How are CNC parts manufactured? You use machines controlled by computers. These machines cut material from a solid block. The machines follow instructions from special software. CNC technology is special because it makes complex shapes. It does this with high accuracy and can repeat the process many times.
- You get parts that match the CAD model very closely. This is true even when tolerances are as small as 0.0002 inches.
- CNC machining helps you change designs fast. You can also make custom parts for special needs.
- You make fewer mistakes and need less manual work. This means you get the same results every time, from the first part to the thousandth.
Key Takeaways
- CNC machining uses computers to control machines that make parts from solid materials. These machines can make parts very accurately. The process begins with a digital design. Next, you pick the material. Then, you program the machine. After that, the machine shapes the part. Finally, workers check the quality. Subtractive manufacturing means taking away material to make the part. This helps get the right shape and a smooth surface. Many industries use CNC technology. These include car, airplane, and medical companies. They need custom and exact parts. Good design helps make parts easier and cheaper to make. For example, do not use thin walls or sharp corners. The operator’s skill is very important. Setting up the machine the right way is also important. This helps keep the parts high quality and accurate. Workers check the parts at every step. This makes sure the parts are correct and work well. Picking the best materials is important. Using the right surface treatments also helps. This makes CNC parts last longer and work better.
- How are CNC Parts Manufactured?
Table of Contents
Overview
To answer “how are cnc parts manufactured?”, you follow a few main steps. First, you make a digital design. Next, you pick the right material. Then, you use cnc machines to shape the part. The cnc milling process uses special software to move the machine. The software gives exact instructions to the machine. This helps you get very accurate results. After making the part, you check it with quality control. This makes sure the part meets your needs. Last, you finish the part to make it look and work better.
Quick Summary:
You design the part, pick the material, program the cnc machine, shape the material with the cnc milling process, check the part, and add finishing touches. Each step helps you get high-quality cnc machined parts.
Main Steps in CNC Manufacturing:
- Design & Engineering for CNC Machining Parts
- Material Selection for CNC Machine Parts
- CNC Machining Operations (like cnc milling, turning, and drilling)
- Quality Control for CNC Precision Machining Parts
- Finishing & Surface Treatment
Both software and hardware help answer “how are cnc parts manufactured?” Software like CAD and CAM makes the design and turns it into instructions. The hardware, such as the cnc machine, follows these instructions to shape the material. Quality control tools check the finished cnc machined parts for accuracy and sameness.
Subtractive Manufacturing
When you ask “how are cnc parts manufactured?”, subtractive manufacturing is the method used. This way, you start with a solid block and remove material to make the shape. The cnc milling process is a main example. You cut, drill, or turn the material with careful moves. The cnc machine follows the program to take away only what you do not need.
- Subtractive manufacturing gives you very exact results.
- You can use many materials, like metals and plastics.
- The cnc milling process makes smooth surfaces and fine details.
- You can make one part or thousands, all with the same quality.
Subtractive manufacturing is helpful because it gives steady results. The cnc milling process makes sure each part matches your design, even if the shape is hard to make.
Key Industries
Many industries use cnc technology because it is accurate and flexible. If you wonder, “how are cnc parts manufactured?”, you will see that many fields use cnc milling and the cnc milling process for their products.
| Industry | Market Share Description |
|---|---|
| Automotive & Transportation | High demand for precision components, expected highest growth rate due to customized components and electric vehicles. |
| Aerospace | Growing adoption of cnc machines for precise manufacturing. |
| Medical | Increasing demand for highly precise medical devices. |
| Semiconductors | Rising adoption in die- and wire-bonding processes. |
| Capital Goods | Growing demand for fabricated metal parts. |
| Energy & Power | Increased demand for efficient and sustainable energy sources. |
The automotive industry is growing the fastest, especially as electric vehicles need more custom parts. Aerospace and medical fields need cnc machined parts for safety and good performance. The cnc milling process also helps the semiconductor and energy fields, where being exact is very important.
CNC Machining Process
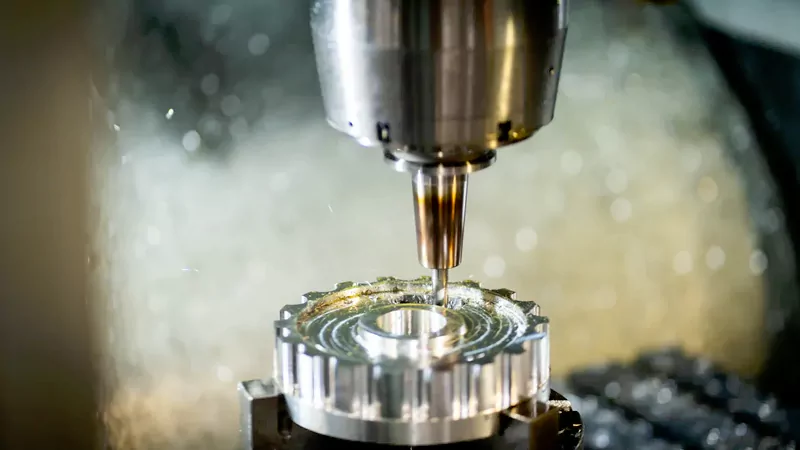

CAD Design
The cnc machining process starts with a digital design. You use CAD software to make a 3D model or a 2D drawing. This lets you show the size, shape, and special parts of your part. Machinists look at this model to help run the cnc machine. You can add tolerances for important features in your design. Model Based Definition lets you put these tolerances right into the 3D model. This step matters because the cnc milling machine needs clear instructions to make your part.
- CAD software helps you:
- Draw hard shapes and smooth surfaces.
- Set close tolerances for key spots.
- Get your design ready for cnc milling and other cnc steps.
Tip: Always check your CAD model before you go on. Even small mistakes in the design can cause big problems when cnc machining.
CAM Programming
After you finish your CAD design, you start CAM programming. CAM software links your digital design to the cnc machine. You use CAM to make toolpaths, which are the paths the cutting tools will take. The software makes G-code, a special code that tells the cnc machine how to move, what tools to use, and where to cut.
- CAM programming steps:
- Put your CAD design into the CAM software.
- Pick the right cutting tools for cnc milling.
- Set up toolpaths for your design and material.
- Make G-code for the cnc machine.
CAM programming helps your cnc milling process work well. You get exact parts because the machine follows the CAM software’s instructions.
Note: Good CAM programming lowers mistakes and makes your cnc machined parts better.
Machine Setup
You must set up the cnc machine before you start cutting. This step changes how accurate and fast your cnc machining process is. You put the raw material in the machine and hold it tight with fixtures. You check tool length offsets and cutter radius compensation to make sure things line up. Each job might need a different setup, especially in job shops or contract manufacturing.
- Main points for machine setup:
- Hold the material tight so it does not move during cnc milling.
- Check all tool offsets and compensation settings.
- Plan the setup to save time and lower scrap.
| Setup Task | Why It Matters |
|---|---|
| Fixture the material | Stops shifting and mistakes |
| Tool offset calibration | Makes sure cuts are exact |
| Cutter radius compensation | Matches the toolpaths |
| Efficient planning | Saves time and cuts down waste |
Good machine setup helps you get the same results every time and high-quality cnc machined parts. Bad setup can cause mistakes and waste material.
Material Removal
Material removal is the heart of the cnc machining process. You start with a solid block of material. The cnc machine cuts away sections to create your final part. This step uses tools like drills, mills, and lathes. You control these tools with precise instructions from the software.
During cnc milling, you watch the machine carve out shapes layer by layer. The cutting tool spins at high speed. It moves along the programmed path. You see chips and shavings fall away as the tool removes material. The process continues until the part matches your design.
You choose the right cutting tool for each job. Some tools work best for rough cuts. Others help you finish surfaces with smooth edges. The cnc milling process lets you switch tools automatically. You do not need to stop the machine. This saves time and keeps your parts accurate.
Tip: Always check the cutting speed and feed rate. These settings affect how much material the cnc machine removes. If you set them too high, you risk damaging the part. If you set them too low, you waste time.
You monitor the cnc machine during material removal. You look for signs of tool wear or vibration. You make adjustments if you see problems. The cnc milling process gives you control over every detail. You can create complex shapes and tight tolerances.
Here is a simple breakdown of the material removal steps in cnc machining:
- Load the raw material into the cnc machine.
- Select the correct cutting tool for cnc milling.
- Start the programmed operation.
- Watch as the cnc machine removes material layer by layer.
- Inspect the part for accuracy after each stage.
| Step | What You Do |
|---|---|
| Load Material | Place the block in the cnc machine |
| Tool Selection | Pick the right tool for cnc milling |
| Start Machining | Begin the cutting process |
| Monitor Progress | Check for issues during cnc milling |
| Inspect Part | Make sure the part matches the design |
You rely on the cnc milling process to deliver consistent results. You can repeat the same operation many times. Each part comes out with the same quality. You use cnc technology to make parts for cars, airplanes, and medical devices. The material removal step is what turns your design into a real product.
CNC Machine Types
3-Axis CNC
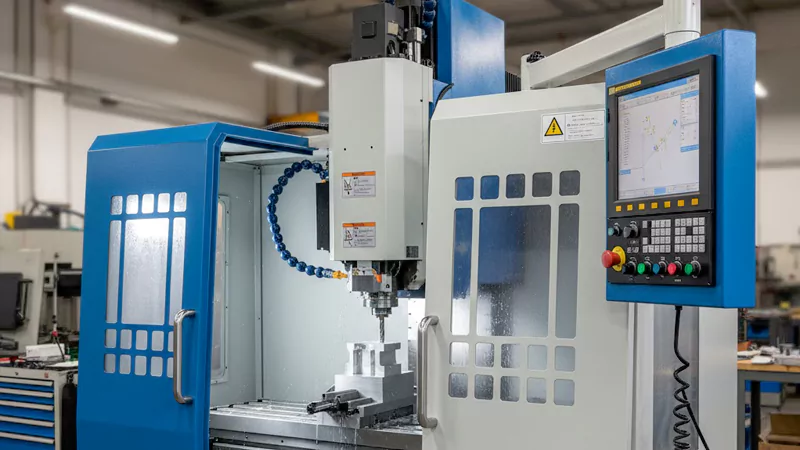

You often start with a 3-axis CNC machine when you need to make simple parts. This machine moves the cutting tool along three axes: X, Y, and Z. You can cut, drill, and mill flat surfaces or shapes with straight sides. Most small businesses use 3-axis machines because they cost less and are easier to program. You do not need advanced skills to run them.
- 3-axis CNC machines work best for 2D and 2.5D designs.
- You can make parts like brackets, plates, and basic housings.
- These machines help you finish jobs quickly when the design is not complex.
Tip: Choose a 3-axis CNC machine if you want to save money and time on simple projects.
You will notice a trade-off. 3-axis machines handle simple shapes well, but they cannot make complex parts in one setup. You may need to reposition the part if you want to cut on more than one side.
5-Axis CNC
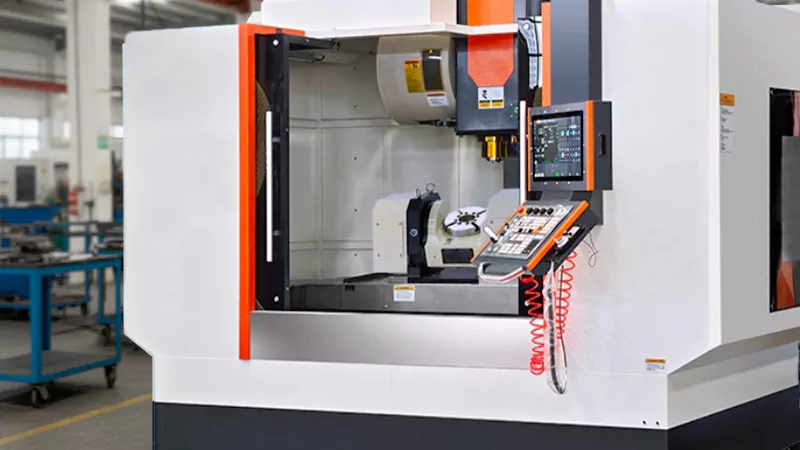

You use a 5-axis CNC machine when your part has complex shapes or needs high precision. This machine moves the tool along five axes. You can tilt and rotate the tool or the part, so you reach every surface without stopping the machine. This feature lets you make parts with curves, angles, and deep pockets.
- 5-axis CNC machines give you more freedom to create intricate designs.
- You can finish a part in one setup, which saves time and improves accuracy.
- These machines work well for aerospace, medical, and automotive parts.
| Feature | 3-Axis CNC | 5-Axis CNC |
|---|---|---|
| Axes of Movement | X, Y, Z | X, Y, Z + 2 rotary |
| Part Complexity | Simple | Complex |
| Setup Changes Needed | Often | Rarely |
| Operator Skill Level | Basic | Advanced |
You will need skilled operators for 5-axis machines. They cost more, but you get better results for difficult jobs. You can machine all sides of a part without manual rotation. This reduces errors and keeps your parts consistent.
Note: 5-axis CNC machines help you make parts that would be impossible or too costly with other machines.
CNC Turning
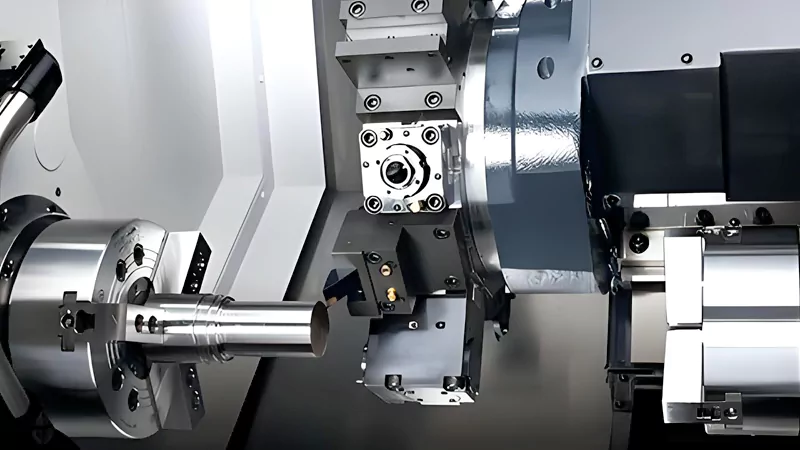
You use CNC turning when your part has a round shape. The machine spins the workpiece while a cutting tool shapes it. This process works best for parts like shafts, bushings, and rings. You can also add milling tools to some turning machines for extra features.
- CNC turning machines excel at making parts with rotational symmetry.
- You get smooth surfaces and tight tolerances on round parts.
- These machines work fast and handle both small and large runs.
You can combine turning and milling in one setup. This gives you more options for complex parts. CNC turning helps you make high-quality parts for industries like automotive, aerospace, and electronics.
Callout: If your design is round or needs threads, CNC turning is the best choice.
You should match the machine type to your part’s shape and complexity. 3-axis machines suit simple jobs. 5-axis machines handle complex parts with high precision. CNC turning is best for round parts. Your choice affects the quality, speed, and cost of your project.
Design for CNC
Design Guidelines
You have to follow some rules when you design parts for CNC machining. These rules help you avoid mistakes and make sure your part is easy to make. When you design for manufacturing, you should:
- Make walls thicker than 0.02 inches. Thin walls can break or bend.
- Do not use deep pockets with sharp corners. Sharp corners are hard to cut and can make your part weak.
- Keep pocket depths less than six times the smallest corner radius. Deep pockets take longer to machine and wear out tools.
- Do not add fancy shapes just for looks. Simple shapes cost less and are faster to make.
- Use chamfers instead of fillets. Chamfers are easier for CNC machines to cut.
- Only use tight tolerances if you really need them. Tolerances tighter than +/- 0.005 inches cost more and may not be needed.
You should also check your design for deep pockets, narrow spots, sharp inside corners, hard-to-reach features, outside fillets, thin walls, and flat-bottomed holes. These things can make machining harder or more expensive.
Tip: Use wall thicknesses of 0.8 mm for metals and 1.5 mm for plastics. For threads, sizes like M1 are good. Keep cavity depths to four times the width. Small features should be at least 2.5 mm (0.1 inches). For inside edges, use a vertical radius that is one-third the cavity depth.
Limitations
CNC machining has some limits you need to think about when you design. If you ignore tolerances and material limits, your part might not work right. Hard shapes that are not needed make machining take longer and cost more. Not enough fillets and sharp corners can cause stress and make your part weaker.
- The tool diameter to cavity depth ratio is important. The best depth is four times the width.
- Tool shape limits the final cut, especially in inside corners.
- Longer tools shake more and are less accurate.
- The size of the CNC machine limits how big your part can be.
- How far the CNC can move affects the size of parts you can make.
Note: Always design parts that fit your CNC machine. Big parts or features may need special setups or tools.
Material Choices
Picking the right material is very important in CNC machining. The material you pick changes how your part works and how easy it is to machine. You must make sure the material does what you need and fits your budget.
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Material Properties | The features of materials that change how they work in machining. |
| Fulfillment of Performance Requirements | The material must do what your part needs. |
| Cost | The material you pick changes your total project cost. |
| Product Design | Your design and the material work together for the result you want. |
| Machining Process | The material must work with your CNC machining method. |
| Product Scalability | You need to make many parts without losing quality. |
Do not use brittle materials if your part needs to bend. Materials that do not resist chemicals will not last in harsh places. The material you pick changes how strong and reliable your part is.
Finishing and Inspection
Deburring

You must take off burrs and sharp edges from CNC parts before using them. Burrs are tiny bits left after machining. If you do not remove them, they can hurt people. Burrs also make it hard to put parts together. They can make parts weaker and cause cracks. Deburring makes parts safer and helps them fit better. It also lowers stress that could break the part.
Tip: Always look for burrs after machining. Taking them off keeps your parts safe and strong.
You can use different ways to deburr:
- Use hand tools like files or stones to smooth edges.
- Try vibratory polishing to clean many parts at once.
- Use bead blasting for a matte look and to remove small burrs.
- Pick mechanical tools for quick and careful deburring.
| Benefit | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Safety | Gets rid of sharp edges that can hurt people. |
| Alignment | Makes sure parts fit together without trouble. |
| Stress Distribution | Lowers stress spots that could cause cracks. |
| Performance Consistency | Makes sure each part works well and lasts longer. |
Surface Treatment
After deburring, you often treat the surface of CNC parts. Surface treatments protect parts and make them look better. They also help parts last longer. You can pick from many finishing methods, and each has its own good points.
- Mechanical finishing: Use polishing, grinding, or lapping to make surfaces smooth and shiny.
- Thermal finishing: Use heat treatment or lasers to make parts stronger.
- Coating finishing: Add powder or ceramic coating for more protection from wear and rust.
- Brushing and sandblasting: Clean and roughen surfaces with abrasive materials.
- Electroplating and galvanizing: Add metal layers to stop rust and improve looks.
| Surface Treatment Type | Benefits |
|---|---|
| As Machined | Costs less, but shows tool marks. Good for cheap projects. |
| Anodizing | Adds a tough layer, makes parts last longer and look better. |
| Alodine Coating | Helps stop rust, especially for aluminum parts. |
| Black Oxide Coating | Protects steel and copper from rust and damage. |
| Bead Blasting | Makes a matte finish and takes away flaws. |
| Powder Coating | Gives a hard, scratch-proof surface. |
| Painting | Keeps parts safe from water and dirt, helps them last longer. |
Note: Choose the right surface treatment for how and where your part will be used.
Quality Control
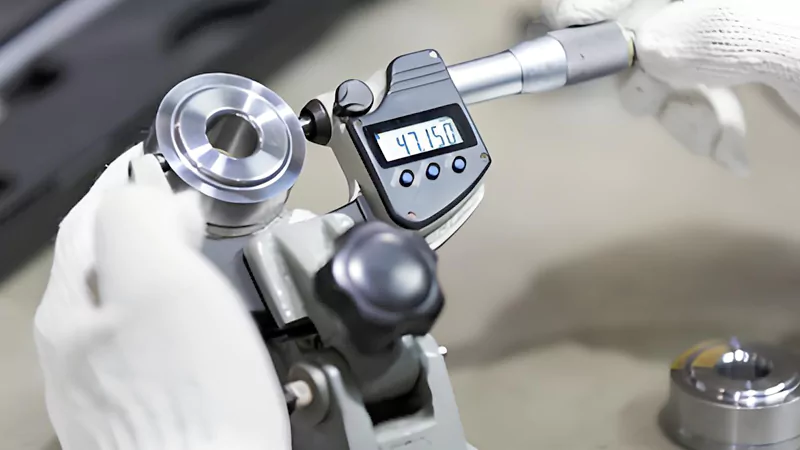

You must check every CNC part to make sure it is good. Quality control starts with checking raw materials and goes through every step. You use special tools to measure size, shape, and surface finish. You also look for problems that could hurt how the part works.
| Quality Control Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Raw Material Inspection | Checks if materials are what you need. |
| In-Process Inspection | Watches size and finish during machining. |
| First Article Inspection | Looks at the first part to find problems early. |
| Final Inspection | Checks finished parts for all quality rules. |
| Statistical Process Control | Uses data to watch and improve the process. |
| Documentation | Keeps records so you can track and prove quality. |
You can use these ways to inspect parts:
- Measure size with calipers and micrometers.
- Check surface finish with roughness testers.
- Look for scratches or dents by eye.
- Use non-destructive tests to find hidden problems.
- Test hardness and function to make sure parts work right.
Callout: Careful checks at every step help you give high-quality, reliable CNC parts every time.
Factors for Quality
Machine Precision
You need machine precision to make good CNC parts. The CNC machine’s accuracy affects every part you make. Many things can change this precision. If you want tight tolerances, you must watch for problems:
- Thermal Effects: Cutting makes heat. Heat can make tools and parts get bigger. This can move the tool and change your part’s size.
- Tool Wear: Tools get dull after use. Dull tools can change the shape and size of your part.
- Machining Position Errors: If the machine moves wrong, your part will not match the design.
- System Errors: Problems inside the machine can lower accuracy.
- Deformation Errors: Cutting forces can bend the machine or part. This makes the part less exact.
Tip: Check your machine for heat, tool wear, and movement problems. Regular checks help keep your parts correct.
Operator Skill
Your skill as an operator is very important for CNC part quality. Even with automation, you must program the machine, set up jobs, and watch for mistakes. Skilled operators can find problems early and fix them fast.
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Role of Operator Skill | You must program and watch CNC machines for good results. |
| Automation | CNC machines do many steps, so you need less skill for easy jobs. |
| Human Error Reduction | Automation lowers mistakes, but skilled people still get the best results. |
You need some training for easy jobs. For hard parts, you need more experience. Skilled operators know how to change settings, pick the right tools, and fix problems quickly. If you want the best parts, train well and keep learning new skills.
- Operator skill matters for programming CNC machines.
- Skilled operators keep the process precise and high quality.
- Basic training is okay for simple jobs, but hard jobs need experts.
Environmental Factors
The shop environment can also change CNC part quality. You must control waste, energy use, and pollution to keep things safe and efficient.
- Material Waste: CNC machining makes a lot of scrap. If you do not handle waste, it can hurt the environment.
- Energy Consumption: CNC machines use lots of power. High energy use costs more and adds to pollution.
- Chemical Emissions: Some fluids and steps release bad chemicals or dust into the air.
- Water Pollution: If you do not handle fluids right, they can pollute water.
- Noise Pollution: CNC machines are loud. Loud noise can hurt your health and bother others.
Note: You can help quality and safety by recycling, saving energy, and following rules for chemicals and noise. Small changes in your shop can help your parts and the environment.
You get good CNC parts by following some steps. First, you design with CAD. Then, you use CAM to program the machine. Next, you set up the machine and take away extra material. Last, you check every part to make sure it is right. You need a strong design, careful programming, and good quality checks. For the best results:
- Make simple CAD models and pick materials that work for you.
- Keep tolerances close, like ±0.002” if you need to.
- Use quality tools such as SPC and special measuring tools.
| Benefit | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Improved efficiency | Good software and planning help stop waste and mistakes. |
| Better collaboration | Clear designs make it easier to work with others. |
Think about both your skills and the steps you take. This helps you make each project more exact and dependable.
FAQ
You can pick metals like aluminum, steel, and titanium. Plastics such as ABS and nylon are good choices too. The material you pick depends on how strong, tough, or cheap you want your part to be.
CNC machines can make parts with tolerances as close as ±0.002 inches. They follow programmed paths very carefully. This means every part comes out the same.
Simple parts can be ready in just a few days. If the part is complex, it might take one or two weeks. The time depends on the design, material, and if the machine is free.
CNC technology lets you make custom parts easily. You can change designs fast. You get parts that fit your needs exactly.
The price depends on the material, how hard the part is to make, and how many you need. Simple parts are cheaper. Complicated shapes and tight tolerances cost more. Making more parts at once saves money.
You use calipers, micrometers, and look at the parts closely. You check parts while making them and after they are done. Quality control makes sure every part is right.
CNC parts are used in cars, planes, medical tools, electronics, and energy. These fields need parts that are exact and work well.
Tip: Always tell your CNC supplier what you need and your tolerances. This helps you get the best parts for your project.


