You might wonder, what is forging, and is it always stronger than casting? In most manufacturing environments, Forging delivers about 26% higher tensile strength compared to casting. When you choose Forging, you benefit from improved grain structure and fewer internal defects.
- Forging can provide up to 50% longer fatigue life and 37% greater fatigue strength.
- Cast metal parts often contain gas bubbles and other internal flaws that reduce their strength.
| Metric | Forged Components | Cast Components |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | 26% higher | Lower |
| Yield Strength | 400 MPa | 300 MPa |
| Fatigue Strength | 37% higher | Lower |
| Fatigue Life | Up to 50% longer | Shorter |
Understanding what is forging helps explain why Forging is the superior choice for high-performance parts.
Key Takeaways
- Forging gives about 26% more tensile strength than casting. This makes it better for important parts.
- The forging process makes the grain structure better. This means there are fewer problems inside and the product works well.
- Forged parts can last up to 50% longer under stress. This makes them good for tough jobs.
- Casting can cause problems inside, like gas bubbles. These can make the product weaker.
- Picking the right metal and forging way is very important. It helps get the strength and toughness you want.
- Forging removes many problems that casting has. This makes the parts thicker and more trustworthy.
- For tricky shapes or lots of parts, casting can cost less. But forging is better when you need strong parts.
- AFI Industrial Co., Ltd knows a lot about forging and casting. They make sure you get good parts made just for you.
Table of Contents
What is forging
When you ask about forging, you learn about a key metalworking process. Forging shapes metal by pressing or hammering it. This method is used in cars, planes, and buildings. AFI Industrial Co., Ltd is a company that does precision forging and machining. They make strong metal parts for tough jobs.
Forging process overview
Forging begins with planning and design. You pick the right metal first. Then you heat the metal until it is ready. Next, you shape it with a die or hammer. After shaping, you heat treat the metal to make it better. Cooling and finishing steps come last to make sure the part is just right.
| Step Number | Step Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Metal Selection |
| 2 | Heating |
| 3 | Forging |
| 4 | Heat Treatment |
| 5 | Cooling |
| 6 | Finishing |
There are different types of forging. Hot forging heats the metal above its recrystallisation temperature. This helps make complex shapes and stronger parts. Cold forging and warm forging are other ways to forge metal. Each type has its own good points.
Grain structure in forging
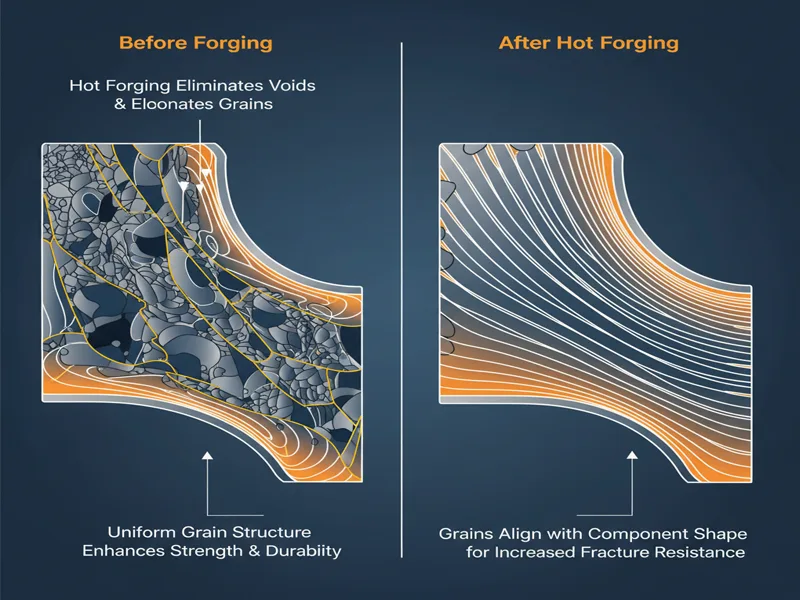
Forging changes how the grains in metal line up. The grains follow the shape of the part. This makes the metal stronger and tougher. In hot forging, grains move in the same direction as the force. This fixes defects inside and makes the grain structure even. Parts made this way are stronger and resist breaking.
- Metal forging aligns grains for greater strength.
- Hot forging gets rid of empty spaces and stretches grains.
- Even grain structure helps the part last longer.
Note: Good grain flow in forging helps your parts work better under stress.
Defect reduction in forging
Forging helps make parts that are strong and dependable. It gets rid of defects found in other methods. Forging removes gas pockets and empty spaces inside the metal. The pressing closes up any holes. This means the parts have fewer weak spots and can hold more weight.
- Forging fixes holes inside the metal.
- Hot forging removes trapped gas.
- Metal forging keeps the inside structure even.
Metal forging and strength
You pick forging when you need parts that can take a lot of stress. Forging makes parts stronger by changing how the grains flow. The grains follow the shape, which makes the part tougher. Forging does not trap gas or make empty spaces like casting. You get parts that are more even and reliable.
AFI Industrial Co., Ltd uses special forging and machining methods to make strong parts. They are experts in hot forging and precision metal forging. Their parts meet high standards. When you learn about forging, you see why it is best for important jobs.
- Metal forging makes parts stronger and tougher.
- Hot forging helps stop cracks from forming.
- Good grain flow in forging makes parts work better.
If you want parts that last and work well, try metal forging. AFI Industrial Co., Ltd can help you pick the best forging method. They make sure you get great results every time.
Casting vs forging process
Casting process basics
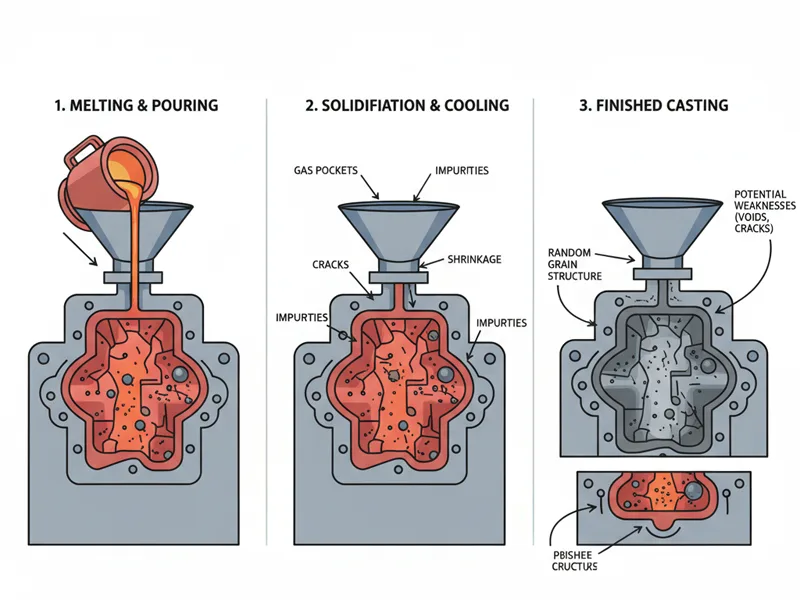
Casting is when you pour melted metal into a mould. The metal cools and gets hard in the mould’s shape. Casting is good for making big or tricky shapes. People use it for engine blocks and pump housings. It also works for making decorations. But casting does not control how the grains inside line up. The grains form in random ways as the metal cools. This can cause problems like holes, shrinking, or cracks. Sometimes, gas bubbles or extra bits show up in cast parts. These problems can make the part weaker.
AFI Industrial Co., Ltd uses special machines to work on cast parts. Their team uses CNC milling and turning to make the surface smoother. They also help the part fit better. Even with these steps, casting still has more problems than forging.
Forging process comparison
Forging shapes metal by using strong force. You start with a solid piece of metal and heat it. Then you press or hammer it into the shape you want. This makes the grains inside line up with the part’s shape. The part gets stronger and tougher. Forging closes up empty spaces and gets rid of trapped gas. This means the part has fewer weak spots. It is strong and works well.
AFI Industrial Co., Ltd is very good at forging and machining. They use special dies and careful heating to make strong parts. Their parts have grains that flow in the right way. This helps the parts not crack and work well under stress.
Metal forging vs casting
| Process | Grain Structure Formation | Strength Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Forging | Makes grains line up and even inside the part. | Makes the part stronger and tougher. |
| Casting | Grains do not line up well and can have problems. | The part is not as strong or even. |
- Forging uses force to make the grains inside better.
- Casting does not make the grains line up, so it is weaker.
- Forging makes the metal stronger and tougher than casting.
Tip: Forging makes grains follow the part’s shape. This helps the part last longer and not break easily.
Effects on metal strength
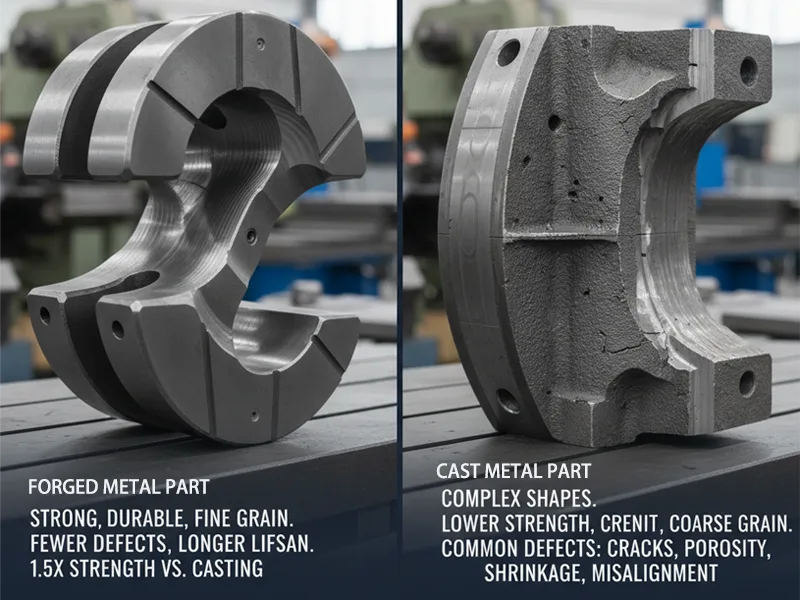
Forged metal is much stronger than cast metal. The grains inside the forged metal line up with the part’s shape. This makes the part tough to break. Casting does not have this grain flow, so it is not as strong. Studies show forged parts have higher strength than cast parts. Forging also lowers the chance of problems inside the part. This means forged parts last longer and work better.
Studies show cast parts often have problems like mould shifting, cracks, rough surfaces, shrinking, holes, and extra bits. These problems happen even when people are careful. Cast parts get rejected more often than forged parts. Forged parts have fewer problems because of how they are made.
Tests show parts made by advanced forging, like Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing, are much stronger. They are about 1.5 times stronger than cast parts. This is because forged parts have finer grains and better quality inside.
AFI Industrial Co., Ltd can machine both cast and forged parts. Their skills help you get the best part for your needs. You can pick casting for tricky shapes or forging for strong parts.
Note: If you want the strongest and most reliable parts, you should pick metal forging.
Why forging is usually stronger
To know why forging is stronger than casting, you need to look inside the metal. Forging changes the metal’s internal structure. This makes it tougher and more dependable. Forged parts last longer and work better when stressed.
Metallurgical advantages
Forging has some big metallurgical advantages over casting. It changes how the grains inside the metal form and line up. This makes your parts much stronger and tougher.
Grain flow alignment
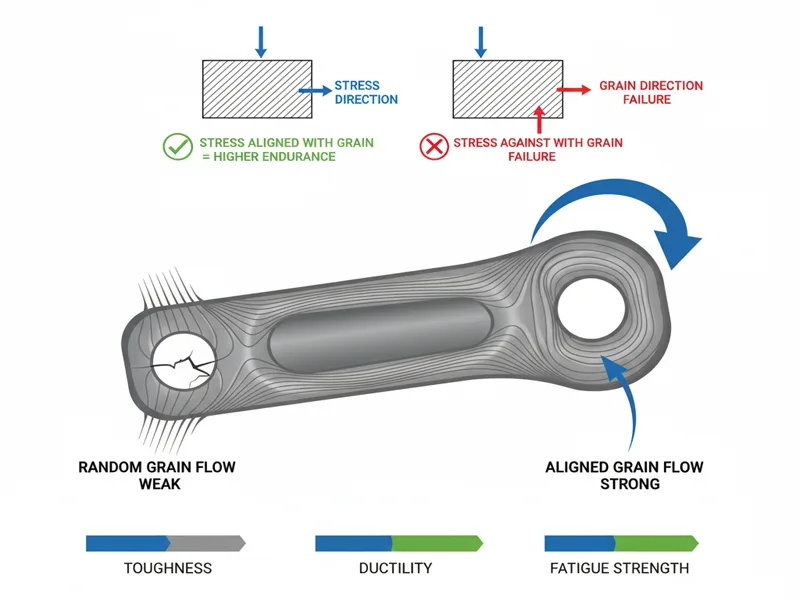
Grain flow alignment is a key reason forging is stronger. In forging, you press or hammer the metal. This makes the grains follow the part’s shape. The part gets stronger where it needs to handle stress.
- Grain flow alignment helps stop breaking and cracking.
- Grains move with the part’s shape, not against it.
- You get better toughness, ductility, and fatigue strength.
- When stress lines up with grain flow, the part can take more force and last longer.
Tip: Drop forging makes grains even stronger. It forces them to follow the part’s shape. That’s why forged parts are used in cars and airplanes where safety is important.
Defect elimination
Forging also helps remove many defects that can weaken metal parts. Pressing the metal hard closes empty spaces and gas pockets inside. This makes the metal denser and more even.
- Forging cuts down on voids and cracks inside.
- You avoid casting problems like porosity, laps, and surface cracks.
- The part is more reliable and less likely to fail.
| Mechanism | Contribution to Strength |
|---|---|
| Grain Refinement and Alignment | Makes grains finer and more even, which boosts strength and ductility. |
| Elimination of Porosity and Defects | Closes holes and pores, making the metal denser and stronger. |
| Work Hardening and Microstructure Optimization | Makes the metal resistant to bending and improves its internal structure for better properties. |
Forging gives you a part with fewer weak spots. That’s why people trust forged parts for important jobs.
Mechanical properties
Forging makes metal parts stronger in ways casting cannot. You get higher yield strength, better fatigue resistance, and more toughness.
- Forged parts have a more even and fine grain structure.
- The grain flow matches the part’s shape, so it handles stress better.
- Properties like toughness, ductility, and fatigue strength get much better with good grain alignment.
- Forged parts resist fatigue more, which is important for parts that get used a lot.
| Property (at RT) | Casting (316 SS) | Forging (316 SS) |
|---|---|---|
| Yield Strength (0.2% MPa) | 170–240 | 240–310 |
| Fatigue Strength (MPa, 10⁷ cycles) | ~170 | ~240 |
You can see that forging gives you better yield and fatigue strength. This means your parts can take more force and last longer, even with lots of use.
AFI Industrial Co., Ltd uses strict quality checks to make sure every forged part is top quality. Their process includes:
| Quality Control Measure | Description |
|---|---|
| Quality Planning | Set clear goals and steps for quality. |
| Supplier Management | Pick and check suppliers for the best quality. |
| Process Control | Watch and improve every step of making parts. |
| Review | Check often to keep quality high. |
| Product and Process Validation | Make sure products and steps meet all needs. |
| Quality Training | Teach workers to keep skills sharp. |
| Continuous Improvement | Always look for ways to get better. |
When you pick forging from AFI Industrial Co., Ltd, you get parts that are strong, steady, and reliable. Their skill in forging and machining gives you the best results.
Note: Forging is the best choice when you need parts that are strong, tough, and built to last.
When casting matches forging
Forging is usually stronger, but casting can be just as strong. Sometimes, casting is even better. This depends on the material and design you pick.
Material and design factors

You can use special materials for casting. These materials can be as strong as forged ones. Superalloys like nickel, cobalt, and titanium work well in tough places. If you choose the right material, your part lasts longer. Casting is good for making tricky shapes. You can make thin walls or tiny channels with casting. Forging cannot always make these shapes. If your part needs to bend easily or has a special shape, casting might be best.
Tip: Think about how your part will be used and where it will go before you pick forging or casting.
Advanced casting techniques
New casting methods are much better now. Factories use robots to do the same jobs over and over. This makes work safer and more steady. Computers watch the process and fix problems fast. They help stop mistakes before they happen. You get better parts with fewer problems.
High-performance castings
Investment casting makes parts with hard shapes and good detail. Die casting is fast for making lots of parts. These ways help you get strong and tough parts. They work even better with good materials.
- Forged parts are strong and last long because of grain alignment.
- Cast parts bend more and cost less for big batches.
- Use casting for parts with hard shapes or that need to bend.
Specialized treatments
You can heat treat cast parts to make them stronger. Here are some common ways:
- Solution heat treatment heats aluminium castings and cools them fast to make them strong.
- Ageing makes the part harder and stronger.
- Annealing helps the part bend and removes stress.
- Stress relief heat treatment takes away leftover stress.
- T6 and T7 heat treatments give aluminium castings special benefits.
You can also use 3D scanning to check parts. Real-time systems catch problems early. These steps help keep parts good and stop mistakes.
AFI Industrial Co., Ltd can machine both cast and forged parts. Their team can finish castings to meet exact needs. Their CNC machines make sure cast parts are strong and last long.
Note: Always look at what your project needs, the materials, and the design. With the right choices, casting can be as good or better than forging.
Choosing forging or casting
Application requirements
When you pick how to make a metal part, think about what the part must do. If your part needs to be strong or work in hard places, forging is usually best. Forging makes parts that are tough and strong. That is why car, plane, and machine parts are often forged. Forging lines up the grains in the metal. This helps the part handle more stress and last longer.
Casting is good for making parts with tricky shapes or small details. If your part has thin walls or special curves, casting can make it. Casting works well for parts that do not need to be very strong. You might use casting for covers or parts with lots of shapes.
Tip: Pick forging if you need strength. Pick casting if you need a complex shape.
| Criteria | Forging | Casting |
|---|---|---|
| Strength | Stronger along the grain direction | Isotropic, uniform strength |
| Ductility | Typically less ductile | Can be more ductile, e.g., aluminum die cast |
| Hardness | Generally harder and stronger | Hardness varies; it can be softer |
| Temperature Performance | Reliable under high-stress conditions | Can use speciality alloys for better performance |
| Size and Weight | Preferred for small/medium parts | More practical for large/heavy components |
| Shape Complexity | Better for simple shapes | Suited for complex geometries |
| Production Costs | Better value for high-volume runs | Lower upfront costs, higher per component |
| Quality Control | Fewer defects, more reliable | Defects can occur, requiring quality checks |
Cost and production
You should also think about cost and how many parts you need. Forging costs more at first, but it saves money if you make lots of parts. You use more of the metal and waste less. Forged parts often need less work after shaping, so you save time and money.
Casting costs less to start. It is faster to make many parts, especially with high-pressure die casting. But casting can waste more metal and often needs extra work to finish. You may need to machine or treat the surface to make it right.
| Factor | Forging | Casting |
|---|---|---|
| Tooling Costs | Higher initial costs, good for high volume | Lower initial costs, may need more post-processing |
| Material Utilization | Less scrap, better use of metal | More scrap, less efficient |
| Cycle Time | Longer heating cycles, slower | Fastest for high volume |
| Post-Processing | Less machining needed | More machining and treatments often required |
Note: Forging can save money if you make lots of parts. Casting is better if you need many tricky parts fast.
AFI Industrial Co., Ltd machining solutions
You want a company that can do both forging and casting. AFI Industrial Co., Ltd helps with every step of your project. They help with design, forging, casting, and final machining. Their team uses CNC machines to make sure your parts are just right.
- You can pick precision forging for strong parts.
- You can use advanced casting for tricky shapes.
- You get help with casting, from mould design to die-casting.
- You get careful control over size and surface finish.
- You get solutions that save money and help your project.
| Service Type | Description |
|---|---|
| CNC Machining | Precision machining for any project, ensuring tight tolerances and smooth finishes. |
| Precision Forging | High-quality forging for parts that need strength and durability. |
| Casting Methods | Multiple casting options for custom shapes and cost savings. |
AFI Industrial Co., Ltd helps you from start to finish. You get advice on picking forging or casting. You get quality parts, whether you need strength, tricky shapes, or both.
Real-world applications
Automotive and aerospace
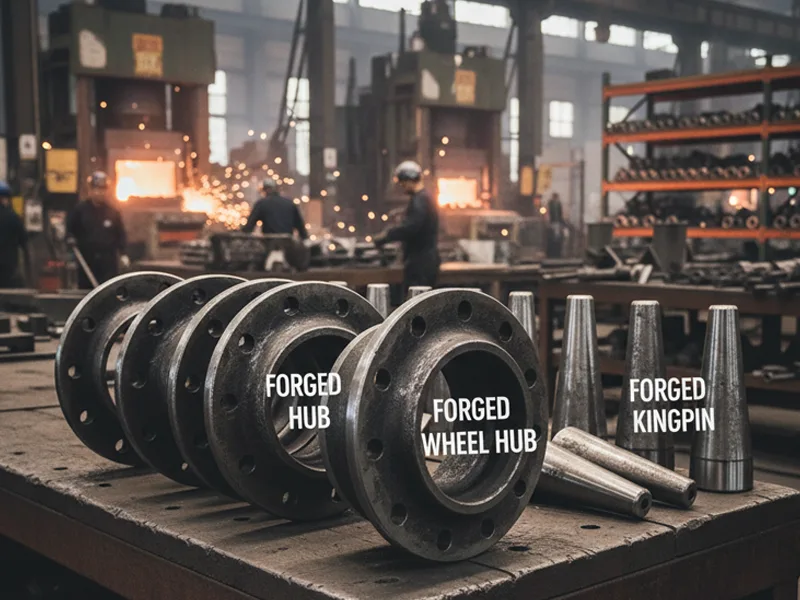

Forging is used a lot in cars and aeroplanes. When you ride in a car, forged wheel spindles and kingpins help keep you safe. Trucks use forged axle beams and shafts for strength. Powertrain systems have forged connecting rods and gears. These parts must handle lots of stress and movement. Aeroplanes and helicopters use forging for bulkheads and wing roots. Landing gear is also made by forging. These parts hold heavy loads and keep you safe in the air. Forged parts are chosen because they are strong and reliable.
- Cars use forged wheel spindles and kingpins.
- Trucks need forged axle beams and shafts.
- Engines have forged connecting rods and gears.
- Jets use forged bulkheads and wing roots.
- Aeroplanes have forged landing gear.
Tip: Forged parts help you trust your car or plane every time.
Industrial and consumer products
Forging is found in many factory machines and tools. Pumps, valves, and gear blanks are often forged. These parts work under pressure and last a long time. Construction machines use forged parts for strength. You also see forging in things you use at home. Hand tools, bike parts, and kitchen knives are often forged. Forged parts do not bend or break easily. This means your tools and bikes last longer.
Casting is used for parts with tricky shapes. Engine blocks, pump housings, and decorations are often cast. Casting is good for parts with fine details or thin walls. Both forging and casting help make strong and useful things for daily life.
| Product Type | Forging Application | Casting Application |
|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Axle beams, gears | Engine blocks, housings |
| Aerospace | Landing gear, wing roots | Turbine blades, covers |
| Industrial | Pump shafts, gear blanks | Valve bodies, impellers |
| Consumer | Hand tools, bike parts | Decorative items, cookware |
AFI Industrial Co., Ltd case studies
AFI Industrial Co., Ltd helps many industries with their machining skills. They work on cars, planes, and factory machines. Their team uses forging to make strong parts for cars and aeroplanes. For example, they make forged gears and shafts for car transmissions. In planes, they make forged landing gear and bulkheads that meet safety rules.
They are also good at casting. AFI Industrial Co., Ltd makes cast pump housings and engine blocks for factories. Their CNC machines make sure every part is just right. You get great parts whether you pick forging or casting. Their engineers help you choose the best way, thinking about strength, cost, and design.
Note: When you work with AFI Industrial Co., Ltd, you get help with both forging and casting. You receive parts that work well in real life.
You can see that forging is often stronger than casting. The table below shows how forging gives metal parts more tensile and fatigue strength.
When you pick between forging and casting, think about the part’s shape, the metal’s features, and what you need to make it. Here are some steps to help you:
- Find out what forces your metal part will face.
- Think about the size and shape of your metal part.
- Choose the right metal and process for your needs.
- Remember to check tooling costs and how many parts you need.
- Pick a supplier with good engineering help.
- Decide early on the surface finish and how exact you need it.
Casting is good for tricky shapes and special alloys. Forging works best for simple and strong metal parts. The table below helps you compare both ways:
In the future, metalworking will use new ways like additive manufacturing, lighter alloys, and more machines. These changes make metal parts lighter, stronger, and work better.
Tip: Always think about both the technical and real-life needs before you pick forging or casting for your metal project.
FAQ
Forging shapes metal by using heat and strong force. Special tools help make the metal into the right shape. This makes the grains inside line up well. The parts have fewer problems inside. Forging is used for cars, planes, and factory machines.
Forging usually makes parts that are stronger. The grains inside line up and there are fewer weak spots. Casting can be strong if you use special materials and treatments. But forging is still best for parts that need to handle a lot of stress.
Pick casting if you need parts with tricky shapes or thin walls. Casting is good for big parts or when you need many parts fast. It also costs less at the start.
Grain flow means the grains follow the shape of the part. This makes the part tougher and helps it last longer. Good grain flow helps the part not break under stress.
Machining can fix problems on the outside and help parts fit better. But it cannot fix holes or gas bubbles inside the part. You need to check for these problems early with quality control.
Forged parts are used in cars, planes, building machines, and big equipment. These jobs need parts that are strong and work well in hard places.
AFI Industrial Co., Ltd does careful forging, casting, and CNC machining. They give you expert help and check quality at every step. You get custom parts made just for your project.
Forged parts last longer because their grains are fine and even. There are fewer problems inside. The parts can handle stress again and again without breaking.


