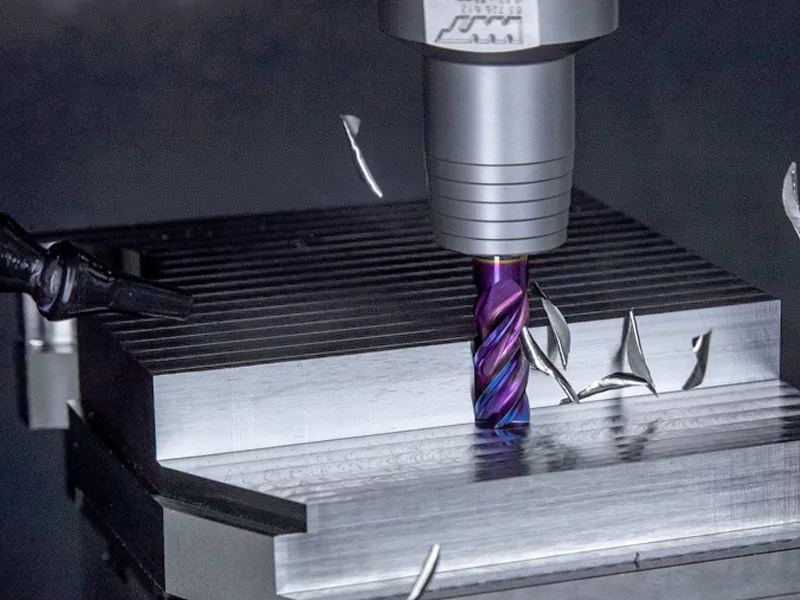
In today’s world of ever-increasing demands for precision and efficiency, milling technology occupies a central position in modern manufacturing, playing a crucial role in precision machining and CNC system operations. In precision machining, CNC milling processes enable the realization of even the most complex designs through automation and optimized workflows, further enhancing machining accuracy, achieving greater consistency, and reducing human error.
Metal milling, the core of milling, involves removing material from a workpiece to form specific shapes, textures, or features. The seamless integration of advanced technology, cutting forces, and precision makes CNC milling a vital tool in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and medical device manufacturing. Today, we will explore how CNC milling remains central to manufacturing and how it drives industry development, as well as the possibilities of aluminium design.
Table of Contents
CNC Milling Basics: Definition, Principles, and Classifications
Milling is a process that removes material from a solid piece. It uses a spinning cutter with sharp teeth. The cutter moves very fast and cuts away layers from the workpiece. This shapes the workpiece into the right form. Unlike CNC turning, where the workpiece rotates, CNC milling involves a stationary workpiece and rotating tools, allowing for multi-directional cutting and complex geometries.
Technical Standards and Machining Tolerances
At AFI Parts, we don’t just “cut metal”; we engineer precision. Our CNC milling process is strictly governed by international standards to ensure interchangeability and functionality.
- General Tolerances: We adhere to ISO 2768-m (Medium) for standard features and ISO 2768-f (Fine) for high-precision requirements.
- Precision Capabilities: Using our advanced 5-axis machining centers, we routinely achieve:
- Dimensional Tolerance: ± 0.005mm (for critical features)
- Positional Accuracy: ± 0.01mm
- Surface Roughness: Standard Ra 3.2, capable of reaching Ra 0.4 – Ra 0.8 with high-speed finishing passes.
- Material Specifics:
- Aluminum (6061/7075): Spindle speeds optimized up to 12,000 RPM for mirror-like finishes.
- Stainless Steel (304/316): Low cutting speeds with high torque to prevent work hardening.
Key Classifications of CNC Milling
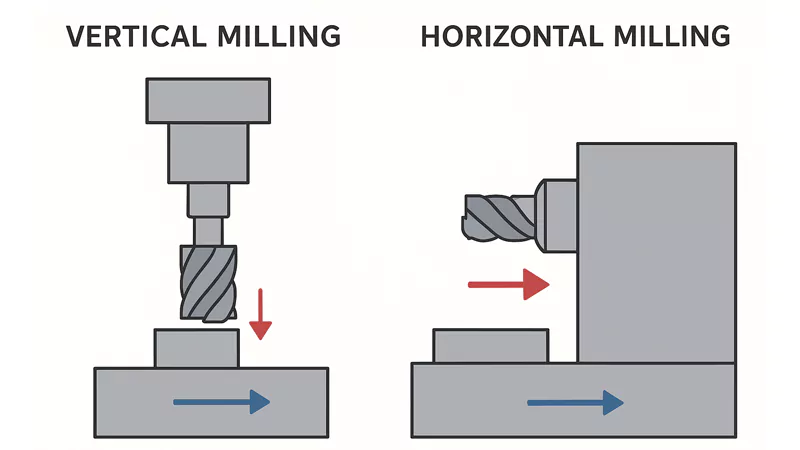
Vertical Milling vs. Horizontal Milling: These refer to the orientation of the milling machine’s spindle. Vertical milling is ideal for precision, detailed work, while horizontal milling is better suited for larger, heavier components.
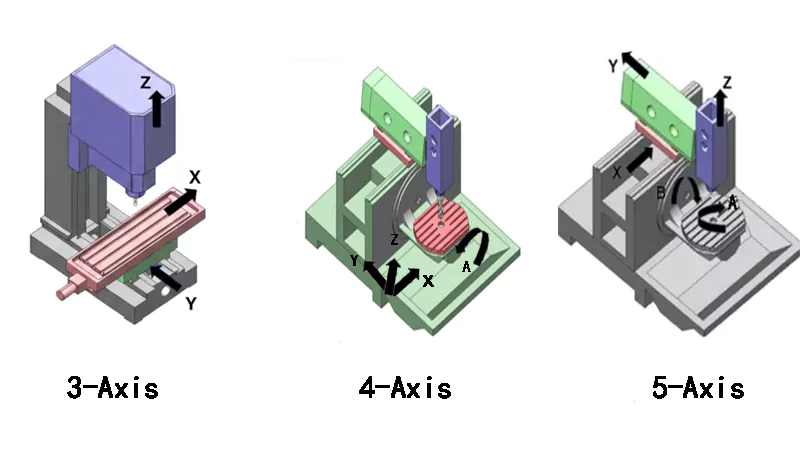
3-Axis, 4-Axis, and 5-Axis Machining: These refer to the number of directions the cutting tool can move. 5-axis CNC milling is particularly valuable for producing highly complex geometries and parts with intricate details. The ability to process parts in multiple directions simultaneously increases precision and reduces setup time, making it an industry-leading choice for high-precision applications.
CNC Milling Machines: These sophisticated machines are at the heart of CNC machining processes. They automate the milling process, increasing consistency and reducing human error while achieving precise cuts.
How does the CNC Milling Process Achieve Superior Performance and Precision?
1. Cutting Tool Selection
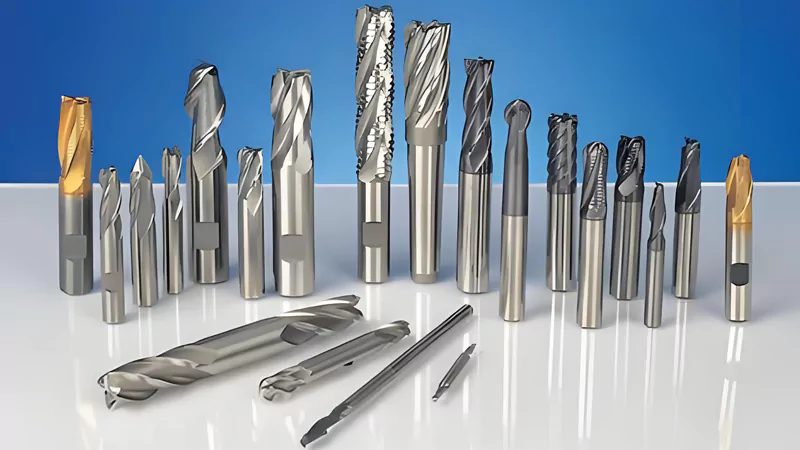

Choosing the right tool is essential for ensuring precision and efficiency. Materials like carbide, high-speed steel (HSS), and coated tools are commonly used in CNC milling because they can withstand high temperatures and maintain sharpness even during extended use. Coatings like titanium nitride (TiN) further enhance tool life and performance.
2. Spindle Power and Rigidity
The spindle speed (measured in RPM) and feed rate determine the cutting force during machining. High-powered spindles with rigidity help maintain precision while processing tougher materials. The right combination of speed and feed rate allows for efficient material removal while ensuring high-quality surface finishes.
3. Cooling and Lubrication
Proper cooling is crucial for tool longevity and surface quality. Coolants or cutting fluids are applied to keep temperatures low and reduce friction. Depending on the material and process, wet machining (using coolant) or dry machining (using air or mist) can be chosen to optimize tool performance and finish quality. This helps in extending tool life, improving surface roughness, and ensuring tight tolerances.
4. Tools used for different milling types
| Milling type | Milling method | Purpose | Features | Machining tools |
| Planar milling | Face Milling | Mainly used for machining the horizontal or inclined planes of workpieces. | With the main cutting edge located on the end face of the tool, the cutting force is primarily borne by the tool end face. It is the main method for removing large amounts of excess material and obtaining large, flat workpieces. It often uses indexable inserts for end mills. | Face Mill; Indexable Face Mill |
| Planar milling | End Milling | It is the most common milling method, using an end mill to machine planes, sides, contours, cavities, or grooves. | Both the side and end cutting edges of the cutting tool participate in the cutting process. Depending on the feed direction, it can be climb milling (climbing milling) or conventional milling (conventional milling), and is commonly used for milling steps, cavities, and partially continuous grooves. | End Mill; Ball Nose Mill |
| Planar milling | Side Milling | Specifically designed for machining the sides or vertical surfaces of workpieces. | Cutting is primarily achieved using the side cutting edge of the cutting tool. Typically, the side cutting edge of a side end mill or end mill is used to trim and shape the edges of the workpiece. | Side Milling Cutter; Three-Side Milling Cutter |
| Planar milling | Straddle Milling | Used for machining opposite sides of a workpiece in one operation, typically for machining square or hexagonal heads. | It is a highly efficient compound milling process that requires mounting two (or more) side cutters or three-sided cutters on the same spindle and adjusting them to the desired distance. | Gang of Side/Three-Side Milling Cutters |
| Milling of slots and special geometries | Slot Milling | Used to machine grooves of various shapes on workpieces, such as straight grooves and keyways. | The cutting width of the tool should match the width of the desired groove. A full-width cutter can be used (commonly used), or a saw blade cutter (for deep, narrow grooves), or a keyway cutter can be used. | Two-Flute End Mill; Keyway Cutter; Slitting Saw |
| Milling of slots and special geometries | T-Slot Milling | T-slots are used on machine tool worktables or fixtures. | It is a special-purpose slot milling cutter. A straight slot must first be milled out with an end mill before a T-slot cutter (with a cutting edge larger than the shank) can be used to mill the transverse slot at the bottom. | T-Slot Cutter |
| Milling of slots and special geometries | Angular Milling | Used for machining bevels, grooves, or chamfers on workpieces. | When using an angle milling cutter with a specific angle (such as a single-angle or double-angle milling cutter), the cutting edge of the cutter forms a fixed angle with the workpiece feed direction or axis. | Single-Angle Milling Cutter; Double-Angle Milling Cutter |
| Milling of slots and special geometries | Ramping/Inclined Cutting | Used for end mills to enter the material via a helical or inclined path, often used for entry into cavities. | The tool simultaneously feeds along the X-Y plane (planar feed) and the Z-axis (vertical feed). This is a feed method that is smoother and causes less tool wear than direct drilling or plunge milling. | End Mill (Machine tools and cutting tools that support diagonal feed are required) |
| Precision and special profile milling | Form Milling | Used for cutting surfaces with complex or non-standard contours in a single operation, such as arcs, flanges, and grooves. | When using a form milling cutter, the cutting edge shape perfectly matches the desired contour shape. For example, using a convex semi-circular milling cutter to machine a concave semi-circular groove. | Form Cutter; Convex Cutter; Concave Cutter |
| Precision and special profile milling | Gear Milling | Used for machining various types of gears (such as spur gears, helical gears, herringbone gears, etc.). | It is a special type of form milling. It can be performed using disc milling cutters (lower efficiency but high precision) or hobs based on the gear hobbing principle (high efficiency, often used in mass production). | Disc-type Module Cutter; Hob (For mass production) |
| Precision and special profile milling | Rough Milling | In the first stage of machining, a large amount of excess material is quickly removed from the workpiece using the maximum feed rate and depth of cut. | Pursuing high metal removal rates often leaves a large amount of residual material on the workpiece surface, resulting in lower surface quality. | Roughing End Mill / Hogger; Indexable Face Mill |
| Precision and special profile milling | Finish Milling | Performed after rough milling, using small feed rates, shallow depths of cut, and high cutting speeds to achieve the final dimensions, tolerances, and surface roughness required by the design. | To achieve high machining accuracy and high-quality surfaces, remove residual material left from rough milling. | Multi-Flute End Mill; Finishing Face Mill |
The Advantages of CNC Milling: Why is It the Top Choice for Complex Parts?
CNC Milling is the go-to solution for creating complex parts, but traditional machining of mechanical parts cannot achieve this. What makes it stand out in specific industries?
Applications in Precision Industries
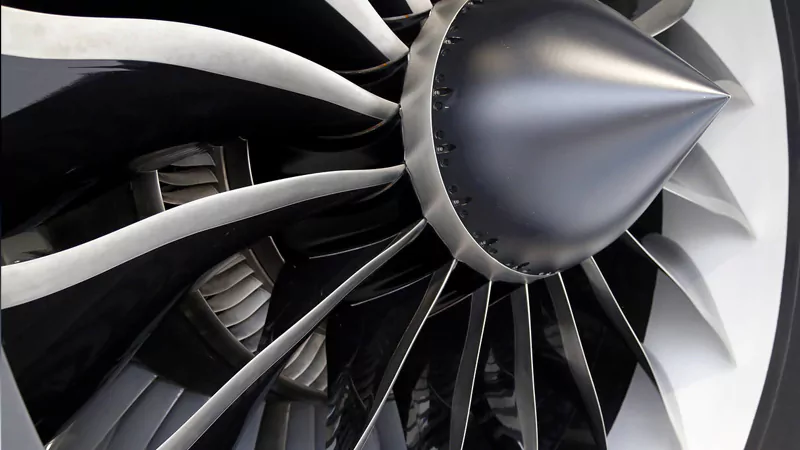

Aerospace Components: Aerospace parts demand high precision and tight tolerances. CNC milling is capable of producing highly intricate parts like turbine blades, structural components, and engine components, often from difficult-to-machine materials like titanium and high-strength alloys. By utilizing five-axis machining, complex contours can be completed in one go, ensuring the geometric accuracy and aerodynamic performance of the parts.

Medical Devices: CNC milling is indispensable in the production of medical devices, such as implants and surgical instruments. Biocompatible materials (such as stainless steel and special alloys) have the highest requirements for processing precision and surface roughness. These products often require small-batch production with high precision to meet stringent regulatory standards.

Automotive Parts: From engine components to precision transmission parts, CNC milling ensures automotive manufacturers can meet complex design specifications and produce durable, reliable components. In addition, high-speed CNC milling machines, combined with automation solutions, enable rapid and economical mass production.

Tooling and Molds: Milling is essential for the creation of custom molds, dies, and other tools that require high accuracy and fine details.
Case Study: Overcoming Deformation in Thin-Wall Aluminum Housings
The Challenge: A client in the optical industry required a batch of aluminum 6061 lens housings. The design featured a wall thickness of only 0.8mm. During initial trials with standard clamping, the clamping force caused the parts to warp, leading to a concentricity error of >0.05mm.
Our Solution:
- Custom Fixturing: We designed a vacuum fixture to distribute holding pressure evenly across the base, eliminating localized stress points.
- Step-Down Machining: We utilized a “Roughing-stress relief-Finishing” workflow. We removed 90% of material, paused to allow thermal dissipation, and then performed the final pass.
The Result:
- Concentricity Achieved: < 0.015mm
- Pass Rate: Increased from 85% to 99.8%
- Cost Savings: Reduced material waste by 12% for the client.
Material Versatility
| Material Type | Examples | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Metals | Steel 40Х, 17G2SAF, Aluminum 7075, AISI P-2 | High strength, durability |
| Plastics | G-10, GPO, FR4, phenolic laminates | Lightweight, corrosion resistance |
| Composites | Al alloy SiC particle composites | Custom properties, design freedom |
Aluminum Milling: A common material in the manufacturing world due to its light weight and versatility. CNC milling is ideal for creating intricate aluminum parts process used in industries like automotive and electronics.
Stainless Steel Milling: Stainless steel is often challenging to machine due to its hardness, but CNC milling excels at producing complex parts with excellent precision.
Titanium Milling: Known for its strength-to-weight ratio, titanium is widely used in aerospace and medical industries. CNC milling allows manufacturers to handle this tough material with ease, creating parts that meet exacting standards.
Speed and Efficiency
CNC milling machines work faster than old machines. Automation means no need to set gears by hand. Setup takes less time. Machines can run all day and night with little help. Tool changers can hold up to 30 tools for quick changes. It can respond quickly to provide prototype service to customers
| Performance Aspect | CNC Milling Machines | Conventional Machines |
|---|---|---|
| Operation Time | Can run all day with little help | Needs people to run and watch |
| Setup and Tool Change Time | Fast setup and tool changes | Takes longer to set up and change tools |
| Precision | Very accurate; less chance for mistakes | Depends on worker skill; not always exact |
| Production Capacity | Can make lots of parts quickly | Slower and needs more work from people |
| Labor Requirements | One person can watch many machines | Needs more workers with special skills |
| Waste and Scrap Rates | Less waste because of high accuracy | More waste and costs to fix mistakes |
| Task Changeover Speed | Quick changes with programs and tools | Changing jobs takes more time |
| Consistency and Reliability | Makes the same part every time | Parts can be different as more are made |
Comparative Analysis: CNC Milling vs. 3D Printing vs. Die Casting
To help you decide if CNC milling is the right process for your project, we have compared it against other common manufacturing methods based on our production data.
| Feature | CNC Milling | Metal 3D Printing (SLM) | Die Casting |
| Ideal Volume | 1 – 1,000 units | 1 – 50 units | 10,000+ units |
| Precision | High (±0.005mm) | Medium (±0.1mm) | Medium (±0.05mm) |
| Setup Cost | Low (No tooling required) | Low | High (Expensive Molds) |
| Material Properties | 100% Isotropic (Strongest) | Porous/Layered | Good, but can have voids |
| Surface Finish | Excellent (Ra 0.8) | Rough (Ra 10+) | Good (Ra 1.6) |
Verdict: CNC Milling remains the most cost-effective and precise choice for low-to-medium volume production where structural integrity is non-negotiable.
Our CNC Milling Power: Factory Competitive Advantage
When it comes to CNC machining, precision, efficiency, and quality are paramount. At our factory, we’re proud to offer cutting-edge CNC milling solutions that give our customers a competitive edge.
Our Equipment
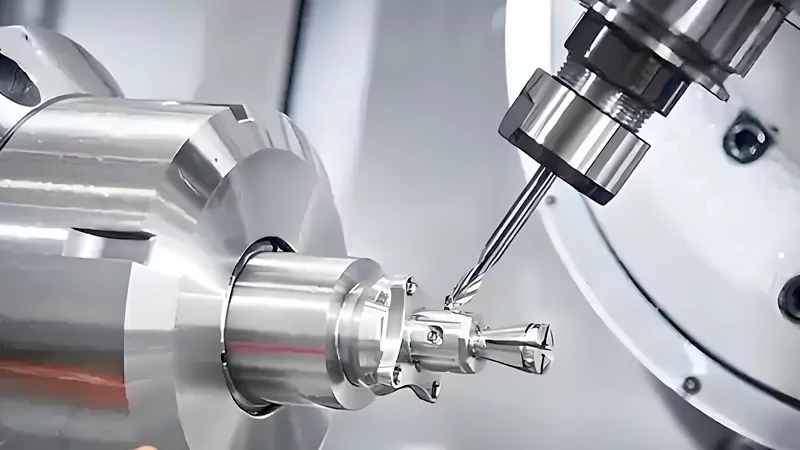
We use advanced CNC milling machines, including high-speed and 5-axis CNC machines, which allow us to tackle even the most complex geometries and easily provide all kinds of custom non-standard parts to our customers.
Quality Control
We employ coordinate measuring machines (CMM) and other sophisticated inspection tools to ensure that each part meets stringent quality standards. This ensures consistency and performance, no matter the size or complexity of the project. Precision is not an accident; it is a guaranteed process. AFI Parts operates under a quality management system certified to ISO 9001:2015 standards.
Every CNC milled part undergoes a rigorous inspection process before shipment:
- Raw Material Verification: We provide a COA (Certificate of Analysis) to verify the material’s chemical composition.
- In-Process Inspection: Real-time monitoring of critical dimensions.
- Final CMM Inspection: We utilize Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMM) to verify complex geometries against your CAD files. A full dimensional inspection report is included with every shipment.
Engineering Expertise
Our experienced engineers optimize machining processes, ensuring efficiency and precision in every part we produce. From initial design to final inspection, we work closely with our clients to provide tailored solutions that meet their exact requirements.
Looking for reliable CNC machining services? Give us your design drawings.
Unlock Your Design Potential
The power of milling lies in its ability to turn the impossible into possible. It’s not just a method of material removal, but a key technology for achieving high precision, high strength, and complex geometries.
Ready to start your project? Share your designs with us. As a professional CNC machining manufacturer, we’ll provide a free quote or discuss the best technical solutions for your needs.
Contact Us Now:
For CNC machining services
For custom CNC machining parts inquiries
For pricing and quotes
Summary
CNC milling is more than just a cutting technique—it’s a powerful technology that transforms complex designs into high-performance, precise parts. With advancements in CNC milling machines, tool selection, and quality control, this technology continues to play a pivotal role in the manufacturing world, powering industries such as aerospace, automotive, and medical devices. Whether you’re looking to create complex geometries or achieve high tolerance precision, CNC milling is the solution you need.
FAQ
CNC milling removes material from a stationary or moving workpiece using a high-speed rotating tool. It is mainly used to manufacture planes, cavities, and asymmetrical features. CNC turning, on the other hand, involves rotating the workpiece at high speed and removing material with a fixed tool. It is mainly used to manufacture cylindrical and symmetrical parts.
5-axis machining refers to the ability of a CNC milling machine to simultaneously control three linear axes (X, Y, Z) and two rotary axes (A, B, or C). Its main advantage is the ability to complete the machining of highly complex parts in a single setup, reducing setup time, eliminating re-clamping errors, and thus achieving higher machining accuracy and better surface finish. It is particularly suitable for machining aerospace parts.
Key factors affecting machining accuracy include: the rigidity and thermal stability of the CNC machine tool, the wear condition of the CNC cutting tool, the degree of optimization of the toolpath (CAM programming), and the temperature control of the cutting fluid during machining.
Our expertise includes precision machining of challenging materials, particularly titanium alloys (due to their high strength and poor thermal conductivity) and various grades of stainless steel. We also provide efficient, high-quality aluminum alloy machining services.
Yes, we professionally provide flexible small-batch machining and prototyping services to support the development and iteration of new products. We typically do not have strict minimum order quantity (MOQ) limits; please contact us for a quote on custom machine parts.


