When you consider titanium vs aluminum, titanium is stronger and lasts longer, while aluminum is lighter than titanium. These factors are crucial when selecting materials for planes, medical tools, or buildings. It’s important to evaluate price, strength, and longevity. The table below illustrates how these metals compare in the context of titanium vs aluminum:
| Property | Titanium | Aluminum |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | 240–550 MPa | 110–700 MPa |
| Density | 4.51 g/cm³ | 2.70 g/cm³ |
| Durability | Highly durable | Less durable |
| Cost | More expensive | More affordable |
Choose the metal that best meets your needs. Aim to balance performance and cost effectively.
Key Takeaways
- Titanium is stronger and lasts longer than aluminum. This makes it good for hard jobs like in planes and medical tools. Aluminum is lighter and easier to shape. This makes it cheaper for things we use every day. Think about the environment. Titanium does not rust as fast as aluminum. This is true in tough places like near the ocean. If you need to save money, aluminum costs less than titanium. It works well for jobs that do not need a lot of strength. Look at the strength-to-weight ratio. Titanium is very strong and you need less of it. Aluminum is light but not as strong. If you need something to last a long time and work very well, pick titanium. It costs more but is worth it for these jobs. Aluminum is easy to find and simple to use. This is why people use it a lot in building and cars. Always pick the right material for your project. Think about strength, weight, price, and where you will use it.
Table of Contents
Comparative Analysis of Titanium vs Aluminum
Key Differences
When you look at titanium vs aluminum, you find big differences. Titanium is very strong and does not rust easily. Aluminum is much lighter and simple to shape. The table below shows the main titanium properties and aluminum properties:
| Property | Titanium | Aluminum |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 4.5 g/cm³ | 2.7 g/cm³ |
| Tensile Strength | 230–1400 MPa | 90–690 MPa |
| Yield Strength | 230–1400 MPa | 7–600 MPa |
| Melting Point | 1668 °C | 660 °C |
| Strength-to-Weight Ratio | Higher than aluminum | Lower than titanium |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent (stable oxide layer) | Good, less effective in harsh environments |
| Durability | Excellent | Lower than titanium |
| Machinability | Challenging | Excellent |
| Cost | $10–$15 per pound | $1–$1.50 per pound |
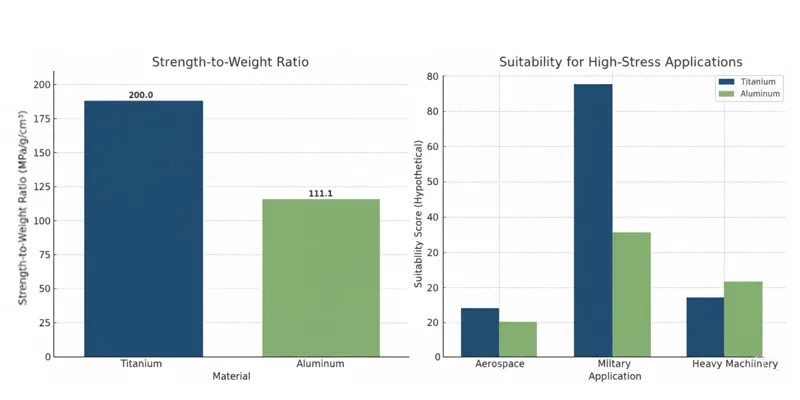
Titanium has a higher strength-to-weight ratio than aluminum. You need less titanium to get the same strength as more aluminum. Titanium properties include a high melting point and strong resistance to rust. Aluminum properties are low weight, good for carrying electricity, and easy to cut or shape.
Titanium is better for jobs that need high strength and durability because it has a higher strength-to-weight ratio than aluminum.
Strength, Weight, Durability Overview
You might ask which metal is stronger, lighter, or lasts longer. The answer depends on what you need. The latest facts help you compare:
- Strength: Titanium is stronger than aluminum. Its tensile strength goes from 230 MPa up to 1400 MPa. Aluminum ranges from 90 MPa to 690 MPa. You get more strength from titanium for tough jobs.
- Weight: Aluminum is lighter than titanium. Its density is 2.7 g/cm³. Titanium is 4.5 g/cm³. If you want less weight, pick aluminum.
- Durability: Titanium lasts longer and fights rust better than aluminum. It works well in rough or wet places. Titanium needs less fixing over time.
Here are the main ideas:
- Titanium gives you more strength and lasts longer.
- Aluminum is lighter and easier to work with.
- Titanium costs a lot more than aluminum, so you must think about price and performance.
If you need a metal for tough, long-lasting parts, choose titanium. If you want something light and cheap, use aluminum. Comparing titanium vs aluminum helps you pick the best material for your project.
Strength Comparison
Titanium Strength
Yield Strength
Titanium has a high yield strength. It can hold heavy loads before bending. Engineers use titanium in jet engines. It keeps its shape under strong pressure. Most titanium alloys, like Ti-6Al-4V, have yield strengths from 800 MPa to 950 MPa. Titanium is chosen for parts that must not break, even under stress.
Tensile Strength
Tensile strength shows how much force a material can take before breaking. Titanium has great tensile strength, especially with alloys. Ti-6Al-4V can reach up to 1,100 MPa. Pure titanium, called Grade 2, has a range of 340–410 MPa. Titanium is used in race car frames and bike parts. It does not break easily when pulled.
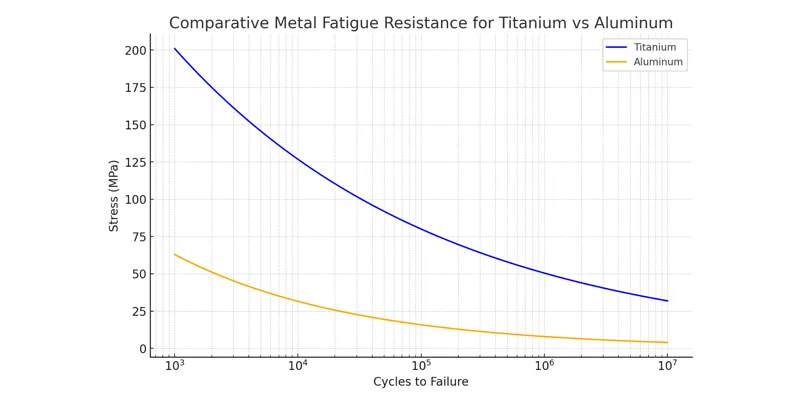
Fatigue Resistance
Fatigue resistance means how well a metal handles repeated stress. Titanium does very well here. It stays strong after many cycles of loading and unloading. This makes titanium good for airplane landing gear and medical implants. Titanium lasts longer in tough places.
Aluminum Strength
Yield Strength
Aluminum has lower yield strength than titanium. It still works well in many industries. Common aluminum alloys, like 6061 and 7075, have yield strengths from 240 MPa to 500 MPa. Aluminum is used in car frames and sports gear. It gives enough strength for daily use and keeps weight low.
Tensile Strength
Tensile strength in aluminum depends on the alloy. 7075 aluminum can reach up to 570 MPa. 6061 aluminum ranges from 310 to 350 MPa. Aluminum is not as strong as titanium. It is chosen when weight matters more than strength. Aluminum is found in airplane wings, bike frames, and baseball bats.
Fatigue Resistance
Aluminum has moderate fatigue resistance. It can handle repeated stress, but not as well as titanium. Over time, aluminum may crack if it vibrates or bends a lot. Use aluminum where loads stay steady or parts are easy to replace.
Difference Between Titanium and Aluminum in Strength
There are clear differences between titanium and aluminum:
- Titanium has a much higher strength-to-weight ratio. It is perfect for planes where weight matters.
- Aluminum is light and cheaper, but not as strong as titanium.
- Titanium alloys like Ti-6Al-4V reach up to 1,100 MPa. The strongest aluminum alloys, like 7075, reach about 570 MPa.
- In sports, titanium frames are strong and light. Aluminum frames are cheaper.
- Car makers use titanium for engine parts. Aluminum is used for body panels and wheels.
| Material | Tensile Strength (MPa) |
|---|---|
| 6061 Aluminum | 310–350 |
| 7075 Aluminum | 560–570 |
| 5052 Aluminum | 230–260 |
| 2024 Aluminum | 430–500 |
| Ti-6Al-4V (Grade 5 Titanium) | 900–1100 |
| Grade 2 Titanium (Pure Ti) | 340–410 |
| Ti-3Al-2.5V (Grade 9 Titanium) | 620–700 |
| Ti-6Al-2Sn-4Zr-6Mo | 1050–1200 |
Note: Titanium alloys have much higher tensile strength than aluminum alloys. Titanium is better for parts that need to handle heavy loads or tough conditions.
Alloying helps both metals get stronger:
- Alloying elements make titanium and aluminum stronger.
- Titanium alloys like Ti-6Al-0.3O can reach 1.26 GPa and stay flexible.
- Aluminum alloys like 7075-T6 can reach about 572 MPa.
- Adding titanium to aluminum-lithium alloys makes them almost 46% harder. Alloying can help close the strength gap and give more choices.
Pick titanium when you need the most strength and durability. Aluminum is best when you want to save weight and money. Both metals have special benefits, but titanium is the strongest for tough jobs.
Weight and Density
Titanium Density
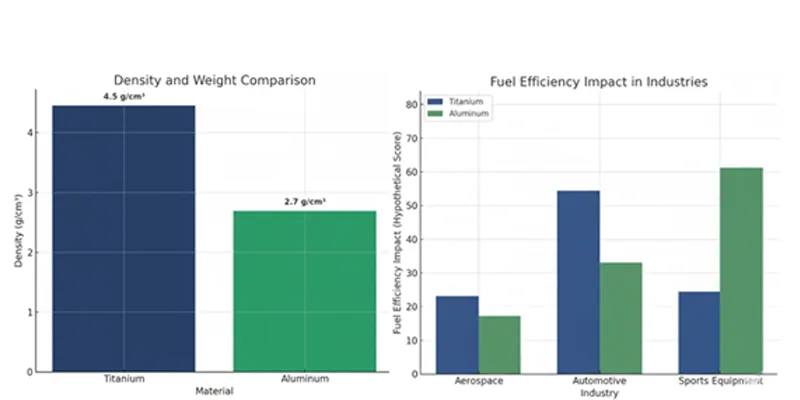
Titanium has a density of 4.5 g/cm³. This is higher than many other metals. Titanium feels solid and strong. It does not bend or break easily. The high density helps titanium fight rust. This is good for tough places. In aerospace, titanium’s density helps make strong parts. You see titanium in jet engines and spacecraft. These places need both strength and low weight.
| Metal | Density (g/cm³) |
|---|---|
| Titanium | 4.5 |
Aluminum Density
Aluminum is known for its low density. It is only 2.7 g/cm³. Aluminum is much lighter than titanium. This makes aluminum great for saving weight. You find aluminum in cars, planes, and soda cans. Aluminum’s light weight makes parts easy to move. When you compare aluminum to titanium, you save a lot of weight. This is why aluminum is used to save fuel and energy.
| Metal | Density (g/cm³) |
|---|---|
| Aluminum | 2.7 |
High Strength-to-Weight Ratio
You should look at the strength-to-weight ratio. This shows how strong a metal is for its weight. Titanium has a high strength-to-weight ratio. You can use less titanium for the same strength. Even though titanium is heavier, it can make lighter parts. In planes, titanium builds strong, thin frames. In bikes, titanium makes frames strong and light. This helps bikes go faster and be easier to ride.
| Material | Tensile Strength (ksi) | Density (lb/in³) | Strength-to-Weight Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| Titanium | 140 | 0.16 | 0.875 |
| Aluminum | — | 0.1 | — |
Tip: Pick materials with a high strength-to-weight ratio for best weight savings. Titanium is great for tough jobs that need this.
Remember, choosing between titanium and aluminum depends on your needs. Aluminum is light and saves weight. Titanium’s strength-to-weight ratio can make designs even lighter when you need strong parts. Both metals help cut weight, but titanium is better for high performance and lasting strength.
Titanium vs Aluminum in Lightweight Design
When you make something for good performance, you need to think about strength and weight. Titanium and aluminum both have special benefits for lightweight design. Titanium feels heavier than aluminum. Titanium is about two-thirds denser than aluminum. This means titanium weighs more for the same size. But you should not only look at density when picking a material for light structures.
Titanium is great because it has a high strength-to-weight ratio. This lets you use less titanium and still get strong parts. You can make thinner pieces with titanium. These pieces stay in shape and do not bend, even with heavy loads. Sometimes, titanium parts are lighter than aluminum ones, even though titanium is denser.
You see this in real life. Airplane engineers pick titanium for important parts. They want to make planes lighter but still safe and strong. Using titanium, they make thinner wings, landing gear, and fasteners. These parts handle stress but do not add much weight. The plane uses less fuel and can carry more people or cargo.
Bike makers use titanium for top frames. Riders want bikes that are light and strong for hard rides. Titanium frames use less material than aluminum frames. The high strength-to-weight ratio helps the bike feel light and last long. You get a smooth ride and a frame that does not dent or crack.
Here is how titanium helps with lightweight design:
- You can use thinner titanium and still keep strength.
- Titanium parts can weigh less than aluminum parts for the same job.
- The high strength-to-weight ratio means you do not need extra material for safety.
- Both airplane and bike frames get lighter and stronger.
Tip: If you want to make things lighter but keep them strong, titanium gives you more choices. You can build products that are light, strong, and last a long time.
Picking titanium or aluminum depends on what you want. If you want the lightest weight and easy shaping, aluminum is a good choice. If you need the best mix of weight and strength, titanium is better, especially for planes and bikes.
Durability
Corrosion Resistance
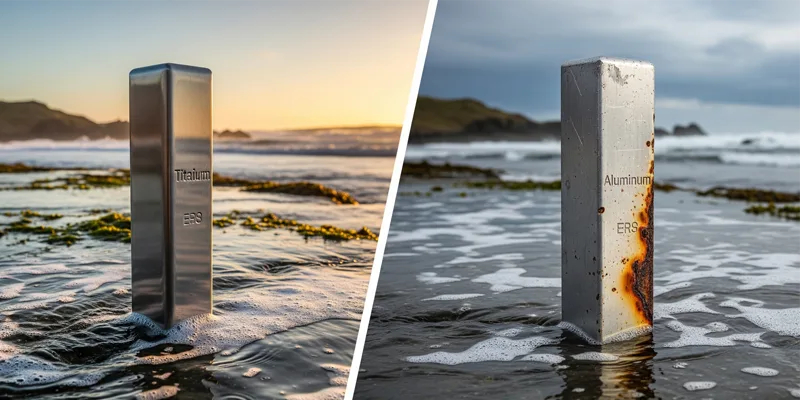

If you need a metal for tough places, corrosion resistance is very important. Titanium is special because it makes a strong oxide layer on its surface. This layer keeps it safe from rust and chemicals. You can see this in the ocean and in hospitals. In saltwater, titanium stays strong and does not change shape for a long time. Aluminum also fights rust, but it is not as good as titanium in hard situations.
Let’s check a recent test with titanium and aluminum in saltwater. The table below shows how much weight each metal lost after the test:
| Material | Initial Weight (g) | Final Weight (g) | Weight Loss (g) | Weight Loss (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ti-6Al-4V | 6.6471 | 6.6470 | 0.0001 | 0.0015% |
| AA 2024-T3 | 3.6921 | 3.6879 | 0.0042 | 0.1138% |
You can see titanium lost almost no weight, but aluminum lost more. This shows titanium is better at fighting rust. In the body, titanium stays clean and safe for medical use. Aluminum can rust faster, especially with salt or chemicals. If you need a metal for wet or salty places, titanium is the best pick.
Wear Resistance
Wear resistance means how well a metal handles rubbing or scratching. Titanium is very good at this. Its hard surface and oxide layer help it last in tough jobs. You find titanium in jet engines and doctor tools because it works well for many years.
Aluminum is okay at wear resistance, but it does not last as long as titanium in rough places. It can wear out faster if there is a lot of rubbing or dirt. Some coatings can help aluminum, but titanium is still stronger for lasting a long time.
- Titanium: Very good at stopping wear, strong oxide layer, great for hard jobs.
- Aluminum: Okay at stopping wear, can wear out faster, sometimes helped by coatings.
If you want a metal that keeps its shape and looks good for a long time, titanium is a better choice.
Longevity
Longevity means how long a metal lasts before you need to fix or change it. Titanium is best here because it fights rust and wear so well. You can use titanium in the sea, in hospitals, or in factories and it will last for many years. It needs less fixing and fewer changes.
Aluminum also lasts a long time, mostly in dry or easy places. But in hard or rough spots, you may need to check and change aluminum parts more often. If you want something that lasts the longest and needs the least work, titanium is the top choice.
Tip: If you want your project to last a long time and need little fixing, pick titanium instead of aluminum.
Titanium vs Aluminum in Harsh Environments
When you pick a metal for tough places, you must think about how it handles stress, wetness, and chemicals. Both titanium and aluminum are used in many jobs, but they act differently when things get hard. You see them in the ocean, factories, and hospitals.
Titanium stands out in tough conditions. It makes a shield called an oxide layer. This shield stops water and salt from hurting the metal. Titanium does not rust or break down in saltwater. That is why people use titanium for ship parts, oil rigs, and medical implants. These jobs need metals that stay strong for a long time.
Aluminum fights rust too, but not as well as titanium. Saltwater can make aluminum rust faster. You see aluminum in boat bodies and outdoor buildings. But aluminum needs special coatings to last as long as titanium.
Here’s a quick comparison:
| Environment | Titanium Performance | Aluminum Performance |
|---|---|---|
| Marine | Excellent corrosion resistance; minimal maintenance | Good, but needs coatings; higher risk of corrosion |
| Medical | Biocompatible; resists body fluids | Used in some devices; less durable in body |
| Industrial | Handles chemicals and heat well | Performs well, but can degrade faster |
Tip: If you work near the sea or with chemicals, titanium is a safe pick. It keeps its strength and shape for many years.
You should also think about how much care each metal needs. Titanium parts do not rust much, so you do not need to fix them often. They are trusted for important jobs. Aluminum parts work well in easy places, but you must check them more for rust or damage.
For best results, do these things to keep both metals working well:
- Regular Inspection: Look for rust, damage, or loose parts. Make sure everything is tight and smooth.
- Proper Cleaning: Wash with gentle soap and a soft brush. Do not use strong chemicals or rough tools.
- Environmental Adjustments: Change your cleaning routine for salty or wet places. Rinse off salt and check more often.
Titanium is strong and lasts a long time in hard places. You spend less time fixing it and it works for many years. Aluminum is lighter and costs less, but you must protect it and check it more. When you pick between titanium and aluminum, think about where you will use it and how much work you want to do to keep it safe.
Cost and Manufacturability
Material Cost

Titanium and aluminum have very different prices. Titanium is much more expensive than aluminum. The price changes based on grade and purity.
- Commercially Pure Titanium (Grade 1 & 2): $6–$10 per pound
- Titanium 6-4 Alloy (Grade 5): $15–$30 per pound
- Aluminum: $1–$3 per pound, depending on grade and purity
Aluminum is a cheaper choice for many projects. You can use aluminum if you do not need super high strength. Titanium is picked for jobs that need top performance. You see titanium in planes, hospitals, and boats. It is strong, fights rust, and has a good strength-to-weight ratio. Titanium costs more, so people use it only when they need these special features.
💡 Tip: If you want to spend less and do not need the most strength, aluminum is usually the best pick.
Processing
Titanium and aluminum are made in different ways. Aluminum is much easier to cut and shape. Titanium is harder to work with and needs special tools. You must go slow with titanium because it gets hard fast.
| Aspect | Titanium | Aluminum |
|---|---|---|
| Machining Speed | Needs slow speeds, which takes more time and money | Can be cut faster and costs less |
| Tool Wear | Wears out tools faster, so you change them more | Tools last longer, so it costs less |
| Post-Processing | Often needs extra steps like heat treatment | Usually needs less extra work |
Working with titanium costs more. Cutting takes longer and tools break faster. You may need to do more steps, like heat treatment, to get it just right. Aluminum is easy and quick to cut. You save time and money on tools and extra steps.
- Titanium costs more to buy and make.
- You must cut titanium slowly.
- Tools break faster with titanium.
- Aluminum is fast and does not wear out tools as much.
Availability
Think about how easy it is to get each metal. Aluminum is easy to find almost everywhere. It comes in many types and shapes. Titanium is harder to find and comes from fewer places.
- Both metals now have better supply chains. Mining, making, and engineering companies work together to meet needs.
- Problems like crowded ports or high energy prices can slow shipping and cause shortages.
- Rules and politics in different countries change where you can buy titanium and aluminum.
- Places with lots of resources and big buyers affect trade and supply.
- Other suppliers help recycle and keep materials moving.
You might wait longer or pay more for titanium if there are supply problems. Aluminum prices and supply usually stay steady. Always check the market and supply before you start your project with either metal.
Titanium vs Aluminum in Production
When picking a metal for making things, you need to think about more than just strength and weight. Titanium and aluminum act very differently when you make products. Each metal has its own problems and good points.
Pricing factors are important when you decide. Titanium costs more because it is harder to get and needs special steps to make. Aluminum is easier to find and make, so it costs less. The table below shows the main pricing differences:
| Material | Pricing Factors |
|---|---|
| Titanium | More expensive due to complex extraction and processing methods; subject to supply chain disruptions. |
| Aluminum | More readily available and easier to machine, resulting in lower production costs. |
You should also think about how easy it is to shape each metal. Titanium needs workers with special skills and tools. You have to go slow and change tools often. This makes titanium harder to work with and causes more waste. Aluminum is much easier to cut and shape. You can work faster and your tools last longer. This saves time and money.
- Titanium needs skilled workers and special ways to cut.
- Aluminum is easier to shape and does not wear out tools as fast.
When using CNC machines, titanium can make more leftover pieces and waste. Titanium is tough, so it is hard to shape and you lose more metal. Aluminum is easy to shape, so you finish faster and waste less.
- Titanium makes more scrap and waste when using CNC machines.
- Aluminum is easy to shape, so you save time and tools.
Problems with getting metals can change your choice. Titanium’s price goes up if mining slows or if world events stop supply. You might wait longer or pay more if there are problems. Aluminum is easier to find and buy. It comes in many types and you do not often run out.
Titanium costs more because of these risks. You pay extra for the metal and for the work to shape it. Aluminum is cheaper and easier to use, so people pick it for making lots of products.
Tip: Always think about cost and what you need. Aluminum is a good choice for saving money. Titanium costs more but gives you great strength and lasts a long time for important parts.
Application Suitability
Aerospace
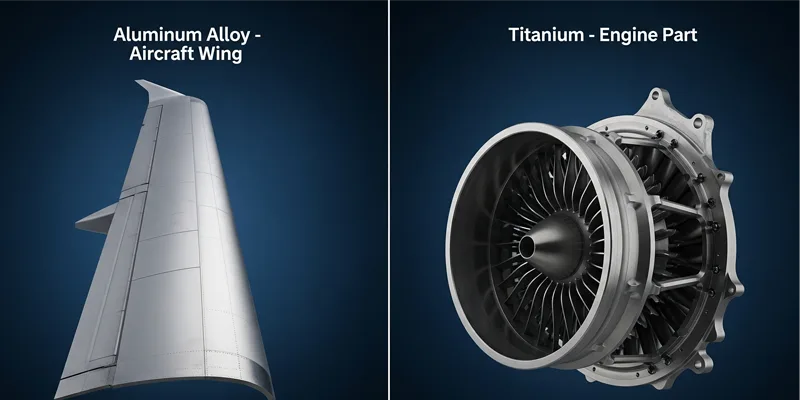

Titanium and aluminum are used in airplanes. Both metals help make planes lighter and safer. Titanium is very strong for its weight. It is found in landing gear and engine parts. Titanium does not rust or get damaged by heat. This means it lasts longer and needs less fixing. It is great for jet engines and tough jobs.
Aluminum is also important for planes. It is used for wings and the main body. Aluminum is light and strong enough for many uses. It is easy to shape and costs less than titanium. You can make many different parts with aluminum. Aluminum gets a layer that helps stop rust, especially when treated.
Here is a simple comparison of their uses in planes:
| Property | Titanium | Aluminum |
|---|---|---|
| Strength-to-Weight Ratio | Great for strong, light parts | Good for light structures |
| Corrosion Resistance | Very good, even in tough places | Good, better with treatments |
| High-Temperature Use | Works for hot engine parts | Only for cooler areas |
| Typical Applications | Landing gear, engine parts, tough spots | Wings, main body, inside panels |
Tip: Pick titanium for parts that face heat and stress. Use aluminum for big, light parts.
Automotive
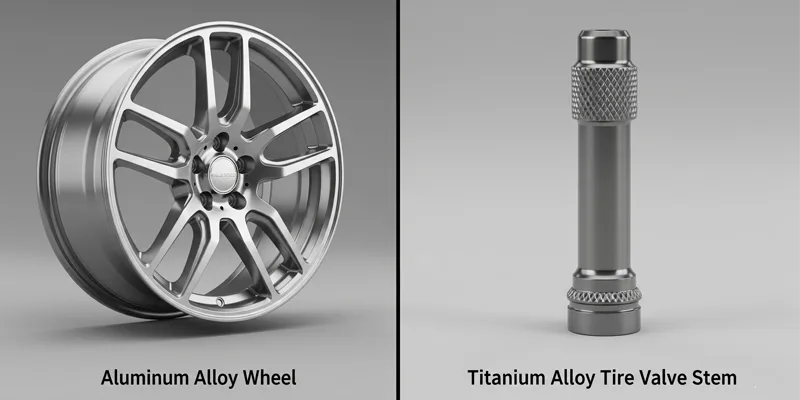

Titanium and aluminum are used in cars. Aluminum is common in car bodies and frames. It keeps cars light and saves fuel. Aluminum is easy to cut and shape. This makes it good for making lots of cars. Aluminum costs less, so car makers like it.
Titanium is used in special car parts. You see it in springs, exhausts, and valves. Titanium is strong and light, so it helps cars go faster. It also does not wear out quickly. This is good for race cars and sports cars. Titanium can handle heat and tough driving.
Titanium and aluminum help cars in different ways. Titanium makes cars faster and last longer. Aluminum keeps cars cheap and light for daily driving.
- Aluminum: Best for car bodies, frames, and wheels because it is light and cheap.
- Titanium: Best for strong, hot parts in race and sports cars.
Sports
Titanium and aluminum are used in sports gear. Both metals make equipment lighter and stronger. Titanium is used for bike frames, golf clubs, and rackets. It is strong, light, and lasts a long time. Titanium does not rust, so gear stays good in wet places. But titanium costs more and is harder to shape.
Aluminum is also used for sports gear. You see it in bats, bike frames, and climbing tools. Aluminum is cheap, light, and easy to shape. You get good gear for less money. But aluminum is not as strong as titanium. It can rust in tough places.
Here is a table to compare:
| Material | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Titanium | Strong, light, does not rust, lasts long | Costs more, needs special tools |
| Aluminum | Cheap, light, easy to shape | Not as strong, can rust in tough places |
Note: Pick titanium for the best and longest-lasting gear. Choose aluminum for cheap, light gear.
Medical
When picking materials for medical devices, you need to think about how the body reacts and how long they last. Titanium is the best choice for implants and surgical tools. It makes a special oxide layer that protects it inside the body. This layer keeps titanium safe from chemical changes. The body accepts titanium easily. It does not cause problems. Titanium does not rust or break down over time.
Aluminum does not work as well in the body. It can rust and is not as safe for implants. You might see aluminum in some medical equipment cases. But it is not used for parts that stay inside the body for a long time.
Here is a quick comparison:
| Material | Biocompatibility | Durability and Corrosion Resistance | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Titanium | High | Exceptional corrosion resistance | Artificial joints, bone screws, dental implants |
| Aluminum | Limited | Susceptible to corrosion | Some sterilized medical equipment housings |
Tip: If you need something for implants or parts that stay in the body, titanium is safer and lasts longer.
Studies show titanium’s oxide film helps it stay safe in the body. This makes titanium the top pick for artificial joints, bone screws, and dental implants. You can trust titanium to last many years without causing harm or needing lots of repairs.
Electronics

You see titanium and aluminum in electronics, but they do different jobs. Aluminum is used because it carries electricity well and is light. You find aluminum in wires, heat sinks, and laptop or phone cases. Aluminum is easy to shape and helps cool devices.
Titanium is not as good at carrying electricity. But it is stronger and looks fancy. You see titanium in luxury watches, smartphone frames, and special laptop cases. Titanium does not rust and can handle heat. It is harder to cut and shape.
Here is a side-by-side comparison:
| Property | Titanium | Aluminum |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | 3.1% of copper’s | 64% of copper’s |
| Strength | Higher strength | Lower strength |
| Melting Point | Higher melting point | Lower melting point |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent corrosion resistance | Good corrosion resistance |
| Machinability | More difficult to machine | Easier to machine |
| Applications | Consumer electronics, premium look | Electrical wiring, heat sinks |
Note: Pick aluminum for parts that need to carry electricity or stay cool. Choose titanium for strong, stylish, and tough parts.
If you want a device that looks fancy and lasts long, titanium is a great pick. For most electronics, aluminum is best for cost, weight, and performance.
Construction
In building, you want materials that are strong, light, and last many years. Titanium and aluminum both have these qualities, but in different ways. Titanium gives you top strength and fights rust very well. You see titanium in big buildings, bridges, and places with harsh weather.
Aluminum is strong and even lighter than titanium. Builders use aluminum for window frames, roofs, and panels. It is easy to work with and keeps buildings light.
Here is a comparison table:
| Property | Titanium | Aluminum |
|---|---|---|
| Strength | Superior strength | Good strength |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent corrosion resistance | Good corrosion resistance |
| Weight | Lightweight yet robust | Lightweight |
| High-Temperature Tolerance | High-temperature tolerance | Moderate temperature tolerance |
| Applications | Aerospace, medical, marine | Construction, automotive, electronics |
- Titanium is best for places that need top strength and rust resistance.
- Aluminum works well when you want to save weight and money.
- Your choice depends on what your project needs, your budget, and the environment.
Tip: For buildings near the ocean or in tough weather, titanium lasts the longest. For most homes and offices, aluminum is strong and costs less.
Difference Between Titanium and Aluminum in Applications
When you pick between titanium and aluminum, think about your project needs. Titanium and aluminum are not the same. They have different strengths, weights, and how long they last. These differences make each metal good for certain jobs.
Titanium is used when you need strong and long-lasting parts. You see titanium in planes and hospitals. Titanium is great for aircraft frames and engine parts. It does not rust much and can hold heavy things. In hospitals, titanium is used for implants and tools. Titanium lasts many years inside the body or in tough places.
Aluminum is chosen when you want to save money and shape things easily. Aluminum is found in buildings, electronics, and everyday items. Aluminum makes window frames and roofs light and strong. Car panels and heat exchangers use aluminum too. Aluminum is easy to cut and shape, so it works for many products. Sports gear, bike frames, and furniture use aluminum because it is light and cheap.
Here is a simple table to help you choose:
| Industry | Best Metal | Why It Works Well |
|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Titanium | High strength, low weight, resists rust |
| Medical | Titanium | Safe for body, lasts long, does not corrode |
| Marine | Titanium | Handles saltwater, strong, durable |
| Automotive | Aluminum | Light, affordable, easy to shape |
| Construction | Aluminum | Cost-effective, light, simple to use |
| Consumer Goods | Aluminum | Cheap, light, easy to make |
| Electronics | Aluminum | Good for heat sinks, light, conducts electricity |
Tip: Pick titanium for hard jobs or tough places. Choose aluminum if you want to save money and build things fast.
Match the metal to what you need. Titanium is best when safety and strength are important. Aluminum helps you spend less and build things easily. Both metals have special uses. You get the best results when you pick the right one.
- Titanium Applications:
- Aircraft frames, engine parts, landing gears
- Medical implants, surgical tools, prosthetics
- Offshore rigs, ship components
- High-performance car parts
- Aluminum Applications:
- Window frames, roofing, building panels
- Car body panels, heat exchangers
- Bicycle frames, sports equipment, furniture
- Heat sinks, electronics enclosures
You make better choices when you know how titanium and aluminum work in each job. Think about what matters most—strength, weight, durability, or cost. This helps you pick the right metal every time.
Choosing Between Titanium and Aluminum
Decision Factors
When you pick titanium or aluminum, you need to think about a few things. Every project is different, so you should choose the metal that fits your needs. Here is a table to help you compare the main points:
| Decision Factor | Titanium | Aluminum |
|---|---|---|
| Strength | Extreme strength, good for tough jobs | Decent strength, works for cheaper projects |
| Cost | Costs more to buy and shape | Cheaper because it is easier to cut |
| Weight | Heavier but very strong for its size | Very light, great for saving weight |
| Corrosion Resistance | Fights rust very well, good for rough places | Fights rust okay in normal places |
| Thermal/Electrical Conductivity | Not great at carrying heat or electricity | Carries heat and electricity well |
| Machinability | Hard to cut, needs slow work | Easy to cut, can work fast |
| Application Suitability | Used in planes, medical tools, and sea parts | Used in cars and electronics |
Pick titanium if you need something super strong or that fights rust and heat. Jet engines and deep-sea tools use titanium a lot. Aluminum is better if you want something light and cheap. You see aluminum in phones and car bodies.
Tip: Always pick the metal that matches your project’s place, money, and what you need it to do.
Best Uses for Titanium
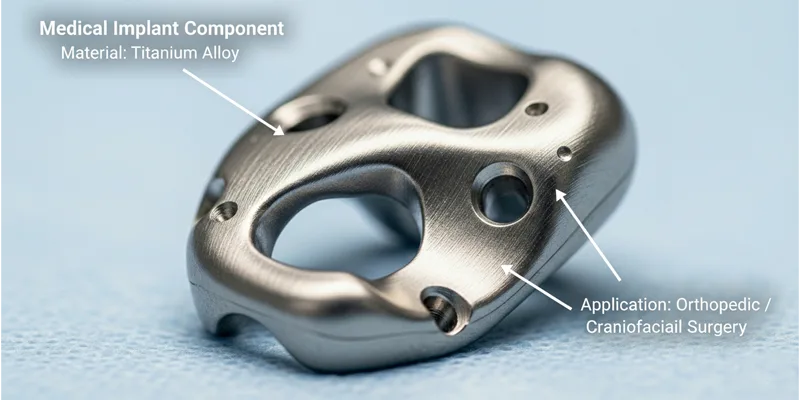
Titanium is used where things need to be strong and last long. You find it in planes, where it makes frames and engine parts. Titanium helps planes fly far and use less fuel. Doctors use titanium for implants and tools. It is safe for people and lasts many years.
Titanium is also used in art and buildings. It looks cool and does not break easily. Sports gear like bikes and golf clubs use titanium for strength and lightness. Some everyday things, like paint and electronics, use titanium too.
- Aerospace: Plane frames, engines, and bolts
- Medical Devices: Implants, surgery tools, dental parts
- Art/Architecture: Building fronts, statues
- Sporting Products: Bike frames, golf clubs, rackets
- Everyday Products: Paint, some electronics
Titanium is best because it is strong, does not rust, and is safe for people.
Best Uses for Aluminum
Aluminum is great for things that need to be light and work well without costing a lot. Many industries use aluminum because it is easy to shape and cut. Car makers use aluminum for bodies, frames, and wheels. This makes cars lighter and saves gas.
Electronics use aluminum for cases, cooling parts, and wires because it carries heat and electricity well. Builders use aluminum for windows, roofs, and panels. Aluminum comes in many types, so you can use it for lots of things.
| Aluminum Grade | Strength Characteristics | Corrosion Resistance | Formability | Cost Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7000 Series | Very strong | Okay | Okay | Costs more |
| 6000 Series | Pretty strong | Good | Easy to shape | Costs a bit |
| 5000 Series | Strong | Very good | Good | Costs a bit |
| 3000 Series | Pretty strong | Good | Easy to shape | Costs less |
Use aluminum for car parts, electronics, and building things. It is light and cheap, so it works well for making lots of products.
Note: When you pick titanium or aluminum, always think about what your project needs for strength, weight, price, and how long it should last.
Titanium vs Aluminum: Final Considerations
When you pick between titanium and aluminum, think about what you need most. Both metals have special strengths. Your choice depends on your project’s needs.
Key Points to Remember:
- Strength and Durability:
If you want the strongest and longest-lasting metal, pick titanium. Titanium is used in planes, medical parts, and boats. It does not rust easily and can handle tough jobs. Titanium works well in hard places. - Weight and Ease of Use:
Aluminum is light and easy to shape. You can cut and form aluminum without much trouble. Many companies use aluminum because it is light and strong enough. You see aluminum in cars, computers, and buildings. - Cost and Budget:
Price is important. Titanium costs a lot more than aluminum. If you want to save money but still get good results, aluminum is a smart choice. Titanium is best if you need top performance and can spend more. - Application Environment:
Think about where you will use the metal. Titanium is good for wet, salty, or chemical places. Aluminum works best in dry or easy spots. You can add coatings to aluminum to help it last longer. Titanium needs less care.
Tip: Always pick the metal that fits your project. Do not choose titanium just because it is famous. Do not pick aluminum only because it is cheap. Look at what your project really needs.
Quick Decision Table:
| Need/Factor | Choose Titanium | Choose Aluminum |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum strength | ✔️ | |
| Lowest weight | ✔️ | |
| Best corrosion resistance | ✔️ | |
| Tight budget | ✔️ | |
| Easy machining | ✔️ | |
| Long-term durability | ✔️ |
Ask yourself these questions:
- Do you need the strongest and toughest part?
- Is saving weight the most important thing?
- Will the part be near water, salt, or chemicals?
- How much money can you spend?
- Do you need to make lots of parts fast?
When you answer these questions, you will know which metal is best. Titanium and aluminum are both used in many designs. You make the best choice when you match the metal to your project’s needs.
🛠️ Expert Advice: If you are not sure, ask a materials engineer. They can help you test samples and check your design. This step saves time and money later.
Picking the right metal helps you build safer, stronger, and cheaper products. Take your time, think about your needs, and choose the metal that works best for you.
When picking titanium or aluminum, think about what your project needs. Titanium is very strong and lasts a long time. It works well for hard jobs. Aluminum is light and strong enough for easy tasks. Always match the metal’s strength, weight, and durability to what you are building. Look at your design and test some samples. Ask experts for help if you need it. This way, you can find the best mix of strength, weight, and durability for your project.
FAQ
Titanium has higher tensile and yield strength. This means it is harder to bend or break. Titanium parts last longer and stay strong under heavy loads. Engineers pick titanium for tough jobs.
Yes, aluminum weighs less than titanium. Using aluminum makes things lighter. This is helpful for cars, planes, and sports gear.
You can weld aluminum with normal tools. Titanium is harder to weld. It needs special tools and a clean place to stop dirt from getting in.
Titanium fights rust better than aluminum. You can use titanium in saltwater and chemical plants. Aluminum works well but needs coatings in harsh places.
Pick titanium if you need the most strength and long life. The high price is good for planes and medical parts. For cheaper jobs, aluminum works well and costs less.
Titanium is in medical implants, airplanes, and fancy sports gear. Aluminum is in soda cans, car parts, windows, and electronics. Both metals help products last longer and work better.
Both metals can be recycled. Recycling aluminum is easy and saves energy. Titanium can be recycled but needs special steps.
Titanium is best for medical implants. It is safe for the body and does not react with tissues. Aluminum is not good for implants that stay in the body.


