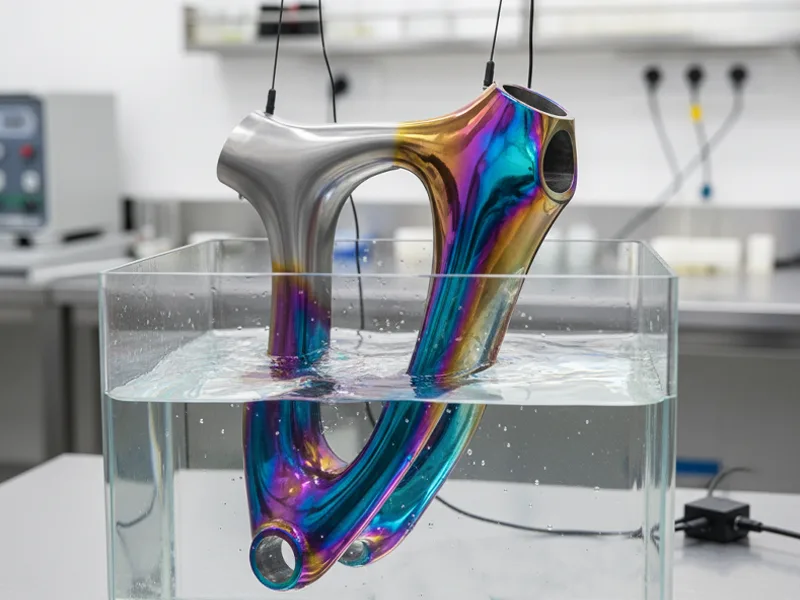
Titanium anodizing is a way to change the outside of titanium parts. This process helps the parts work better and look nicer. When you anodize titanium, you make a thin, strong layer on the metal. This layer helps the metal last longer and stops it from rusting. Many companies use anodized titanium in planes, hospitals, and cars. Titanium is light, strong, and can be colored for easy spotting or style. The outside gets tougher and can fight against scratches. Sometimes, it even becomes slippery by itself. If you want to learn how to anodize titanium and why it is important, you will see this process makes things last longer and look good.
Key Takeaways
- Titanium anodizing makes a tough oxide layer. This layer helps titanium last longer and look better. The anodizing process has several steps. First, you clean the titanium. Then you etch it. Next, you anodize it. After that, you seal it. Last, you do post-treatment to get the best results. Using different voltages in anodizing makes different colors. You can pick colors without using paint or dye. Anodized titanium is used in many industries. These include aerospace, medical, and automotive. People use it because it is strong and does not rust easily. Safety is very important when anodizing. Always wear safety gear. Be careful when using chemicals. Machining the titanium before anodizing is important. It makes the surface smooth. A smooth surface gives better color and strength. To keep anodized titanium nice, clean it gently. Do not use strong chemicals. This helps keep its finish. Anodizing makes titanium look better. It also gives useful benefits. These include less friction and better wear resistance.
Table of Contents
What Is Titanium Anodizing
Definition
Titanium anodizing is a process that changes the surface of titanium parts. It uses electricity and a chemical bath to do this. The titanium goes into a special liquid. Then, electricity is sent through it. This makes a thin, strong oxide layer on the metal. The layer features tiny textures that are imperceptible to the eye. These textures enhance the metal’s performance.
- How thick and strong the oxide layer gets depends on the voltage, how long you run the process, and what chemicals are in the bath.
- You can pick the color and how the surface acts by changing these things.
- The finished surface is tougher, does not rust as easily, and looks nicer.
Note: Titanium anodizing does not use paint or dye. The colors come from how light bounces off the oxide layer, not from added color.
How It Works
First, you clean the titanium part. Dirt or oil can mess up the process. After cleaning, you put the titanium in a bath with an electrolyte. The titanium is hooked to the positive side of a power supply. This makes it the anode. When you turn on the power, oxygen forms on the surface. The oxygen reacts with the titanium. This makes the oxide layer that gives anodized titanium its special features.
Titanium anodizing is not the same as anodizing aluminum. Aluminum anodizing is easier and mostly stops rust. You use a simple bath and steady power. The oxide layer on aluminum is not as thick or strong as that on titanium.
With titanium, you must watch the voltage and the kind of electrolyte you use. The process is harder because you want the oxide layer to be just right. This lets you make many colors and a stronger surface. Anodized titanium is also safe for medical use.
Titanium anodizing is often done after machining. Machining shapes the part to the right size. Anodizing makes the surface work and look better. The oxide layer can lower friction, stop wear, and help you spot the part by color. Many fields, like aerospace, cars, and medicin,e use anodized titanium for these reasons.
Tip: If you want your titanium parts to last longer and look better, anodize them after machining. This step helps both how they work and how they look.
How to Anodize Titanium
If you want to learn how to anodize titanium, you must follow each step carefully. Every step is important for how your part will look and work. You need special tools, must stay safe, and should start with well-machined titanium.
Step-by-Step Process
There are a few main steps in the anodizing process. You need to do each one to get a strong and colorful finish that lasts.
- Cleaning and Preparation
First, clean the titanium to remove dirt, oil, and grease. Use a degreaser and rinse with water. If you leave dirt, the anodizing will not work right. - Etching
Next, put the titanium in an acid bath. This makes the surface rough on a tiny level. The roughness helps the oxide layer form evenly. - Anodizing
Put the titanium in an electrolytic bath. Connect it to the positive side of a power supply. When you turn on the power, the oxide layer forms. This is the main part of how to anodize titanium. - Sealing
After anodizing, seal the titanium. Use hot water or steam to close the pores in the oxide layer. This makes the surface last longer. - Post-Treatment
Last, check the anodized titanium. Look for any problems and make sure the color and finish are what you want.
Tip: Rinse the titanium with clean water after every step. This keeps chemicals from mixing and causing trouble.
Equipment and Materials
You need the right tools and supplies to anodize titanium. Here is a list to help you get ready:
- A power supply that lets you change the voltage
- An electrolytic bath with a solution like trisodium phosphate or sulfuric acid
- Titanium parts
- Cathode, usually made of stainless steel
- Cleaning supplies like degreaser and acid for etching
- Tanks with clean water for rinsing
- Safety gear like gloves, goggles, and an apron
- Hot water or steam for sealing
You also need a safe place with good airflow. Make sure your tools are clean and working before you start.
Safety Precautions
Safety is very important when you learn how to anodize titanium. The chemicals and electricity can be dangerous.
- Always wear gloves, goggles, and a chemical-resistant apron.
- Work in a place with good airflow.
- Never touch the titanium or bath when the power is on.
- Keep water and chemicals away from outlets.
- Throw away used chemicals the right way.
⚠️ Alert: Never skip safety steps. Even small mistakes can cause burns, shocks, or spills.
Preparing Titanium with Machining
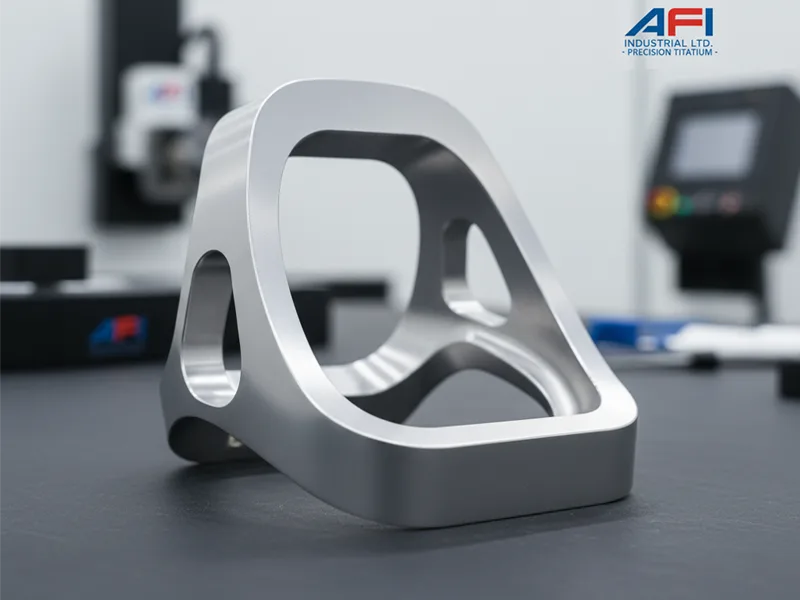

Before you anodize, you must machine the titanium carefully. The way the surface looks after machining will affect the anodized layer.
- A smooth, clean surface gives even color and a strong oxide layer.
- If you see scratches or tool marks, they can show up after anodizing.
- Better machining means a better look and stronger anodized titanium.
AFI Industrial Co., Ltd can machine titanium with high precision. Their parts have the right finish for anodizing and do not have flaws that cause problems later.
Note: For the best results, always use high-quality machining before anodizing. This step is just as important as anodizing.
Voltage and Color Chart
The voltage you use when you anodize titanium changes the color. Here is a simple table to help you pick the right voltage for the color you want:
| Voltage (V) | Color |
|---|---|
| 5 | Gold |
| 20 | Purple |
| 30 | Blue |
| 60 | Orange |
| 75 | Pink |
| 90 | Blue |
| 110 | Green |
You can see that different voltages make different colors. The color may change a little depending on the finish and process.
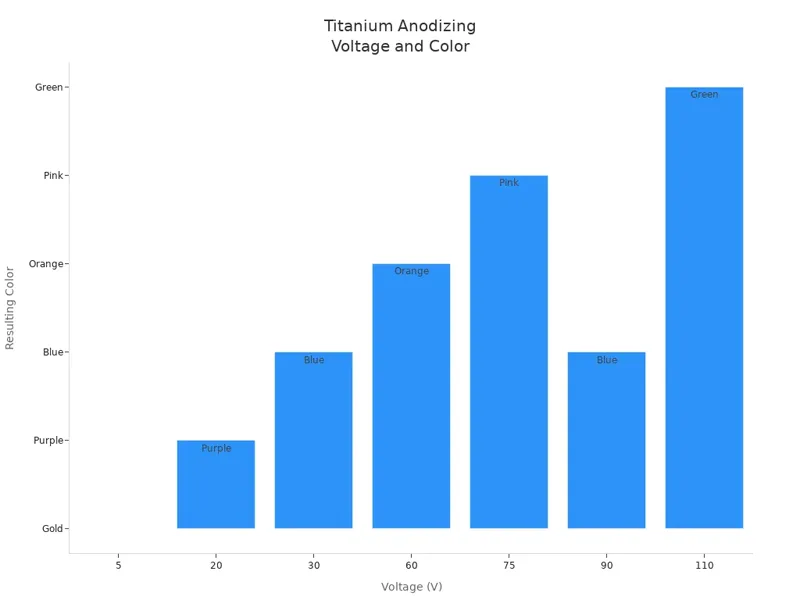
Tip: If you want a certain color, test on a small piece first. The color can look different based on the finish and voltage.
If you follow these steps and use the right tools, you will know how to anodize titanium. You will get a finish that is strong, colorful, and lasts a long time.
What Happens During Titanium Anodizing
Surface Changes
When you anodize titanium, the surface changes in tiny ways. A layer called titanium dioxide (TiO₂) forms on top. This layer is rough and has lots of small holes. It is not just a thin film. It has special features that help the metal work better.
| Microscopic Change | Description |
|---|---|
| Porous TiO₂ Layer | A rough layer with many tiny holes. This helps stop rust and helps the body accept implants. |
| Surface Roughness | The surface gets rougher. This helps bone and tissue grow onto implants. |
| Nanotubular Structures | Tiny tubes can form. They can hold medicine and help bone cells grow. |
| Thickness of Oxide Layer | Thicker layers help the body react better and help bone grow faster. |
| Pore Size Variation | You can change the size of the holes by changing the process. This changes how the metal works. |
Anodizing does more than add color. It changes how the surface acts with its surroundings. For example, a rougher surface helps bone grow onto implants. This makes them stay in place better.
Color Effects
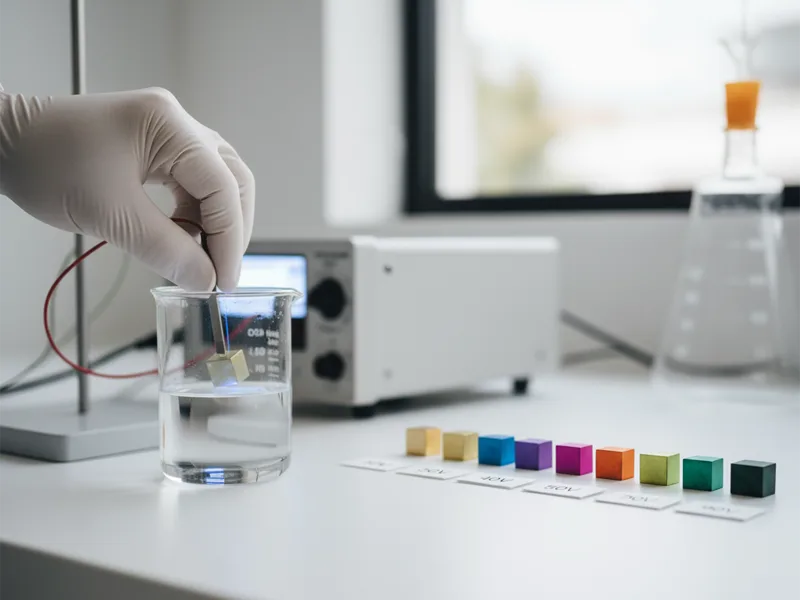

Anodizing titanium makes many colors without paint or dye. The color depends on how thick the oxide layer is. If you change the voltage, the layer gets thicker or thinner. This changes the color you see.
- Thin oxide layers made at low voltage give light colors.
- Thick oxide layers made at high voltage give dark colors.
- The color comes from how light bounces off the oxide layer, not from added color.
- The thickness and tiny holes in the layer change how light moves and what color you see.
You can pick the color you want by changing the voltage. This is good for marking parts, making jewelry, or adding style.
Protective Properties
Anodizing gives titanium a strong shield. The new oxide layer protects the metal from rust, wear, and scratches. It also makes the surface harder and more stable.
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Hardness | The surface gets much harder and resists wear. |
| Lubricity | The surface gets smoother and lowers friction in moving parts. |
| Anti-galling performance | The layer stops surfaces from sticking together under pressure. |
| Hydrogen embrittlement risk | There is no risk of hydrogen damage, so the part lasts longer. |
| Fatigue strength | The part can handle more stress and gets up to 20% stronger. |
| Dimensional stability | The part keeps its shape, which is important for tight fits. |
Studies show anodized titanium fights rust better than plain titanium. The oxide layer makes a strong barrier. It keeps out water and chemicals. In tests, anodized titanium rusted less and stayed strong even in tough places.
Tip: If you want your titanium parts to last longer and work better, anodizing is a smart choice. The process gives you a tough, colorful, and protective surface that stands up to daily use.
Benefits of Titanium Anodizing
Titanium anodizing gives you many good things. When you use this process, your titanium parts look better and last longer. The parts also work better. Many companies use anodizing because they need strong and nice-looking parts.
Aesthetic Advantages
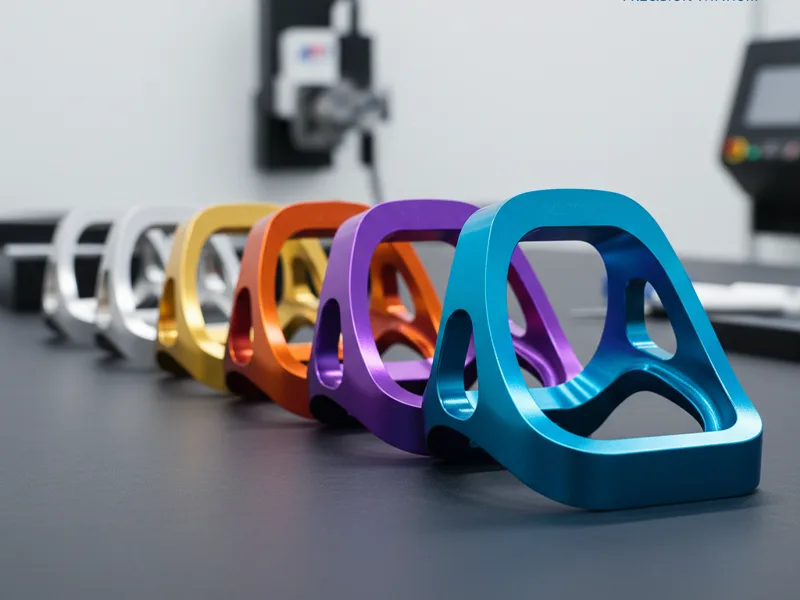

Anodizing lets you make many colors on titanium. You do not need paint or dye. The color comes from the oxide layer’s thickness. This changes how light bounces off the metal. You get a shiny finish that stands out. Designers and makers like anodized titanium for its cool looks and bright colors.
| Feature | Benefit for You |
|---|---|
| Wide color range | Lots of choices for design |
| Metallic, fade-resistant finish | Color stays bright and does not rub off |
| Hypoallergenic surface | Safe to wear on skin or as jewelry |
Jewelry makers like anodized titanium because it keeps its color. You also see it in watches, electronics, and fancy products. The color stays bright even if you use it every day.
Note: You can get different colors by changing the voltage. Each piece can look special.
Corrosion and Wear Resistance
Anodizing helps titanium fight rust and scratches. The oxide layer acts like a shield. It keeps water, chemicals, and sharp things away from the metal. This makes your parts last longer and need less fixing.
| Anodization Voltage (V) | Corrosion Rate (nm/year) | Non-anodized Titanium (nm/year) |
|---|---|---|
| 15 | 2.1 | 10–500 |
| 75 | 0.7 | 10–500 |
You can see that anodized titanium rusts much more slowly than plain titanium. The process also makes the surface harder. This helps parts stay strong in tough places. Big industries like planes, cars, and hospitals use anodizing to keep things safe and working well.
Tip: If you want your titanium parts to last and not rust, anodizing is a great idea.
Identification and Functional Uses
Anodized titanium is not just for looks or protection. You can use the colors to tell parts apart fast. This helps in places like planes and hospitals where you must find the right part quickly.
| Application Area | How Anodized Titanium Helps You |
|---|---|
| Aerospace | Makes putting things together faster and easier |
| Medical | Helps doctors and nurses find the right tools |
You can give each part its own color. This makes sorting and building things easier. It also helps stop mistakes and saves time. In hospitals, colored tools and implants help keep people safe and make work faster.
Note: Many companies pick titanium anodizing because it gives beauty, strength, and easy sorting all at once.
Applications of Anodized Titanium
Jewelry and Decorative Items
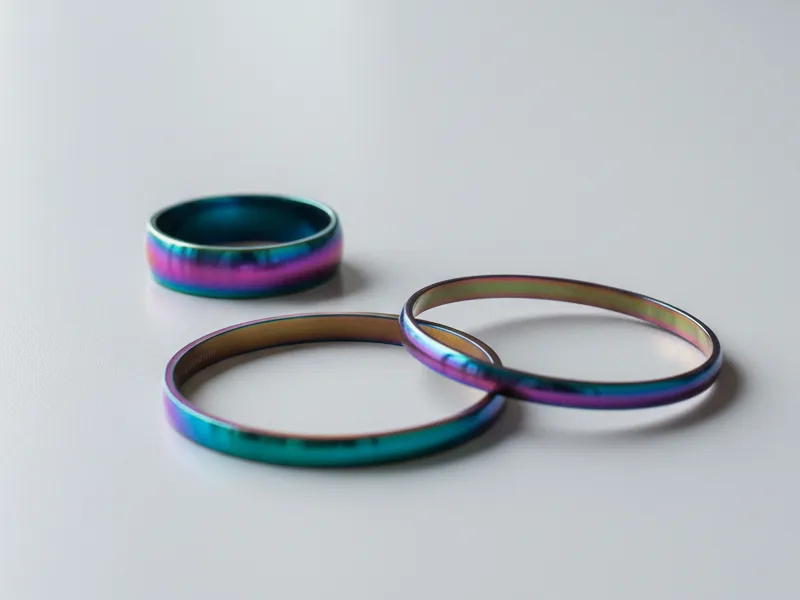

Anodizing can make jewelry and decorations look special. When you pick titanium anodizing for rings or bracelets, you get many bright colors. These colors last a long time. The process does not use paint or dye. The color comes from the oxide layer’s thickness. This means your jewelry will not chip or fade easily. Many artists like anodized titanium because it is light and safe for the skin. You can find anodized pieces in watches, glasses, and art. The colors stay bright, and the surface does not scratch easily. Your items will look new for a long time.
Tip: If you want special colors or cool patterns, anodizing lets you make designs that are hard to copy.
Medical and Dental Devices
Anodizing is important for medical and dental tools. You see it in things like bone plates and dental implants. The process makes a strong oxide layer on titanium. This layer is tough and safe for your body. Doctors trust anodized titanium because it does not react with body fluids. The surface helps bone and tissue grow onto implants. This makes them stay in place better.
Here is a quick look at why anodized titanium is trusted in healthcare:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Process | Anodizing is an electrochemical process that forms a durable oxide layer on titanium. |
| Purpose | Enhances surface properties, performance, and aesthetics of medical parts. |
| Biocompatibility | The oxide layer formed is inert and biocompatible, ensuring safety for patient contact. |
Doctors and nurses can use color coding to find tools fast. This helps stop mistakes and saves time during surgery.
Aerospace and Automotive Parts
You can find anodized titanium in planes and cars. The anodizing process makes a strong oxide layer. This layer helps stop rust and makes parts last longer. This is important for parts that face tough places, like airplane frames or car engines. The layer keeps the metal safe from chemicals and heat. The parts are also lighter, so they help save fuel.
Anodizing can also change how titanium looks without making it weak. You get both style and strength. In planes, colored parts help workers sort things fast. In cars, anodized titanium adds a cool look to trim and bolts.
Note: When you use titanium anodizing for these parts, you help them last longer, work better, and look good, even in hard places.
Role of Machining in Applications
When you use anodized titanium in high-tech fields, you need more than just anodizing. Precision machining is very important. Machining shapes titanium into the right size and form before anodizing. This step is needed for a smooth finish and good performance.
Machining matters in every area that uses anodized titanium. Aerospace, medical, and car companies all need parts with exact sizes and smooth surfaces. If you skip careful machining or use bad methods, the anodized layer may not cover the part evenly. This can cause weak spots, color problems, or even broken parts.
Let’s see what precision machining does for you:
| Capability | Description |
|---|---|
| Precision Manufacturing | Makes parts with tight sizes for high-tech jobs. |
| Turnkey Solutions | Offers complex machining, assembly, and finishing. |
You get many benefits from these skills:
- Your titanium parts fit perfectly, even in tricky machines.
- You avoid expensive mistakes because every part meets tough rules.
- Your parts last longer and work better, even when used a lot.
Military and aerospace jobs have very strict rules for machining. They need parts with exact sizes. These sizes make sure every part works right and stops the equipment from breaking. In medical tools, even a small mistake in machining can mean a safe implant or a failed surgery.
Modern machining uses advanced machines like 5-axis machines. These machines can make detailed titanium parts with fewer steps. This helps in aerospace and medical jobs, where parts are often complex. With 5-axis machining, you get smooth surfaces and sharp details. This makes anodizing work better.
AFI Industrial Co., Ltd is good at making precise titanium parts. If you use their services, your parts are ready for anodizing. Their skill means your parts have the right finish, no bad marks, and the exact size you need. This is very important for good anodizing, especially in jobs where quality is a must.
Tip: Always use well-machined titanium before anodizing. This step gives you the best color, strength, and performance for your anodized titanium.
When you mix expert machining with anodizing, you get the most out of titanium. Your parts are strong, look great, and work well in tough places.
Safety and Best Practices
When you do titanium anodizing, safety is very important. You work with strong chemicals and use electricity. You also need to care about the environment. Follow these tips to keep yourself, your team, and your workspace safe.
Chemical Handling
You use acids and electrolytes during anodizing. These chemicals can hurt your skin or eyes. Always wear gloves, goggles, and a chemical-resistant apron. Make sure your work area has good airflow. If you spill a chemical, clean it up right away. Keep a spill kit close by. Never mix chemicals unless you are sure it is safe. Some chemicals can make dangerous fumes if mixed.
- Store chemicals in containers with labels.
- Keep acids and bases away from each other.
- Wash your hands after touching any chemical.
- If you get a chemical on your skin, rinse with water for at least 15 minutes.
⚠️ Alert: If you feel dizzy or have trouble breathing, leave the area and get help. Some fumes from anodizing can be harmful.
Electrical Safety
You need electricity to make the oxide layer in titanium anodizing. Electricity can shock or burn you. Always check your power supply before you start. Make sure all wires and connections are dry and not broken. Never touch the titanium or bath when the power is on. Turn off the power before you move or fix anything.
| Safety Step | Why It Matters |
|---|---|
| Use insulated gloves | Protects you from electric shock |
| Dry hands and tools | Stops electricity from traveling |
| Check for damage | Prevents short circuits and sparks |
| Turn off power | Keeps you safe during adjustments |
If you see sparks or smell burning, turn off the power right away. Do not try to fix electrical problems unless you know how.
Environmental Considerations
Anodizing makes waste like used chemicals and rinse water. Never pour these down the drain. Used chemicals can hurt water and soil. Collect all waste in special containers. Call a licensed company to pick up and get rid of it. Try to use less water by rinsing parts together. This saves water and produces less waste.
- Reuse rinse water if you can.
- Keep a record of all chemicals you use and throw away.
- Teach your team how to handle waste safely.
Tip: Good waste management keeps your shop safe and helps the planet. It also shows your customers you care about quality and responsibility.
By following these safety and environmental tips, you make sure your anodized titanium parts are made in a safe, clean, and responsible way. You protect yourself, your team, and the world around you.
Troubleshooting and Tips
Common Mistakes
When you do anodizing, some problems can happen. These problems can make your titanium parts not turn out right. If you know the usual mistakes, you can stop them and get better results.
| Mistake | Cause | Consequence |
|---|---|---|
| Incorrect rack selection | The rack does not fit the part’s size or shape | Uneven coating or physical damage |
| Poor rack design | The rack cannot support the weight or surface area | Parts may fall or become unstable |
| Improper current distribution | Wrong rack usage or setup | Blotchy surfaces, poor protection |
Other problems you might see are:
- Lines on parts from the alpha phase during machining.
- Not removing all titanium oxides before anodizing which causes surface problems.
- Skipping a good cleaning, which makes colors look uneven after anodizing.
Tip: Check your racks and clean every part before you start anodizing titanium. Doing this helps stop many common problems.
Achieving Consistent Results
You want every anodized part to look and work the same. To get this, you need to plan well and follow good steps.
- Order all your parts at once. This way, they get anodized together. It helps keep the color and finish the same.
- Give a real sample for color matching. Do not just use a photo. This helps your anodizer know what color you want.
- Use the same anodizer for all your parts. This stops color changes between different batches.
Note: Even small changes in voltage, cleaning, or how the part looks can change the color. Always test on a sample before doing a big batch.
Maintaining Anodized Titanium
To keep your anodized titanium looking nice and working well, you need to take care of it. Follow these steps to help it last:
- Clean gently with mild soap. Mix dish soap with warm water. Wipe the part with a soft cloth. Do not use strong chemicals.
- Do not use rough cleaners or tools. Stay away from hard sponges or powders. These can scratch the oxide layer and make the color fade.
- For tough stains, use vinegar and water. Mix equal parts vinegar and water. Put it on the stain, wait, then wipe with a soft cloth.
- Use car wax to protect the finish. A thin layer of wax keeps the surface safe and makes cleaning easier next time.
Tip: Clean your anodized titanium gently and often. Keep it in a dry place to stop water spots or stains.
If you use these tips for fixing problems and caring for your parts, you will get the best results from anodizing. Your titanium parts will stay bright, strong, and ready to use.
Titanium anodizing helps your titanium parts look better and work well. You get a strong finish with bright colors. The finish does not wear out or rust easily. You can use it for cool designs and useful things. It works for medical tools and airplane parts. To start, pick the best titanium grade. Make sure your part is ready for machining. Work with people who know the process. They help you at every step. This way, your anodized titanium will be high quality and work great.
FAQ
You anodize titanium to help it fight rust. It also adds color so you can tell parts apart. The surface gets harder and looks better. This helps the part last longer in tough places.
Yes, you can do this at home if you have the right tools. You need a power supply and an electrolyte bath. Wear safety gear like gloves and goggles. Always follow safety rules and be careful with chemicals.
Anodizing does not change how strong titanium is inside. Only the outside gets harder. The metal under the surface stays just as strong.
You pick the color by changing the voltage. Each voltage makes a different oxide thickness. This changes the color you see. Test on a small piece first to get the color you want.
Yes, anodized titanium is safe for medical and dental tools. The oxide layer does not react with body fluids. Many implants and surgical tools use anodized titanium because it is safe.
Use mild soap and warm water with a soft cloth. Do not use strong chemicals or rough pads. For tough stains, mix vinegar and water. Dry the part after cleaning to stop water spots.
Check if you cleaned and prepared the part well. Dirt or oil can make the color look uneven. Use the right voltage and rinse between steps. If needed, remove the oxide layer and try again.
Yes, you can re-anodize titanium parts. First, take off the old oxide layer with acid. Clean the part and repeat the anodizing steps. This lets you change the color or fix problems on the surface.


