering a product that balances luxury aesthetics with uncompromising industrial performance.
Critical Variables in PVD Coating Performance
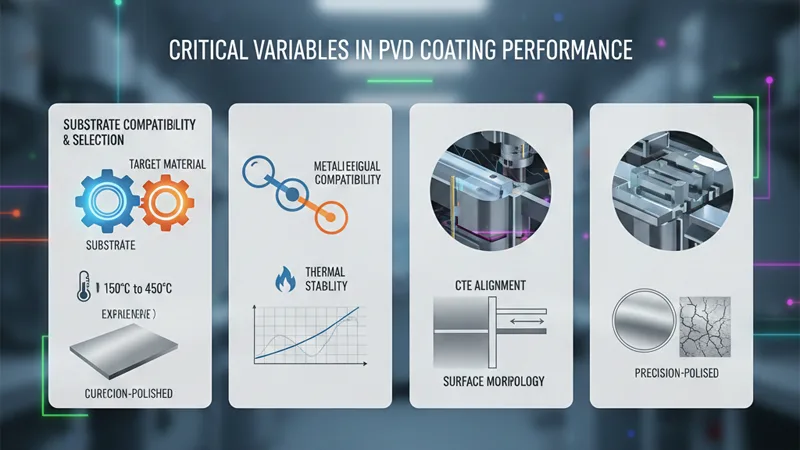
Substrate Compatibility and Selection
The integrity of a PVD film is heavily dependent on the properties of the base material (substrate). Selecting a compatible substrate is essential for ensuring high interfacial bond strength and long-term durability.
- Metallurgical Compatibility: The substrate must be chemically compatible with the target material to prevent interfacial reactions that could weaken the bond.
- Thermal Stability: PVD is a high-temperature process (typically 150℃ to 450℃). The substrate must withstand these temperatures without losing its structural integrity or degassing.
- CTE Alignment: Matching the Coefficient of Thermal Expansion between the substrate and the PVD layer prevents internal stress, which otherwise leads to micro-cracking or “spalling” during cooling.
- Surface Morphology: The substrate must be precision-polished. Because PVD is an atomic-level deposition, any microscopic surface defect will be replicated and potentially magnified in the final finish.
Precision Management of Coating Thickness
Achieving the optimal coating thickness is a balance between aesthetic requirements and functional performance. Thickness uniformity is critical for maintaining color consistency across complex geometries.
- Decorative Thin-Films (0.5-2.0㎛): Ideal for luxury hardware, providing a balance between deep color saturation and cost-efficiency.
- Functional/Tribological Layers (2.0–5.0㎛): Optimized for industrial components requiring high load-bearing capacity and abrasion resistance.
- Optical/Specialty Layers ($50$–$200$ $\text{nm}$): Utilized for specific light-interference effects or anti-reflective properties.
Impact of Thickness Variance:
| Application Category | Consequences of Non-Uniformity |
|---|---|
| Optical Applications | Causes chromatic aberration and interference pattern shifts. |
| Decorative Hardware | Results in color drifting (e.g., gold appearing pale or overly dark in recessed areas). |
| Functional Tooling | Leads to uneven stress distribution, reducing the tool’s fatigue life and hardness. |
Quality Assurance and Process Control
High-performance PVD coatings require rigorous process control and standardized testing to ensure they meet industrial specifications. Advanced monitoring allows for the customization of film density, stoichiometry, and grain structure.
Standardized Quality Metrics:
| Quality Control Measure | Technical Objective |
|---|---|
| ISO 9001 Certification | Evaluates the bond strength between the film and substrate via Rockwell indentation. |
| Adhesion Testing (VDI 3198) | ChecEvaluates the bond strength between the film and substrate via Rockwell indentation. |
| Spectrophotometry | Make sure products ensure a systematic approach to repeatable manufacturing quality. |
| Accelerated Aging (Salt Spray) | Tests how coatValidates corrosion resistance in simulated high-humidity or saline environments. |
| Nano-indentation | Make sure products ensure a systematic approach to repeatable manufacturing quality. |
Environmental Sustainability and Regulatory Compliance

PVD technology is the premier “green” alternative to traditional surface finishing. As global regulations tighten, PVD offers a compliant, eco-friendly solution for high-end manufacturing.
- Zero Toxic Effluent: Unlike hexavalent chrome plating, PVD is a closed-loop vacuum process that produces no hazardous liquid waste or air pollutants.
- Regulatory Alignment: PVD coatings are inherently compliant with RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) and REACH standards.
- Sustainable Material Use: The process utilizes high-purity solid targets, resulting in extremely high material utilization rates and minimal byproduct waste.
Environmental Comparison:
| Process | Environmental Impact Profile |
|---|---|
| PVD Vacuum Coating | GEco-friendly; no hazardous chemicals; safe for medical and food-contact use. |
| Conventional Chrome Plating | High environmental risk; utilizes carcinogenic Hexavalent Chromium . |
By utilizing PVD vacuum deposition, manufacturers can deliver high-performance hardware that meets the most stringent quality standards while upholding a commitment to environmental stewardship.
The Value Proposition for Luxury Hardware
Strategic Long-Term Cost Benefits
In the luxury hardware sector, durability is inextricably linked to value. Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) offers more than a premium aesthetic; it represents a strategic investment in the product’s lifecycle. By creating a high-hardness, wear-resistant surface, PVD minimizes the need for refurbishment or replacement, significantly lowering the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) over time.
| Benefit Category | Technical Impact |
|---|---|
| Reduced Maintenance Costs | High chemical stability eliminates the need for aggressive cleaning agents or frequent polishing. |
| Extended Operational Life | Superior bond strength ensures the hardware remains functional and pristine for decades. |
| Enhanced Surface Resilience | Prevents the localized abrasion and oxidative wear that typically necessitates premature replacement. |
The integration of PVD technology ensures that the hardware retains its structural and visual integrity, safeguarding the manufacturer’s reputation for quality.
Aesthetic Excellence and Functional Integrity
Luxury hardware must deliver a sensory experience that matches its price point. PVD coatings provide unrivaled color permanence and a high-luster finish that does not oxidize or tarnish. Unlike organic coatings, PVD preserves the authentic metallic tactile feel, reinforcing the user’s perception of high-end craftsmanship.
PVD is the standard for high-end architectural metalwork where resale value and long-term brand prestige are paramount.
- High-Fidelity Finishes: Achieves deep, consistent tones across complex geometries.
- Tactile Durability: Maintains a “cold-to-the-touch” metallic feel while providing a shield against oils and salts.
- Asset Preservation: Ensures that luxury installations remain tarnish-free and “as-new” for the duration of the building’s lifecycle.
Choosing PVD-coated hardware is a commitment to functional art—a finish that is as technically robust as it is visually captivating.
Sustainability and Regulatory Leadership
Modern luxury is increasingly defined by environmental responsibility. PVD technology aligns with global sustainability goals by utilizing a clean, vacuum-based process that eliminates the hazardous waste streams associated with legacy finishing techniques.
| Certification/Standard | Achievement Year | Strategic Significance |
|---|---|---|
| BSI ISO 9001:2015 | 2018 | Implementation of rigorous Quality Management Systems for repeatable excellence. |
| ISO 14064-1:2018 | 2023 | Quantification and mitigation of carbon footprints to align with global ESG standards. |
| ISO 14001 | 2024 | Establishing a comprehensive framework for proactive environmental management. |
By adopting PVD coatings, manufacturers significantly reduce their environmental impact through VOC-free production and high material-utilization rates. This process ensures that luxury hardware meets the most stringent ecological and quality standards, making it the definitive choice for the environmentally conscious consumer.
Technical Insight: For your next high-specification project, PVD coatings offer the ultimate synthesis of industrial-grade protection and premium decorative appeal.
FAQ
PVD vacuum coating is one of the most durable finishing options in custom metal manufacturing. It creates a molecular bond with the substrate, resulting in a surface that is significantly harder and more wear-resistant than traditional electroplating. It offers excellent resistance against corrosion, scratches, and fading, making it ideal for high-use precision metal components in the medical, aerospace, and luxury hardware industries.
While PVD can be applied to various substrates, it is most commonly used on stainless steel, titanium, aluminum, and brass. In custom metal parts manufacturing, stainless steel is the preferred substrate because it does not require an initial base coat, allowing the PVD layer to bond directly for maximum adhesion. For other metals like zinc or plastic, a copper or nickel underlayer may be required first.
One of the greatest advantages of PVD coating is its extreme thinness, typically ranging from 0.5 to 5 microns. Because the coating is so thin, it generally does not impact the critical tolerances of high-precision CNC machined parts. This allows you to maintain the exact specifications of your design while adding functional benefits like increased surface hardness and reduced friction.
For most high-end applications, PVD vacuum coating is superior to electroplating. Unlike electroplating, PVD is a dry, environmentally friendly process that does not produce toxic waste. While electroplating is often cheaper for bulk commodity items, PVD provides better uniformity, higher temperature resistance, and a much longer lifespan without chipping or peeling, which is essential for quality-critical custom metal parts.
PVD coating offers a wide range of aesthetic finishes without losing the metallic texture of the underlying part. Popular choices for custom metal hardware include:
- Gold and Rose Gold (using Titanium Nitride or Zirconium Nitride)
- Black and Gunmetal (using Chromium Carbide or DLC)
- Blue, Purple, and Rainbow
- Brass, Copper, and Bronze These colors are vibrant, consistent, and will not tarnish over time like traditional paint or plating.
Yes, PVD coating is highly biocompatible and is widely used in the medical device manufacturing sector. Processes such as Titanium Nitride (TiN) coating are non-toxic and used frequently on surgical instruments and orthopedic implants to improve wear resistance and provide a non-reflective surface. Our PVD processes meet the stringent safety and quality standards required for medical-grade custom metal components.