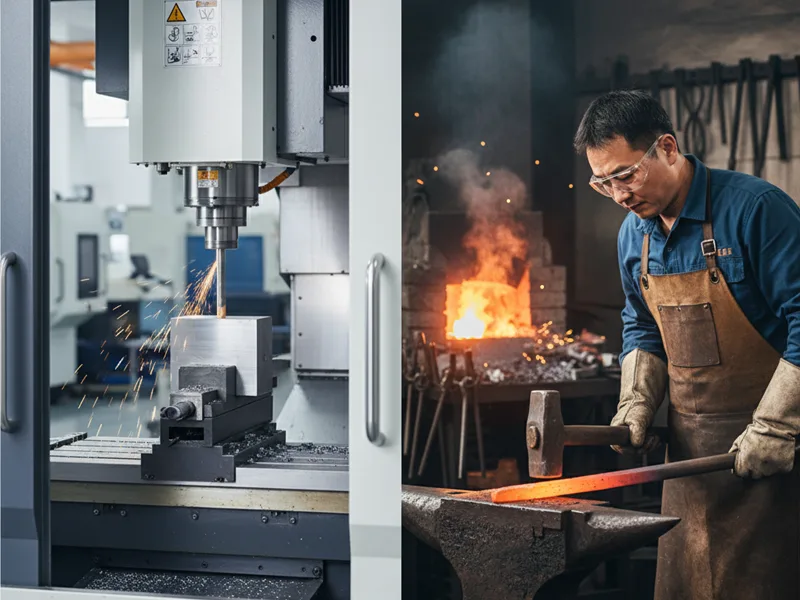
When deciding how to manufacture metal parts, focus on your specific needs. You might want durable metal parts for strength, or you may need precise shapes for your project. Manufacturing metal parts often depends on how strong, accurate, or cost-effective you want them to be. You will find that CNC machining provides high precision, while forging offers greater strength. Is CNC stronger than forged? The answer depends on your application. AFI Industrial Co., Ltd helps you choose the right process for your metal parts.
- CNC machining works best for tight tolerances and low-volume production.
- Forging is ideal for high-volume runs and tough, complex shapes.
Key Takeaways
- CNC machining works well for making exact shapes. It is good for small batches. It gives very smooth surfaces. This makes it great for custom parts.
- Forging makes parts that are strong and tough. These parts work well in places with lots of stress. Forging is cheaper when making many parts. It also makes the metal harder.
- Think about what your project needs before you choose. CNC machining is great for details and can be done easily. Forging is better if you need strong and reliable parts.
- Both ways cost money at first. CNC machining costs more for small groups of parts. Forging needs special tools, which cost a lot. But forging saves money when making many parts.
- Look at how much material gets wasted. CNC machining can waste 15-30% of the metal. Forging uses more of the metal. This makes forging better for large amounts.
Table of Contents
Key Differences of Machining vs Forging
Process Overview
CNC machining and forging shape metal parts in different ways. CNC machining cuts away material from a solid block. Computer tools control the cutting. This happens at room temperature. CNC machining gives very accurate results. Forging uses force to change the metal’s shape. It can use hot or cold temperatures. Forging presses or hammers metal into a mold. The table below shows how these two methods are not the same:
| Aspect | CNC Machining | Forging |
|---|---|---|
| Process Type | Subtractive, computer-controlled | Deformation using compressive forces |
| Temperature | Room temperature | Hot or cold, it affects properties |
| Precision | High, complex shapes possible | Lower may need extra finishing |
| Production Efficiency | Best for low to medium volumes | Best for high volumes |
Material Properties
The method you pick changes how your metal parts act. CNC machining keeps the metal’s structure the same. This means the part’s properties do not change. Forging moves the grains inside the metal. The grains follow the part’s shape. This makes the part stronger and tougher. Forged parts work well when they need to handle stress. Machined parts are more exact but may not be as strong as forged ones.
Typical Uses
Choose the method that fits what you need. CNC machining is good for tight spaces or tricky shapes. It works best for samples, custom pieces, and small groups. Forging is better for parts that must be very strong. It is used for cars and planes. Forging saves money when making lots of parts.
AFI Industrial Co., Ltd checks quality for both methods. The company uses process control, checks samples and whole batches, and validates steps. These actions make sure every metal part meets your needs.
Forging

Pros
You get strong and reliable parts when you choose forging. This process uses force to shape metal, which changes the grain structure inside. The grains follow the shape of the part, making it tough and less likely to break. Forging works well for parts that need to handle heavy loads or high stress. You often see forged parts in cars, airplanes, and heavy machinery. These parts last longer because they resist cracks and wear.
Here is a table that shows why forging gives you better mechanical strength:
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| Grain Structure Refinement | Forging aligns the grain structure, increasing strength and toughness. |
| Work Hardening | The process makes the metal harder and stronger. |
| Directional Strength | Parts are stronger along the grain flow, so they resist cracking. |
| Elimination of Internal Defects | Fewer voids and a more even structure mean less risk of failure. |
| Heat Treatment Compatibility | You can use heat treatment after forging to make parts even stronger. |
| Material Density | Forged parts are denser, which adds to their strength and hardness. |
| Material Toughness | Forged parts handle impacts and temperature changes better. |
| Surface Finish and Quality | Good surface quality helps prevent cracks and adds to part life. |
Forging is cost-effective for large production runs. You save money when you make many parts at once. Machined forgings also give you a good balance of strength and shape.
Cons
Forging does have some limits. You may find it hard to make very detailed or complex shapes. The process needs special tools and dies, which cost a lot at the start. This makes forging less ideal for small batches. Some metals do not work well with forging because of the high heat and pressure. You might also need extra steps to get the exact size or smooth finish you want.
Here is a table that explains the main limitations:
| Limitation | Explanation |
|---|---|
| High Initial Tooling Costs | Special dies and tools are expensive, so small runs cost more. |
| Limited Geometric Complexity | Forging cannot make very complex shapes as easily as other methods. |
| Material Limitations | Not all metals can be forged well. |
| Size Constraints | The size of the part depends on the forging equipment. |
| Surface Finish and Tolerances | You may need machining after forging for a smooth finish or tight size. |
When you look at the pros and cons, you see that forging is best for strong, simple parts made in large numbers. Machined forgings give you extra precision and strength, making them a smart choice for many high-stress metal applications.
Machining with AFI Industrial Co., Ltd

Pros
If you pick machining with AFI Industrial Co., Ltd, you get very exact parts. You can make metal pieces that fit together perfectly. The surfaces are smooth and look nice. AFI uses advanced CNC technology. This helps your parts match your needs. You can design shapes that are hard to make with forging. Machining is great for aerospace, electronics, and medical devices.
AFI Industrial Co., Ltd has some of the best CNC machines. These machines help you get high accuracy and smooth surfaces. The table below shows how these machines work for different metal parts:
| Technology Used | Precision Achieved | Surface Roughness | Application Areas |
|---|---|---|---|
| Five-axis linkage machining centers | ±0.01mm | Ra0.2μm | Medical devices, optical components |
| Five-axis CNC milling machines | ±0.01mm | Ra0.8μm | Aerospace precision parts, electronic communication parts |
| Intelligent numerical control systems | ±0.01mm | Ra0.4μm | Complex structural components |
AFI also cares a lot about quality. The company has important certifications. These show they follow high standards:
| Certification | Description |
|---|---|
| AS9100 | Quality management standard for aerospace sector |
| ISO 9001 | General quality management standard |
| NADCAP | Accreditation for special processes in aerospace manufacturing |
You can expect your parts to work well and last long. You also get quick service and custom solutions for your needs.
Cons
Machining has many good points, but there are some problems. Some metals, like stainless steel and titanium, are hard to machine. You might see vibration or heat. Tools can wear out fast. These things can make the surface rough or slow down work. The table below lists some common problems you may face:
| Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
| Chatter and Vibration | Cutting tool and workpiece can vibrate, causing poor finish or tool breakage. |
| Improper Chip Control | Chips may not clear well, leading to tool damage. |
| Heat-Related Defects | Heat can cause parts to change size or color. |
| Aluminum Burrs | Soft aluminum may form burrs after machining. |
| Adhesion to Cutting Tools | Aluminum can stick to tools, affecting finish. |
| Work Hardening | Stainless steel can get harder during machining. |
| Tool Wear | Hard metals wear out tools quickly. |
| Heat Generation | Titanium machining creates a lot of heat. |
| Chemical Reactivity | Titanium may react with cutting fluids. |
AFI Industrial Co., Ltd uses smart people and good machines to fix these problems. You can trust them to help your project go well. Machining lets you control the shape, size, and finish of your metal parts. This is very useful for tricky or special designs.
Strength: Is CNC stronger than forged
When you pick how to make metal parts, you want them to be strong. People often ask if CNC is stronger than forged. The answer depends on what you need the part to do. Let’s look at the facts to help you choose.
Mechanical Properties
Strength is measured by tensile and yield strength. These numbers show how much force a part can take before it bends or breaks. Forged parts are often stronger. This is because forging changes the metal’s grain structure. The grains move with the shape of the part. This makes the part tough and less likely to crack. CNC-machined parts keep the original grain. But cutting can break up the grain pattern. This can make the part weaker than forged ones.
Here is a table that compares the strength of CNC-machined, forged, and cast parts:
| Manufacturing Process | Yield and Tensile Strength Comparison |
|---|---|
| CNC Machined | 30–50% higher than cast components |
| Forged | 26% higher than cast parts |
Both CNC-machined and forged parts are stronger than cast parts. But forged parts are usually the strongest when you need high strength.
Let’s look at some real numbers:
| Manufacturing Process | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Yield Strength (MPa) |
|---|---|---|
| Forged | 400 | 400 |
| Cast | 300 | 300 |
Forged parts have higher tensile and yield strength. This means they can take more force before breaking.
Structural Integrity
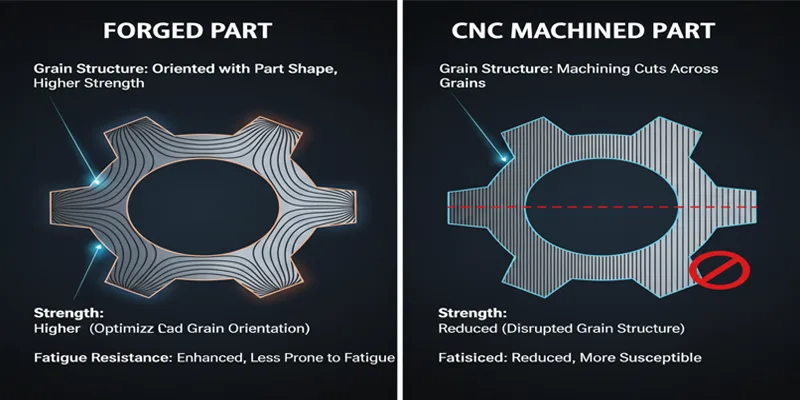
Structural integrity means how well a part stays together under stress. It also shows how long the part will last. Forging lines up the metal grains with the part’s shape. This makes the part stronger and more reliable. CNC machining can cut across the grains. This may make the part weaker and lower its integrity.
Here is a table that shows how grain structure affects mechanical properties:
| Property | Forged Parts | CNC Machined Parts |
|---|---|---|
| Grain Structure | Oriented to shape for greater strength | Disrupted grain pattern due to machining |
| Strength | Higher due to optimized grain orientation | Lower due to disrupted grain structure |
| Ductility | Improved due to continuous grain flow | Reduced due to machining process |
| Fatigue Resistance | Enhanced, less susceptible to fatigue | More susceptible due to grain disruption |
Note: Forged parts usually do not have porosity. This means they have fewer weak spots and last longer.
You can also see how parts work over time. Fatigue limit tells you how much repeated stress a part can take before it fails. Forged parts have a higher fatigue limit than CNC-machined parts. This makes forged parts better for heavy loads or constant use.
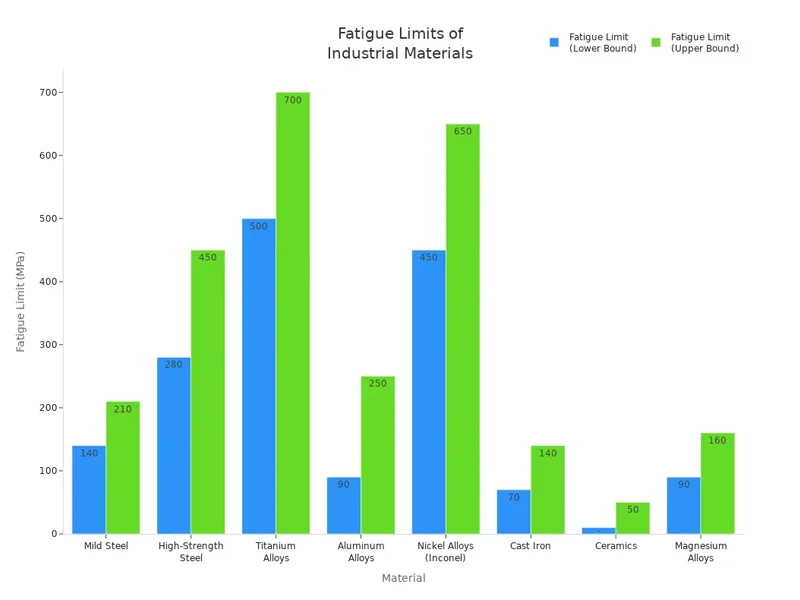
Here are some typical fatigue limits for different materials:
| Material | Fatigue Limit (MPa) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Mild Steel | 140 – 210 | Low-carbon steels have moderate fatigue resistance. |
| High-Strength Steel | 280 – 450 | Steel alloys with higher tensile strength often have higher fatigue limits. |
| Titanium Alloys | 500 – 700 | Excellent fatigue resistance, especially at high temperatures. |
| Aluminum Alloys | 90 – 250 | Aluminum alloys have moderate fatigue resistance, often used in aerospace applications. |
| Nickel Alloys (e.g., Inconel) | 450 – 650 | Nickel-based alloys are highly fatigue-resistant, especially in extreme temperatures. |
Forged parts usually have about 26% higher tensile strength and 37% higher fatigue strength than cast parts. This means forged parts last longer and keep their strength under tough conditions.
If you want the best durability and strength, forging is often the best choice. CNC machining gives you great precision. But forging gives you the most strength and part integrity for hard jobs.
Precision
Tolerances

You want your metal parts to fit just right. Tolerances show how close a part’s size is to what you want. CNC machining can make parts very exact. These parts can be within ±0.0005 inches (0.0127 mm) of your plan. This kind of accuracy is needed in aerospace and car-making. Even tiny mistakes can cause big trouble in these areas.
AFI Industrial Co., Ltd uses advanced CNC machines for tight tolerances. You get parts that fit together well and keep your project safe. Forging cannot be as exact as CNC machining. Forged parts often need more machining to get the right size. If you wonder if CNC is stronger than forged, you should also think about how exact your parts must be.
Here is a table that shows the difference in tolerances:
| Process | Tolerance Achievable |
|---|---|
| CNC Machining | ±0.0005 inches (0.0127 mm) |
| Forging | N/A |
- CNC machining tolerances are important in aerospace and car-making.
- Small mistakes can really hurt safety and how things work.
Surface Finish
Surface finish changes how your part looks and works. CNC machining gives you a smooth and shiny surface. These parts are good for jobs that need high precision or look nice. AFI Industrial Co., Ltd uses special tools to make sure your parts look great and last longer.
Forged parts can have a good surface, but not as smooth as CNC-machined parts. You may need extra steps to make the finish better. If you ask if CNC is stronger than forged, you should also think about how the surface finish helps your part work better.
Here is a table that compares surface finish quality:
| Manufacturing Method | Surface Finish Quality |
|---|---|
| CNC Machined Parts | Excellent, great for looks or high-precision jobs |
| Forged Parts | Good to Excellent, depends on the forging process |
You get the best results with CNC machining for tight tolerances and smooth surfaces. AFI Industrial Co., Ltd helps you get the accuracy you need for your project. When you compare if CNC is stronger than forged, remember that being exact is just as important as being strong.
Cost
Initial Investment

You need to think about money before making parts. Both CNC machining and forging cost a lot at the start. CNC machining requires you to buy machines and pay for setup. You also pay for programming. Forging needs special tools and heavy machines. The table below shows the difference:
| Process | Initial Investment Description |
|---|---|
| CNC Machining | Significant due to setup and programming costs, especially for small batches. |
| Forging | Requires substantial initial investment in tooling and equipment. |
If you only make a few parts, CNC machining can be costly. This is because you split the cost over fewer pieces. Forging also costs a lot at first. But it is better if you make many parts.
Production Volume
How many parts you make changes the cost for each one. If you make just a few, each part costs more. Making lots of parts lowers the cost for each piece. Here are some facts to help you:
- Low-volume production means a higher cost for each part.
- Fewer parts made means fixed costs are spread over fewer.
- High-volume production needs more money at first.
- But making more parts lowers the cost for each one.
- Making more parts saves money because of economies of scale.
- One company saved 30% by making more parts.
- When you make more, the fixed cost per part goes down.
- Buying more materials at once can save money, too.
- Fixed costs happen at the start of a CNC project.
- Making more parts spreads out these costs and saves money.
Material waste also changes your costs. CNC machining can waste 15-30% of metal. This is because you cut away extra material. Forging uses more of the metal, so you waste less.
Tip: To save money, try to make more parts at once. This lowers the cost for each part and uses your materials better.
Think about how big your project is before you choose. Both CNC machining and forging have different costs and benefits. Think about how many parts you need and how much metal you want to save.
Application Suitability
Picking the right way to make metal parts depends on what you need. You should think about what the part will do, how many you want, and your industry. Forging and machining each have their own good points. Look at your project’s needs before you choose.
When to Choose Forging

Pick forging if you need strong parts that last a long time. Forging is best for parts that must take heavy loads or lots of stress. Many car and airplane parts are forged for safety and strength. Here are some parts often made by forging: crankshafts and connecting rods, suspension parts like control arms and steering knuckles, transmission parts such as gears and shafts, brake parts like rotors and calipers, and axles, housings, and frames.
You can use this table to help you decide if forging is right:
| Criteria | Considerations |
|---|---|
| Component Function and Performance | Pick forging for parts that need to be strong and tough. |
| Production Volume | Forging is good for making lots of parts at once. |
| Cost Considerations | Forging saves money for big batches, but tools cost a lot. |
| Material Properties | Use forging for metals that need to be tougher and stronger. |
| Design Complexity | Forging works best for simple or not-too-complex shapes. |
| Production Capabilities | Choose forging if you have the right machines and want strong, solid parts. |
Forging is a good choice if you want parts that will not break under stress, especially for cars or planes.
When to Choose Machining
Pick machining if you need parts with exact shapes or special designs. Machining is great for small batches or when you want to change designs fast. You can get good parts quickly, which helps you keep up with what people want. Here are some reasons to pick machining: low-volume CNC machining saves money because you do not need pricey tools, you can make parts only when you need them so you waste less, machining lets you change how many parts you make quickly, you get custom parts fast, machining works for many things like medical devices and electronics, and you can make more or fewer parts as needed.
AFI Industrial Co., Ltd does machining work for many industries. You can get exact parts for cars, very precise parts for planes, and custom parts for medical devices. The company uses smart CNC machines and systems to help you.
Pick machining if you want to be flexible, need exact sizes, and want parts fast. Machining is best when you need special or tricky parts for different jobs.
You need to pick CNC machining or forging for your project. Each way has its own good points. The table below helps you see the main things to think about:
| Factor | Forging | CNC Machining |
|---|---|---|
| Product Requirements | Handles heavy loads and impacts | Makes complex shapes and big parts |
| Cost-effectiveness | Costs more but is very strong | Costs less and works for many parts |
| Efficiency | Needs more time and workers | Works fast and saves effort |
Think about how strong, exact, and costly you want your part. If you are not sure, AFI Industrial Co., Ltd can help you choose what is best.
FAQ
You shape metal with CNC machining by cutting away material. Forging uses force to press or hammer metal into shape. CNC gives you precision. Forging gives you strength.
You should pick CNC machining when you need exact shapes, tight tolerances, or custom designs. This process works best for small batches or parts with complex features.
Forged parts have grains that follow the shape of the part. This makes them stronger and less likely to crack. You can use forged parts for heavy loads and high stress.
Yes, CNC machining removes extra material to create the final shape. This can lead to more waste. Forging uses most of the metal, so you waste less.


