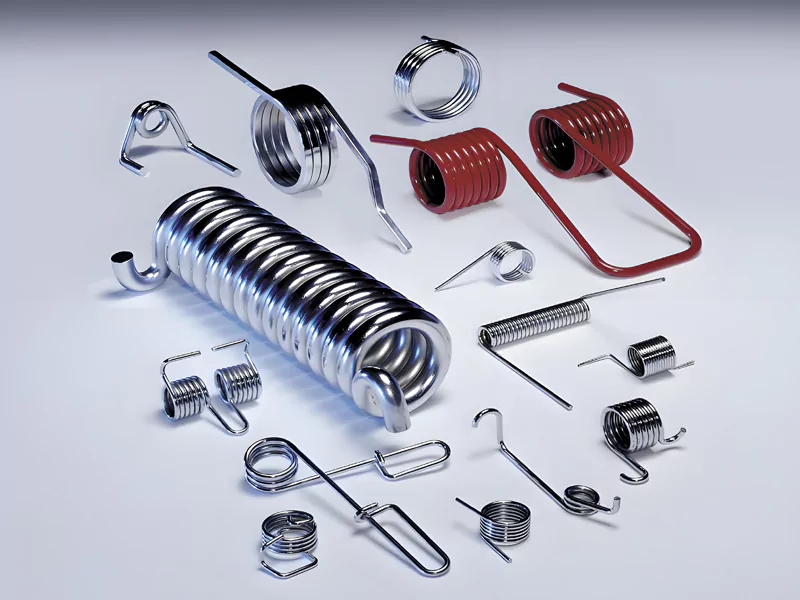
When you explore mechanical design, you quickly find that spring types play a crucial role in how products work and last. Here are the 10 most common spring types you will encounter:
- Compression springs
- Extension springs
- Torsion springs
- Constant force springs
- Leaf springs
- Spiral springs
- Belleville (disk) springs
- Gas springs
- Wave springs
- Double torsion springs
| Spring Type | Market Share (%) | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Helical Springs | > 43% | Automotive, Aerospace, Railway |
| Disk Springs | N/A | High-load industrial uses |
| Leaf Springs | N/A | Heavy-duty vehicles |
Choosing the right spring type matters. Studies show that the wrong choice can lead to poor performance or even failure, especially for parts like compression springs or extension springs. When you understand these options, you can select better solutions for your needs. Companies like AFI Industrial Co., Ltd offer products that help you make the best choice for your project.
Key Takeaways
- Learn about 10 common spring types. These are compression, extension, torsion, constant force, leaf, spiral, Belleville, gas, wave, and double torsion springs.
- Pick the right spring type for your product. This helps it work well and last longer.
- Compression springs hold and release energy. They are used in car suspensions and medical devices.
- Extension springs are good for pulling things. You can find them in garage doors and trampolines.
- Torsion springs give twisting force. They are in door hinges and laptop screens.
- Gas springs help things move smoothly. They are used in adjustable furniture and cars.
- Precision machining makes springs work better. It keeps their size and material correct.
- Think about fatigue resistance and load capacity when you pick springs. This makes your product safer and more reliable.
Table of Contents
Spring Types Overview
Springs come in many shapes and sizes. Each type has a special job in mechanical design. Knowing the differences helps you pick the right spring for your project. Companies like AFI Industrial Co., Ltd use advanced machines to make springs that fit exact needs. Let’s learn about three common spring types.
Compression Springs

Structure
Compression springs are open-coiled helical springs. They look like tight coils that push back when pressed. Makers use materials like music wire, stainless steel, oil tempered wire, phosphor bronze, and brass. The wire thickness, coil size, and number of coils change how much weight the spring holds.
Function
You use compression springs to store and release energy. When you press down, the spring pushes back and tries to return to its shape. This makes them good for holding loads. They also absorb shock and cut down on vibration. Their design helps them resist being squished, so they give strong support.
Tip: Compression springs work best when you need something to push back against a load, like in a car’s suspension or a ballpoint pen.
Applications
Compression springs are found in many things you use daily. You see them in:
- Shock absorbers in cars and bikes
- Mattresses and office chairs
- Manufacturing machines
- Medical devices
| Type of Spring | Characteristics | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Compression Springs | Open-coiled helical springs that push back when pressed. | Manufacturing, shock absorbers, mattresses |
Extension Springs

Structure
Extension springs look like coils with hooks or loops at both ends. These hooks let you attach the spring to other parts. The outside and inside diameters, wire thickness, and material type (like stainless steel or music wire) change how the spring works. The starting tension in the spring matters because it affects how much load the spring can hold.
Function
You use extension springs when you need something to pull back after being stretched. When you pull the ends, the spring stretches and stores energy. When you let go, it goes back to its original length. The spring’s design keeps stress below 60% of the material’s strength, so it lasts longer. The spring follows Hooke’s law, so you can guess how it will act under different loads.
Note: Extension springs are great for balancing loads, opening and closing doors, or controlling movement in machines.
Applications
Extension springs are used everywhere. You see them in:
- Trampolines and garage doors
- Medical stretchers and surgical lifts
- Car trunk hoods and seat adjusters
- Conveyor belts in factories
- Robotic arms for precise movements
| Industry | Typical Applications |
|---|---|
| Medical | Diagnostic devices, stretchers, and surgical lifts |
| Automotive | Trunk hood supports, seat adjusters, and window regulators |
| Manufacturing | Tensioning conveyor belts, packaging machines |
| Robotics | Precision movements in robotic arms or grippers |
Torsion Springs

Structure
Torsion springs are coils that work by twisting. You usually see them as helical coils, but sometimes they are spiral shapes. The ends of the spring attach to other parts, so when you twist one end, the spring stores energy. The wire thickness, coil size, and number of coils change how much torque the spring can handle.
Function
You use torsion springs to make or resist a twisting force called torque. When you twist the spring, it pushes back and tries to return to its starting position. This makes them good for controlling motion and keeping things in place. Torsion springs can handle lots of twisting, so they last a long time in things that open and close often.
Torsion springs help keep laptop screens steady and make sure doors close smoothly. They also help with safety features in electronics.
Applications
You find torsion springs in many places, such as:
- Door hinges and garage doors
- Laptop hinges and gaming controllers
- Motion control parts in machines
- Safety mechanisms in consumer electronics
- Torsion springs give controlled resistance and keep parts in the right spot, which is important for safety and reliability.
Constant Force Springs

Structure
Constant force springs look like tightly wound strips of metal. You see them as flat bands that coil up on themselves. When you pull the end, the spring unrolls smoothly. The spring keeps the same force as it moves, which is different from most other spring types. The material, thickness, and coil diameter all affect how the spring works and how long it lasts.
Function
You use constant force springs when you need a steady force over a long distance. These springs give you a consistent push or pull, no matter how far you extend them. This makes them perfect for jobs where you need smooth, even movement. They can store power for a long time when stretched out. You can count on them for high force output in a small space and for a long reach without the force getting stronger as you pull.
Tip: Constant force springs can last from 2,500 cycles to over 1 million cycles. The lifespan depends on how you use them, the material thickness, coil size, and the environment.
Applications
You find constant force springs in many industries. In the medical field, they help with precise movements in devices like glucose monitors and wearable sensors. These springs make sure sensors stay in the right spot and help patients feel comfortable. You also see them in tape measures, window counterbalances, and point-of-sale machines.
- Provide steady torque in medical devices such as glucose monitors.
- Used in wearable sensors and advanced diagnostic tools.
- Offer high force in small spaces and allow for long, smooth movement.
- Store power for long periods when extended.
Leaf Springs
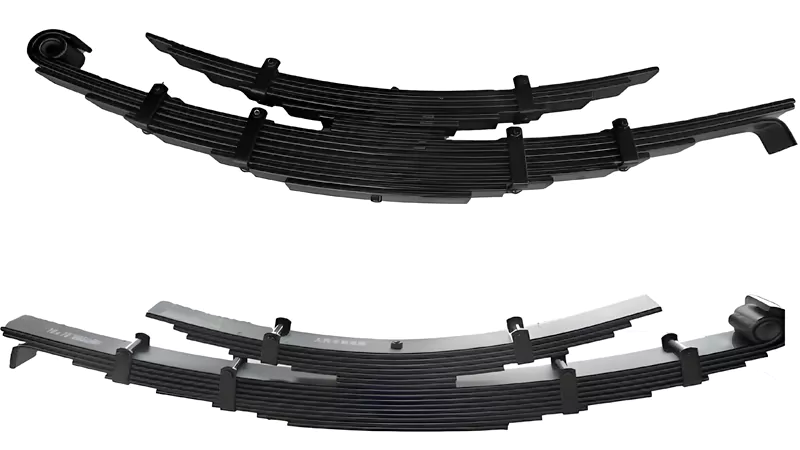

Structure
Leaf springs are long, flat pieces of metal stacked on top of each other. You often see them as curved strips, joined in the middle and spreading out at the ends. The shape and number of leaves decide how much weight the spring can hold. The design lets the spring bend and flex while supporting heavy loads.
Function
You use leaf springs to support weight and absorb shocks. When your vehicle goes over a bump, the leaf spring bends and stores energy. It then releases this energy slowly, making the ride smoother. Leaf springs help keep vehicles stable and safe by spreading out the force from the road.
- Leaf springs play a key role in suspension systems. They absorb impacts from bumps and dips, storing energy as potential energy.
- The stored energy is released gradually, which smooths out the ride and prevents damage to the vehicle.
Applications
You find leaf springs in trucks, trailers, and other heavy-duty vehicles. Their strong design lets them carry big loads without losing control or comfort. Leaf springs are popular in commercial vehicles because they last a long time and handle heavy weights well.
Leaf spring suspensions have a high load-bearing capacity, making them ideal for trucks and commercial vehicles. Their durability and strength help manage heavy loads while keeping the car stable.
Spiral Springs

Structure
Spiral springs are made from flat strips of metal wound tightly in a spiral shape. This design lets the spring store a lot of force in a small space. The flat strip construction sets spiral springs apart from other torsion-based springs, which usually use round wire.
| Feature | Spiral Springs | Other Torsion Springs |
|---|---|---|
| Construction | Flat strip wound in a spiral | Wire wound in a coil shape |
| Mechanical Property | High force in compact form | Withstand twisting forces |
| Applications | Tape measures, infusion pumps | Many mechanical devices |
Function
You use spiral springs to create a turning force, or torque, in a compact space. When you wind the spring, it stores energy. When you let go, the spring unwinds and releases the energy smoothly. This makes spiral springs great for devices that need controlled movement or precise timing.
Applications
You see spiral springs in many precision tools and devices. They are common in watches, clocks, and timing mechanisms. You also find them in sensors, measurement devices, and some automotive parts. Spiral springs help control torque and movement in tools that need accuracy.
- Used in watches and timing devices for accurate movement.
- Found in sensors and measurement tools.
- Used in automotive components and precision instruments that need controlled torque and displacement.
Belleville (Disk) Springs

Structure
Belleville springs are also called disk springs. They look like thin, cone-shaped washers. You can stack them in different ways to change their force. Their shape lets them fit a lot of force into a small space. You can use just one disk or stack more for extra strength or flexibility. Most are made from high-strength steel or stainless steel. This helps them handle heavy loads.
Function
Belleville springs get stiffer as you press them down. The force does not go up in a straight line. It rises quickly as you push the spring. This is called a progressive or non-linear spring rate. The design gives both axial and lateral stability. The spring stays in place even with heavy loads. You can change the force by adding or removing disks or changing how you stack them.
Belleville springs are great when you need to handle changing loads or keep a tight seal, even if temperature or pressure changes.
| Characteristic | Belleville Disc Springs | Wave Springs |
|---|---|---|
| Spring Rate | Progressive, non-linear increase in force | Linear, directly proportional to compression |
| Space Efficiency | Compact design suitable for limited spaces | Requires more space for the equivalent load |
| Stability | Offers axial and lateral stability | May need additional components for stability |
| Application Suitability | Ideal for dynamic loads and variable force needs | Versatile but less compact |
Applications
You find Belleville springs where you need to control force in a small area. They are common in high-pressure valve assemblies. In these valves, Belleville springs help ball valves open and close under high pressure. They stop the valve from getting stuck, which is important in nuclear plants and other critical places. You also see them in live loading for seals, like packing and gaskets, to stop leaks. The spring keeps a steady force on the seal, even if the temperature changes. This helps with thermal expansion and keeps things working safely.
- Belleville springs help with thermal expansion in high-temperature and high-pressure places.
- They give the first sealing force needed for valves to work under pressure.
- You also find them in clutches, brakes, and vibration dampers in heavy machines.
Gas Springs
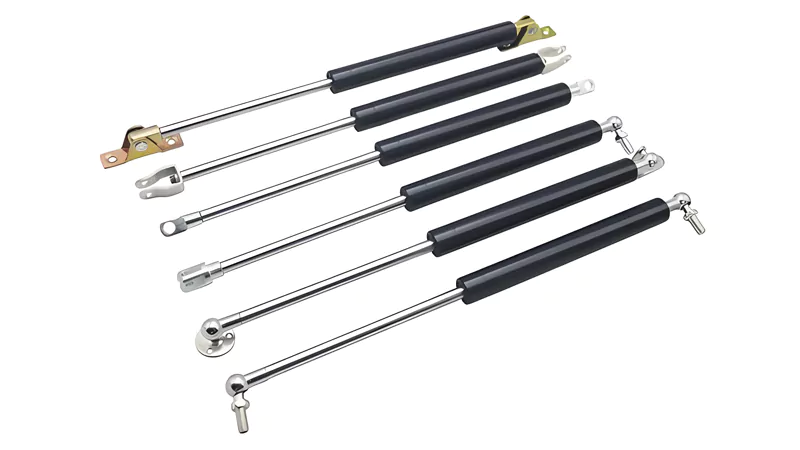

Structure
Gas springs have a cylinder filled with compressed gas, usually nitrogen. Inside, a piston moves back and forth. When you push the piston, the gas gets squeezed and stores energy. The cylinder seals keep the gas from leaking. This design gives smooth, controlled motion. Gas springs come in many sizes and force levels so that you can pick the right one for your job.
Function
You use gas springs for smooth, easy movement and adjustable force. When you press the piston, the gas compresses and pushes back with steady force. The action feels smooth because the gas absorbs shocks and slows movement. Gas springs do not bounce or jerk like some other springs. You can use them to lift, lower, or hold things in place. They work well when you want to control speed and force.
Gas springs are great for furniture and cars. They make seats and desks easy to adjust and help car trunks and hoods open smoothly.
Applications
You see gas springs in many everyday products. In high-end seats and adjustable desks, gas springs let you change the height easily. This helps you keep good posture and reduces strain on your back, neck, and shoulders. In office chairs, gas lift springs give you smooth height changes. In cars, gas springs support hatchbacks and hoods. Most hatchback gas springs have a pressure rating of about 250N (56 pounds of force). This gives just the right lift and keeps the trunk or hood from slamming shut. Gas springs also work in medical beds, windows, and industrial machines.
- Gas springs give smooth action and pull back easily into the cylinder.
- They are used in high-end furniture for comfort and easy use.
- In car hatchbacks, a 250N gas spring makes opening and closing safe and controlled.
Wave Springs
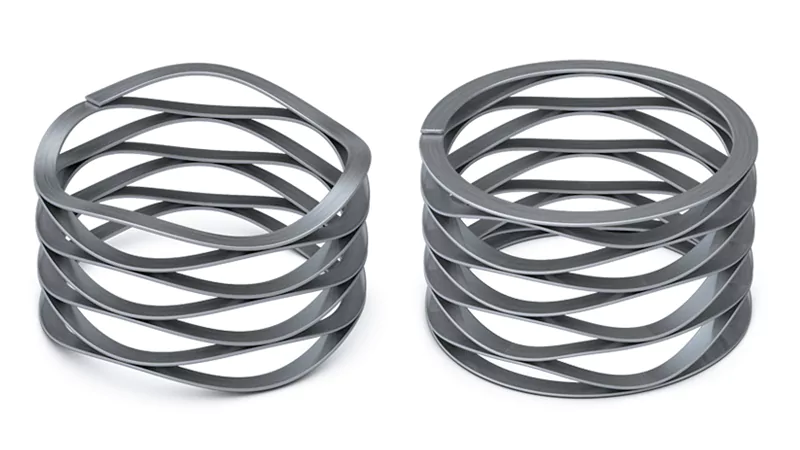

Structure
Wave springs are made from flat wire shaped into a wave pattern. The waves run along the coil, making a spring that can compress and expand. This design lets the spring fit into tight spaces. Wave springs are much shorter than regular coil springs for the same force. You can use single-turn or multi-turn wave springs, depending on how much force you need.
Function
You use wave springs to save space but still get a strong force. The spring compresses in a straight line, so the force goes up evenly as you press it. Wave springs do not twist or make side loads, so they last longer and wear less. You can replace several coil springs with one wave spring to save even more space. The design works well in both still and moving parts.
| Spring Type | Work Height in Static Applications | Work Height in Dynamic Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Wave Springs | Half of the coil springs | One third of coil springs |
| Coil Springs | Standard height | Standard height |
Applications
You find wave springs in electronics, cars, and industrial equipment. In electronics, wave springs load sealing plates in pressure relief valves, help with fluid sealing in face seals, and adjust force in clutch drives. They also give the right force in bayonet connectors and low voltage connectors, making sure connections stay tight in small spaces. Wave springs are popular in small mechanical parts because they save space and work well.
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Pressure Relief Valve | Loads a sealing plate, letting air out when pressure is high. |
| Face Seal | Works with graphite to give the right load for fluid sealing. |
| Clutch Drive | Adjusts force in tight spaces. |
| Bayonet Connector | Gives the needed force for electronic connector assembly. |
| Low Voltage Connector | Provides preload and boosts load performance in small spaces. |
Wave springs help you design smaller, lighter products without losing strength or reliability.
Double Torsion Springs
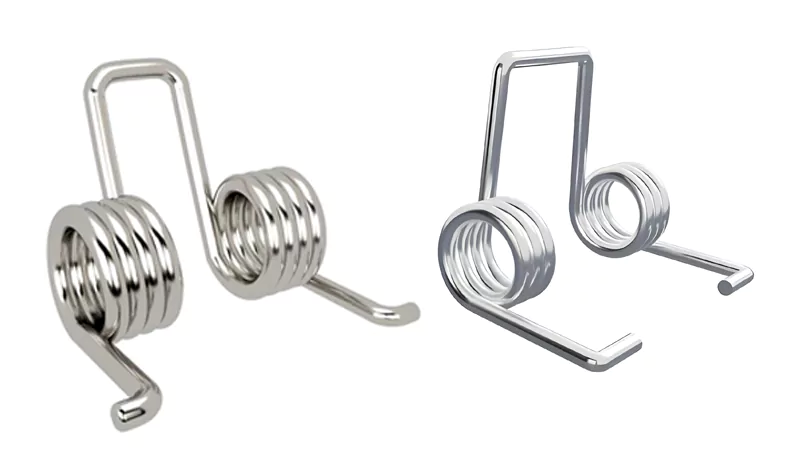

Structure
Double torsion springs have two coils that twist in opposite ways. These coils are joined in the middle by a straight part. Both coils work together to make more force. The ends, called legs, stick out and connect to other parts. When you twist both legs, the coils hold energy. This design makes the spring strong and steady. The double coils help the spring take more force without bending or snapping. Most double torsion springs are made from tough metals like stainless steel or music wire.
Function
You use double torsion springs when you need a twisting force in two ways. The spring holds energy as you twist both ends. When you let go, it goes back to its shape and gives back the energy. This makes torque, which is a turning force. Double torsion springs give more torque than single ones. They also stay steady and do not bend out of shape. This makes them good for jobs that need a strong and steady force.
Double torsion springs are great when you need force in two ways or extra steadiness. They help parts move safely and smoothly.
Here are some main benefits of double torsion springs in machines:
- They give higher torque, so they can handle stronger turning.
- Their design makes them more stable, so they do not bend or lose shape.
- You can use them in many places that need a strong and steady force, like car door hinges or machine switches.
Applications
You see double torsion springs in lots of machines and tools. They are used in things that need to move or hold parts with a strong, even force. For example, you find them in:
- Hinges for car doors and heavy covers
- Counterbalance systems in big machines
- Levers and switches that must return to a set spot
The table below shows how double torsion springs and single torsion springs are different in machines:
| Feature | Double Torsion Springs | Single Torsion Springs |
|---|---|---|
| Torque Direction | Gives force in two opposite ways | Gives force in one way |
| Design Complexity | More complex because of two coils | Simpler with just one coil |
| Load Capacity | Can take more weight | Usually takes less weight |
| Lifespan | May last longer with high torque | Shorter with lower torque |
| Applications | Hinges, counterbalances, levers | Used for force in one direction |
If you need a spring for heavy loads, long life, and force in two ways, double torsion springs are a good pick. Their design helps your machines work safely and well.
Spring Types and Machining
Role of Machining in Spring Manufacturing
Machining is very important when making springs. It helps make springs that fit what you need. Companies like AFI Industrial Co., Ltd use special machines for this. These machines help each spring meet strict rules. You can trust these steps to make springs that work well and last longer.
Here are some main machining steps used for making springs:
| Machining Process | Description |
|---|---|
| CNC Coiling | Computer machines shape springs very accurately. |
| Heat Treatment | Makes springs strong and keeps their shape. |
| Grinding | Makes the ends flat and stable for use. |
| Quality Control Testing | Checks springs at every step to meet all needs. |
After coiling, springs get heat treatment. This step makes the inside strong and less stressed. Next, grinding makes the ends flat and ready to use. Quality control testing happens all the time. Springs go through visual checks, size checks, and load tests. This makes sure each spring matches your design and works right.
Benefits of Precision Machining for Spring Types
Precision machining gives many good things for custom springs. You get springs with the right shape, size, and strength. CNC machines let you control the pitch, diameter, and shape. This means your springs will fit your products perfectly.
- CNC machines let you control every coil exactly.
- Inspection tools like testers and calipers are checked each spring for accuracy.
You also get more choices for materials. Machining works with metals like stainless steel, music wire, and phosphor bronze. You can pick the best metal for your job, whether you need strength, flexibility, or rust resistance.
Quality control is another big plus. You can expect:
- Visual checks for surface problems.
- Size checks for accuracy.
- Load tests to see if springs work under stress.
When you pick precision machining, you get springs that are safe, strong, and last a long time. AFI Industrial Co., Ltd uses these smart methods to make custom springs for many industries. You can trust their skill to help your products work better and meet high standards.
Comparison Table
Spring Types, Functions, and Applications
This table helps you compare the 10 most common spring types. It shows what each spring does best and where you might see it. This makes it easier to pick the right spring for your project.
| Spring Type | Main Function | Typical Applications | Load Capacity | Fatigue Resistance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compression Spring | Pushes back when pressed | Car suspension, pens, mattresses | Medium–High | High |
| Extension Spring | Pulls back when stretched | Garage doors, trampolines, seat adjusters | Medium | Medium–High |
| Torsion Spring | Provides twisting force (torque) | Door hinges, laptop hinges, levers | Medium | High |
| Constant Force Spring | Delivers steady force over distance | Tape measures, medical devices, sensors | Low–Medium | Very High |
| Leaf Spring | Supports heavy loads, absorbs shock | Truck suspensions, trailers, and rail cars | High | Medium |
| Spiral Spring | Stores and releases rotational energy | Clocks, timers, measuring tapes | Low–Medium | Medium |
| Belleville (Disk) Spring | Handles high loads in a small space | Valves, clutches, vibration dampers | Very High | High |
| Gas Spring | Smooth, controlled lifting/lowering | Office chairs, car hoods, medical beds | Medium | High |
| Wave Spring | Saves space, provides even force | Electronics, connectors, pressure valves | Medium | High |
| Double Torsion Spring | Provides torque in two directions | Heavy covers, counterbalances, levers | High | High |
Tip: If you need to lift heavy things, try Belleville (disk) springs or leaf springs. If you want a spring that gives steady force, constant force springs are a good choice.
You can see how each spring type is different for load and how long it lasts. Fatigue resistance means how many times a spring can work before it breaks. Shot peening makes the spring’s surface stronger, so it lasts longer.
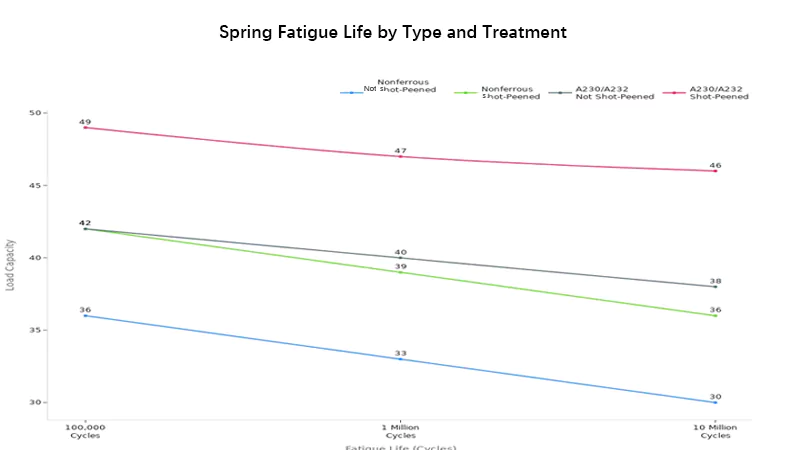
- Disc springs (Belleville) hold a lot of weight in a small space. You often find them in big machines.
- Leaf springs help trucks and trains carry heavy loads and handle bumps.
- Helical springs, like compression, extension, and torsion springs, are used a lot. Each one is made for a special job, like pushing, pulling, or twisting.
How long a spring lasts depends on what it’s made of and how it is treated. For example, shot-peened springs can work much longer than springs that are not treated. If you want your spring to last a long time, pick the right material and finish.
Remember, choosing the right spring type helps your product work better and last longer.
When you pick a spring, it affects how your product works. You should think about its shape, what it does, and where you will use it. The materials used are important for stopping shaking and absorbing shocks. Some springs, like disk springs, need special materials to handle shaking and changes in temperature. Choosing the right spring type, such as ones from AFI Industrial Co., Ltd, makes things safer and more dependable. You get better results if you match the material to your needs. Ask an expert for help or tell us what you think below.
FAQ
You will find compression springs in many products. They push back when pressed. You see them in pens, cars, and machines.
Think about the load, space, and movement you need. Check the spring’s function and material. Ask an expert if you are not sure.
Yes! You can choose from stainless steel, music wire, phosphor bronze, and more. The material changes how strong and flexible the spring is.
Fatigue means how many times a spring can work before it breaks. If you want your spring to last, pick one with high fatigue resistance.
Precision machining gives you springs that fit exactly. You get better performance, longer life, and safer products.
You use gas springs in office chairs, car hoods, and adjustable desks. They help lift and lower things smoothly.
If your spring faces heavy loads, high temperatures, or lots of movement, you may need special treatments like shot peening or coating. This helps your spring last longer.


